Methodology, Parameters, and Calculations
health economics methodology, clinical trial cost analysis, medical research ROI, cost-benefit analysis healthcare, sensitivity analysis, Monte Carlo simulation, DALY calculation, pragmatic clinical trials
Overview
This appendix documents all 47 parameters used in the analysis, organized by type:
- External sources (peer-reviewed): 14
- Calculated values: 19
- Core definitions: 14
Calculated Values
Parameters derived from mathematical formulas and economic models.
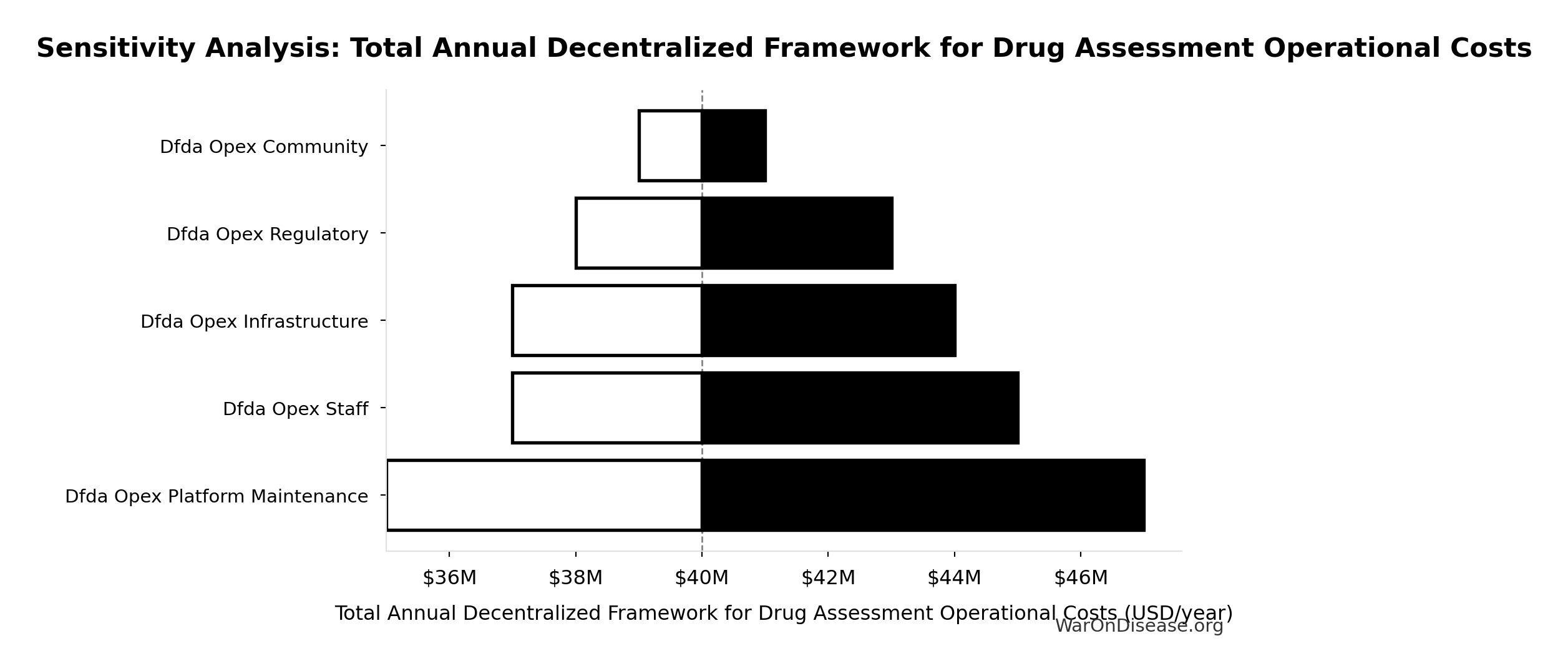
Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs: $40M
Total annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment operational costs (sum of all components: platform + staff + infra + regulatory + community)
Inputs:
- Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Maintenance Costs: $15M (95% CI: $10M - $22M)
- Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Staff Costs: $10M (95% CI: $7M - $15M)
- Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Infrastructure Costs: $8M (95% CI: $5M - $12M)
- Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Regulatory Coordination Costs: $5M (95% CI: $3M - $8M)
- Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Community Support Costs: $2M (95% CI: $1M - $3M)
\[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \]
✓ High confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Maintenance Costs (USD/year) | 0.3542 | Moderate driver |
| Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Staff Costs (USD/year) | 0.2355 | Weak driver |
| Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Infrastructure Costs (USD/year) | 0.2060 | Weak driver |
| Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Regulatory Coordination Costs (USD/year) | 0.1469 | Weak driver |
| Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Community Support Costs (USD/year) | 0.0576 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
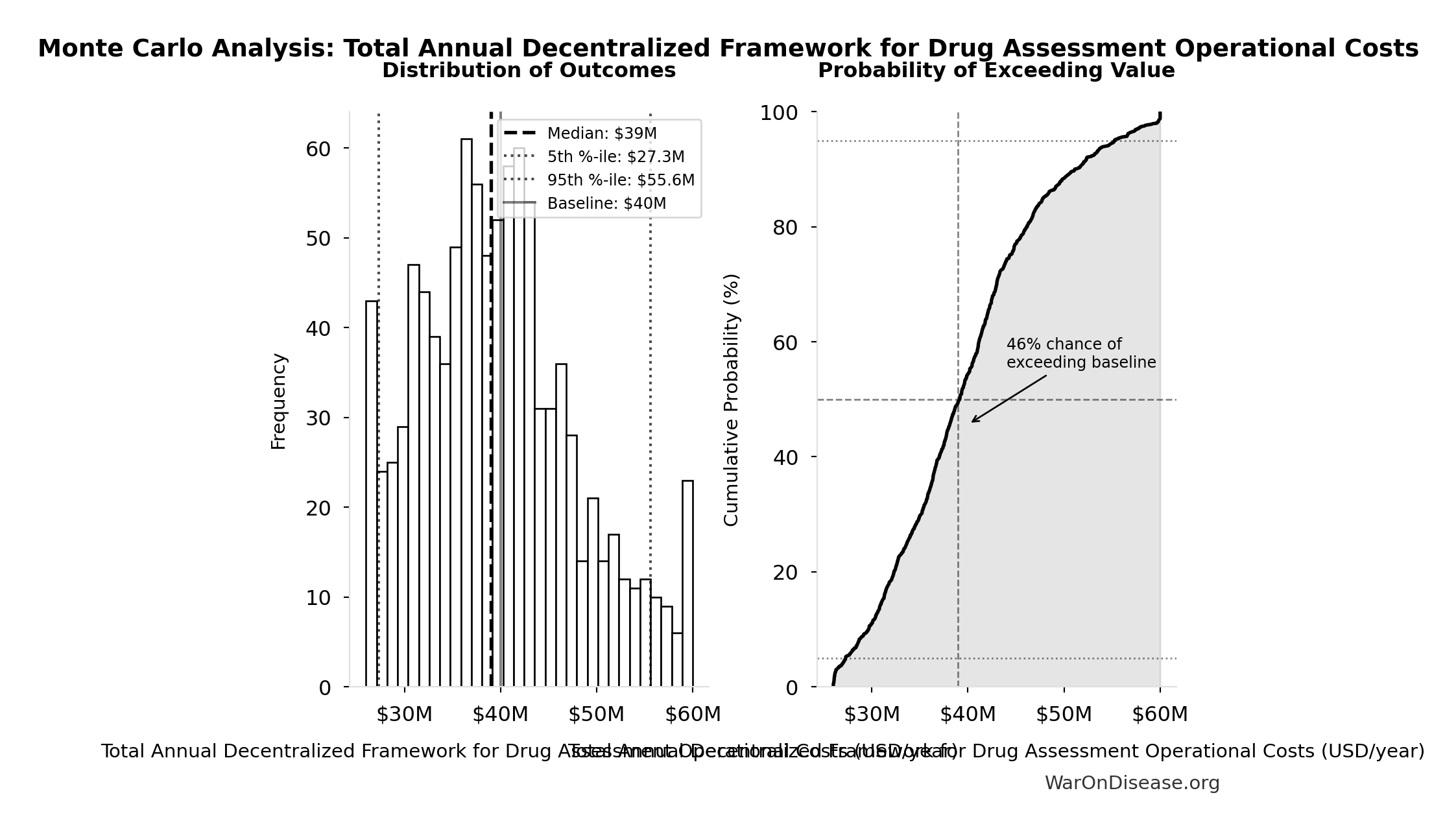
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $40M |
| Mean (expected value) | $39.9M |
| Median (50th percentile) | $39M |
| Standard Deviation | $8.21M |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$27.3M, $55.6M] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
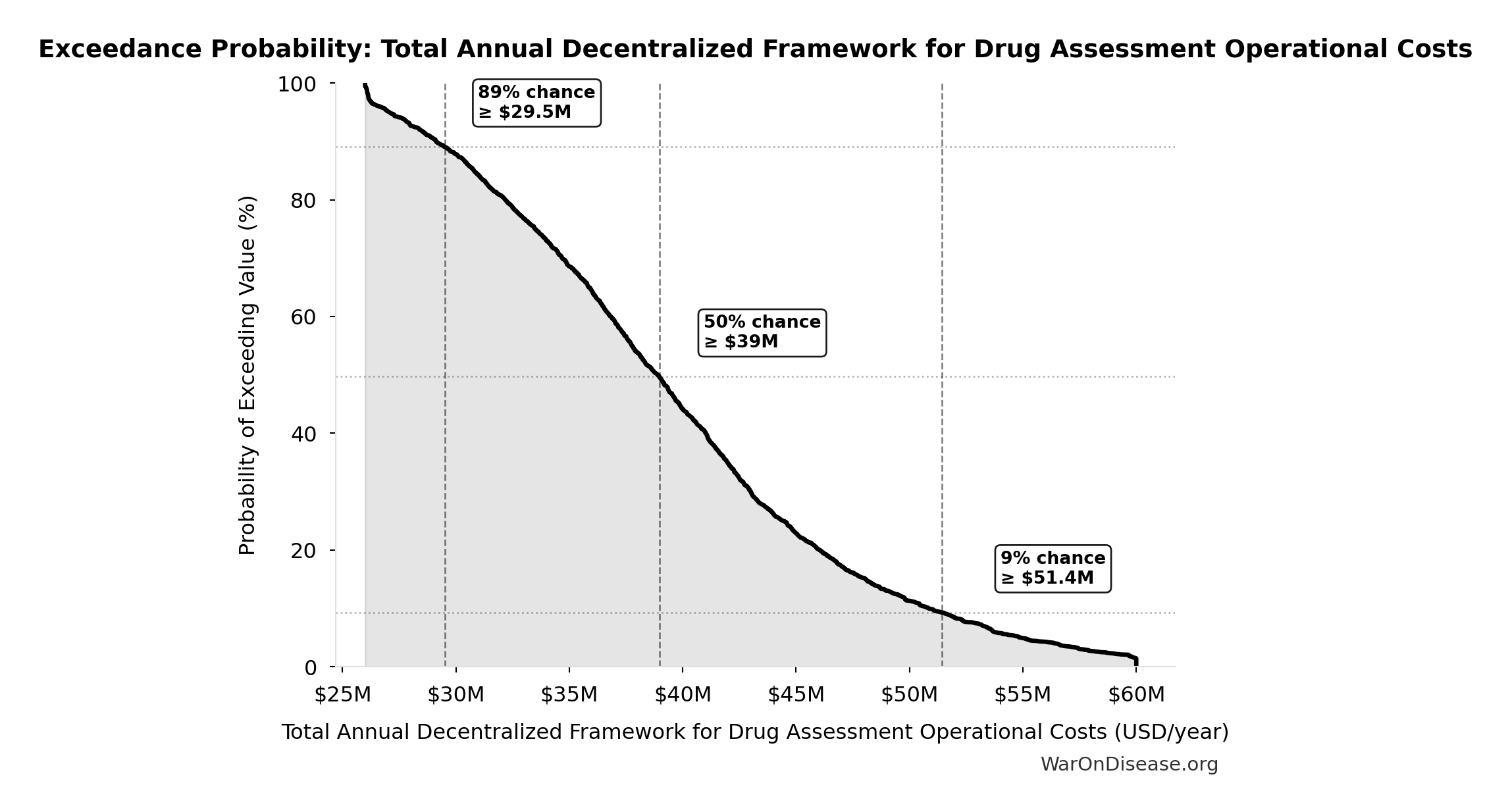
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
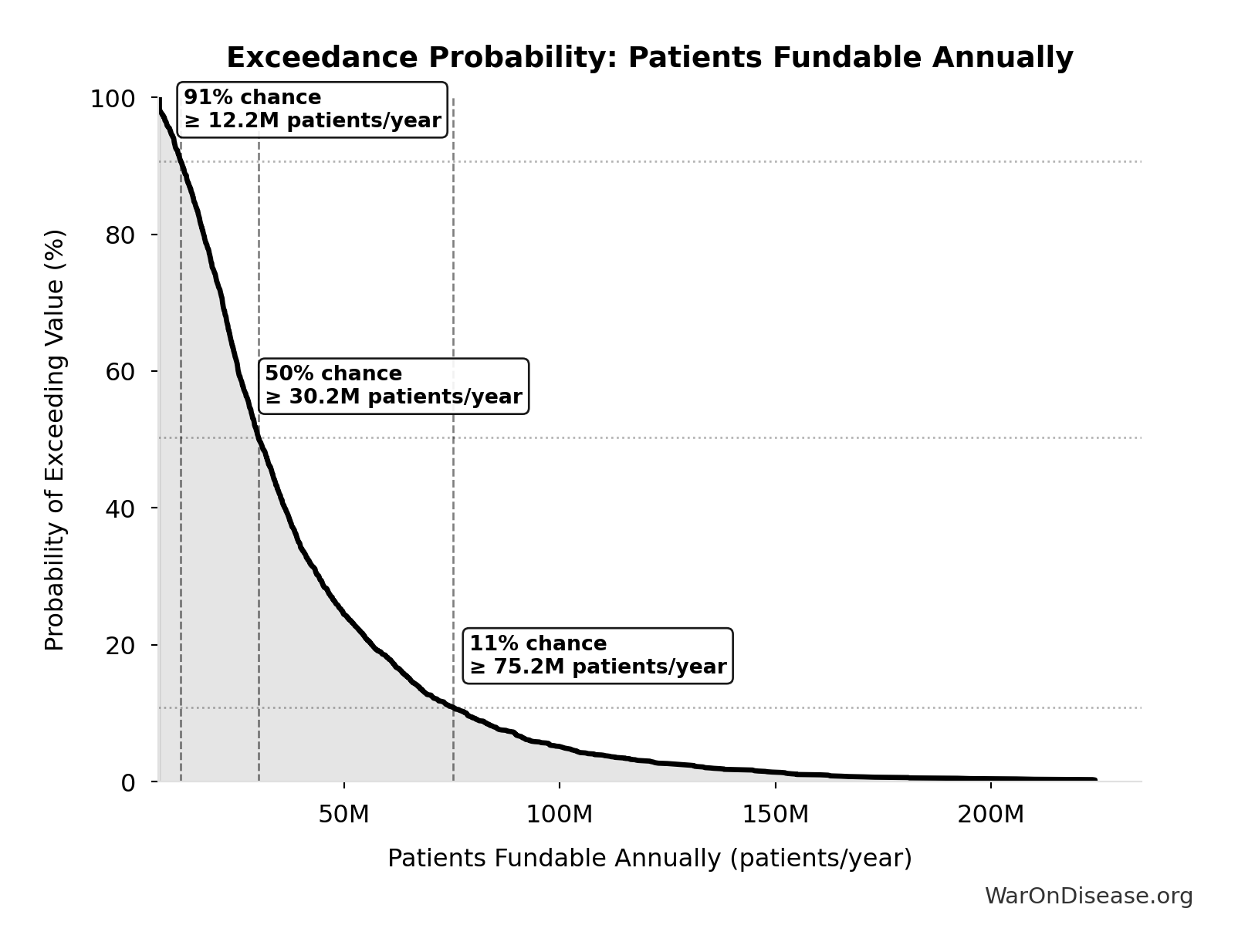
dFDA Patients Fundable Annually: 23.4 million patients/year
Number of patients fundable annually from dFDA funding at pragmatic trial cost. Source-agnostic counterpart of DIH_PATIENTS_FUNDABLE_ANNUALLY.
Inputs:
- dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies 🔢: $21.8B
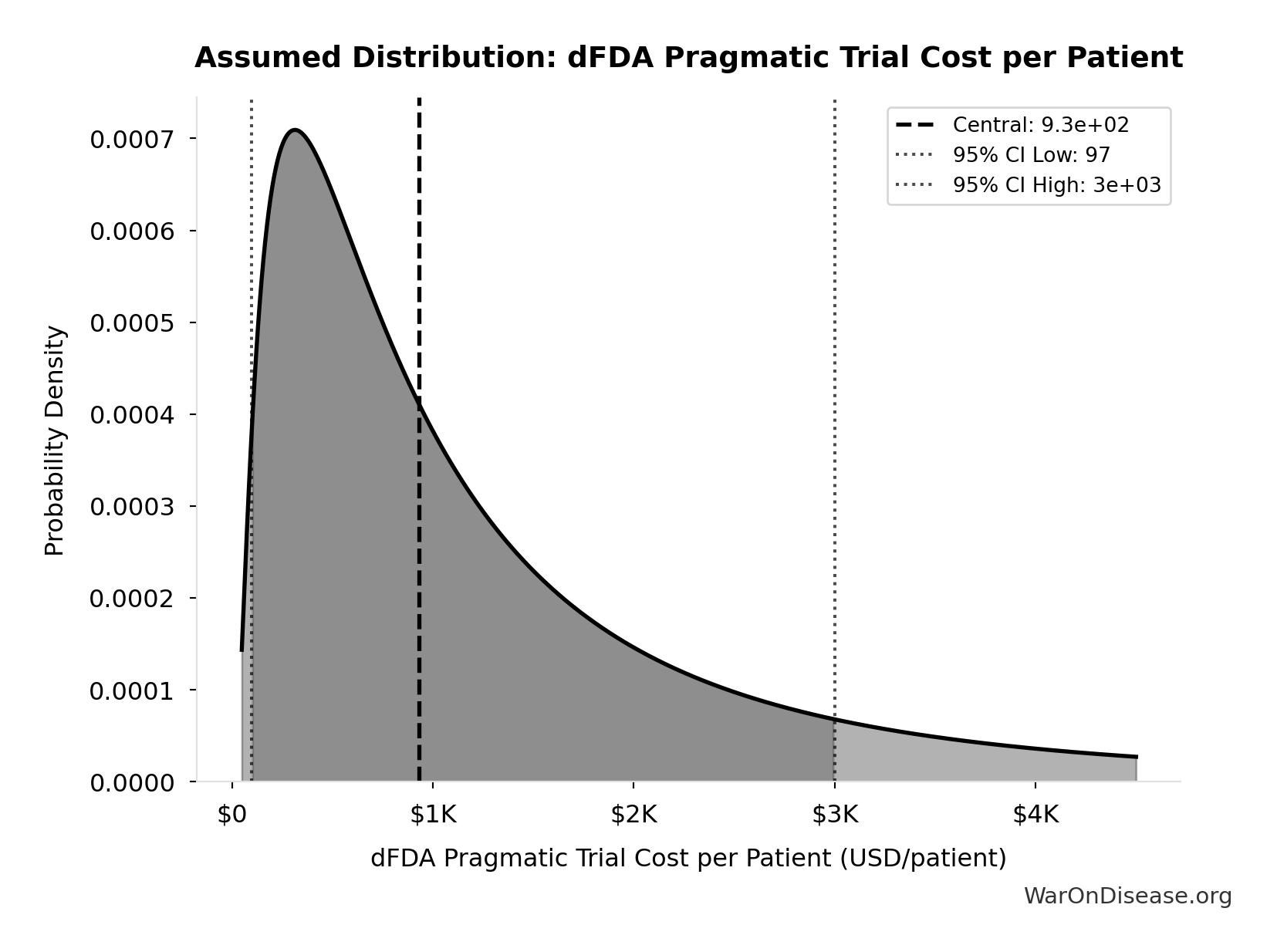
- dFDA Pragmatic Trial Cost per Patient 📊: $929 (95% CI: $97 - $3K)
\[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ✓ High confidence
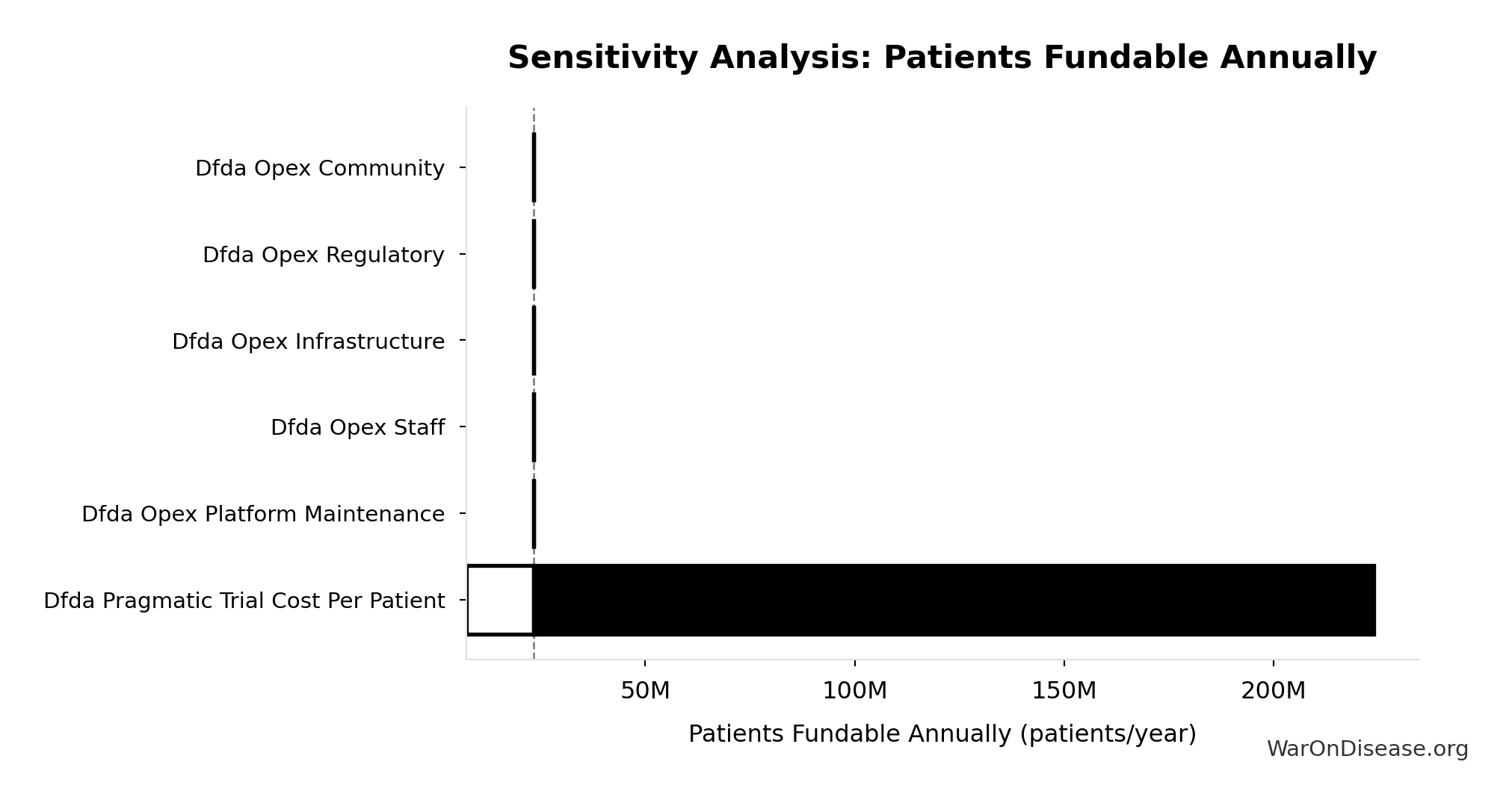
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for dFDA Patients Fundable Annually
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies (USD/year) | 2.3351 | Strong driver |
| dFDA Pragmatic Trial Cost per Patient (USD/patient) | 1.5755 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
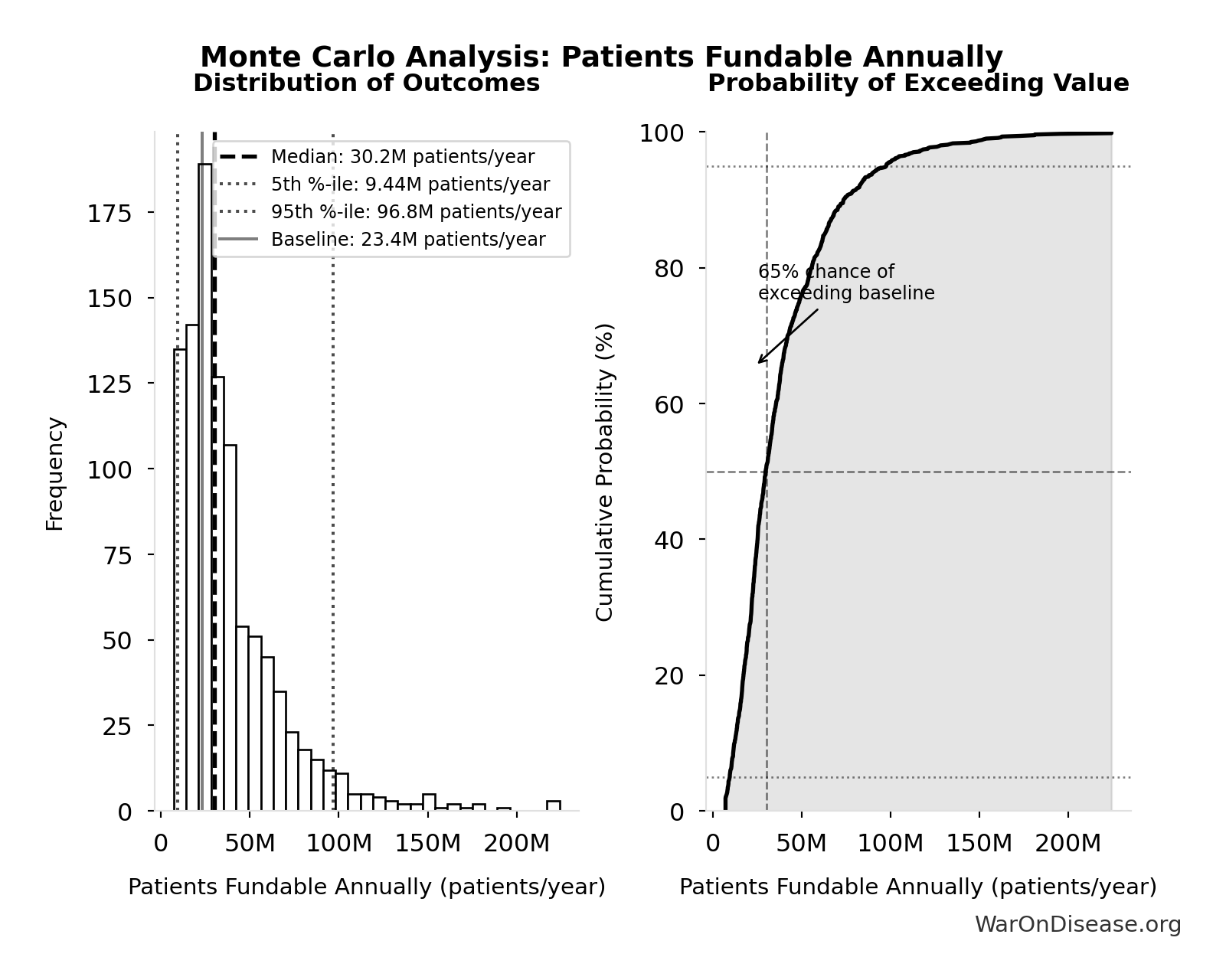
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: dFDA Patients Fundable Annually
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 23.4 million |
| Mean (expected value) | 38.6 million |
| Median (50th percentile) | 30.2 million |
| Standard Deviation | 30.2 million |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [9.46 million, 97 million] |
The histogram shows the distribution of dFDA Patients Fundable Annually across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that dFDA Patients Fundable Annually will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
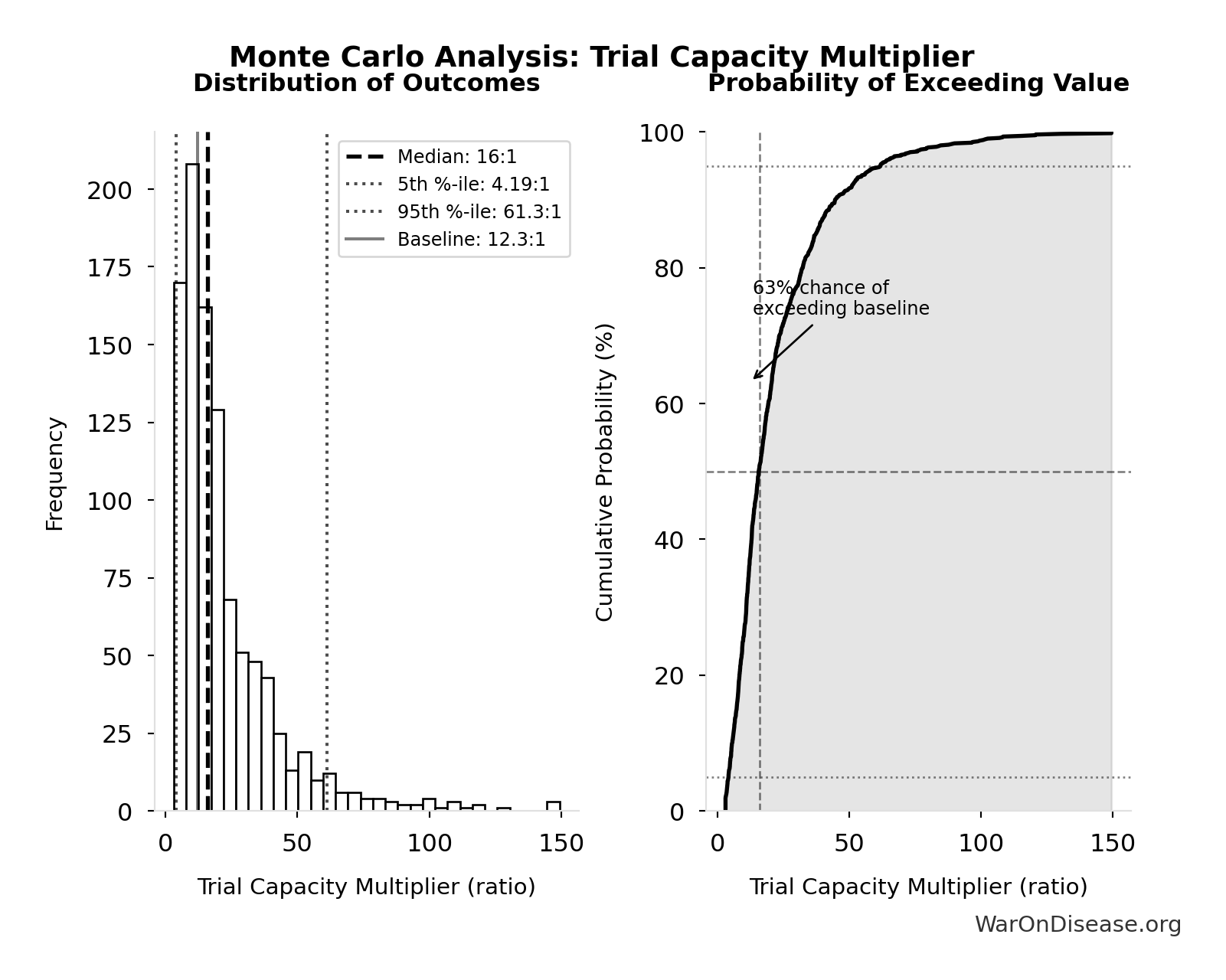
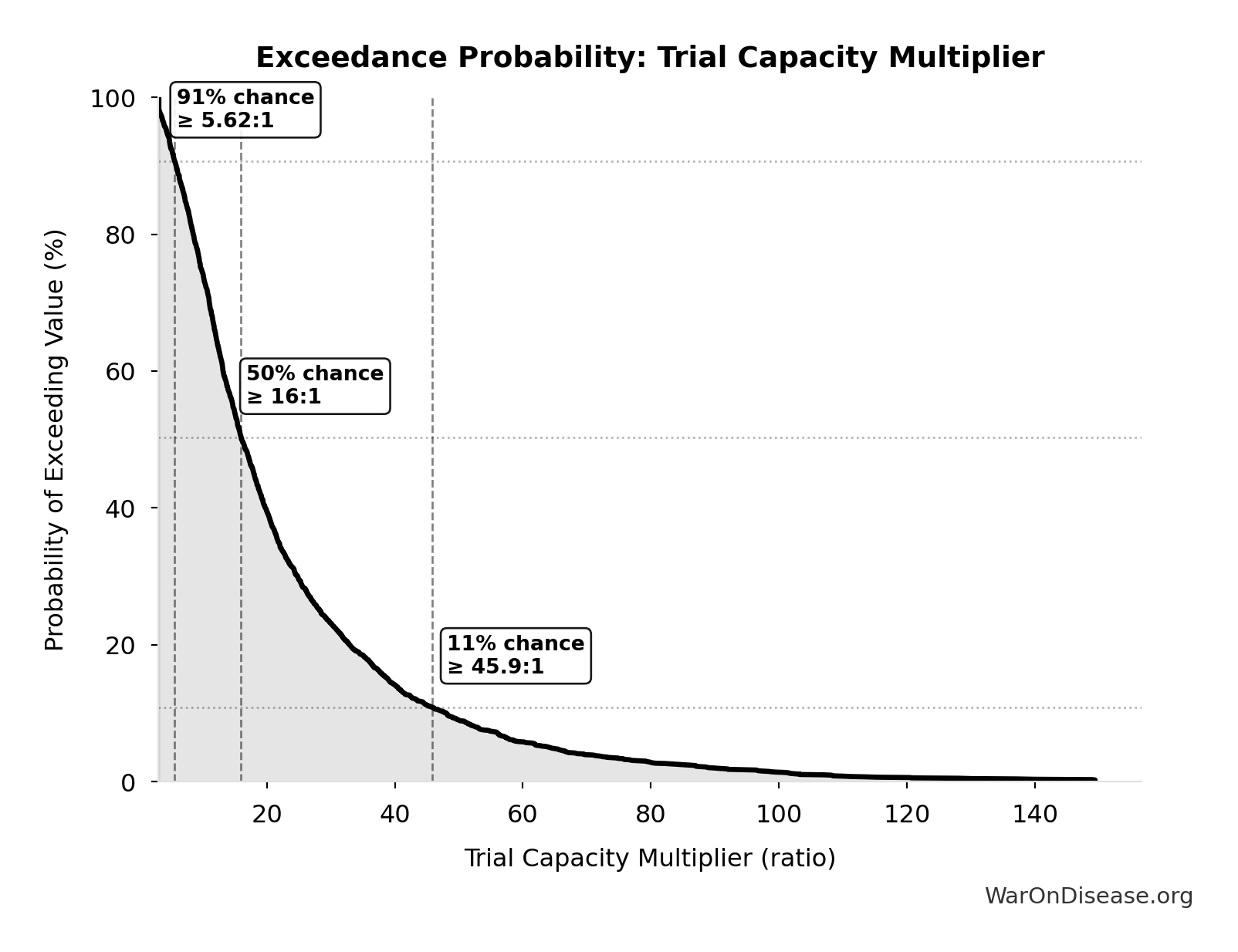
Trial Capacity Multiplier: 12.3x
Trial capacity multiplier from dFDA funding capacity vs. current global trial participation
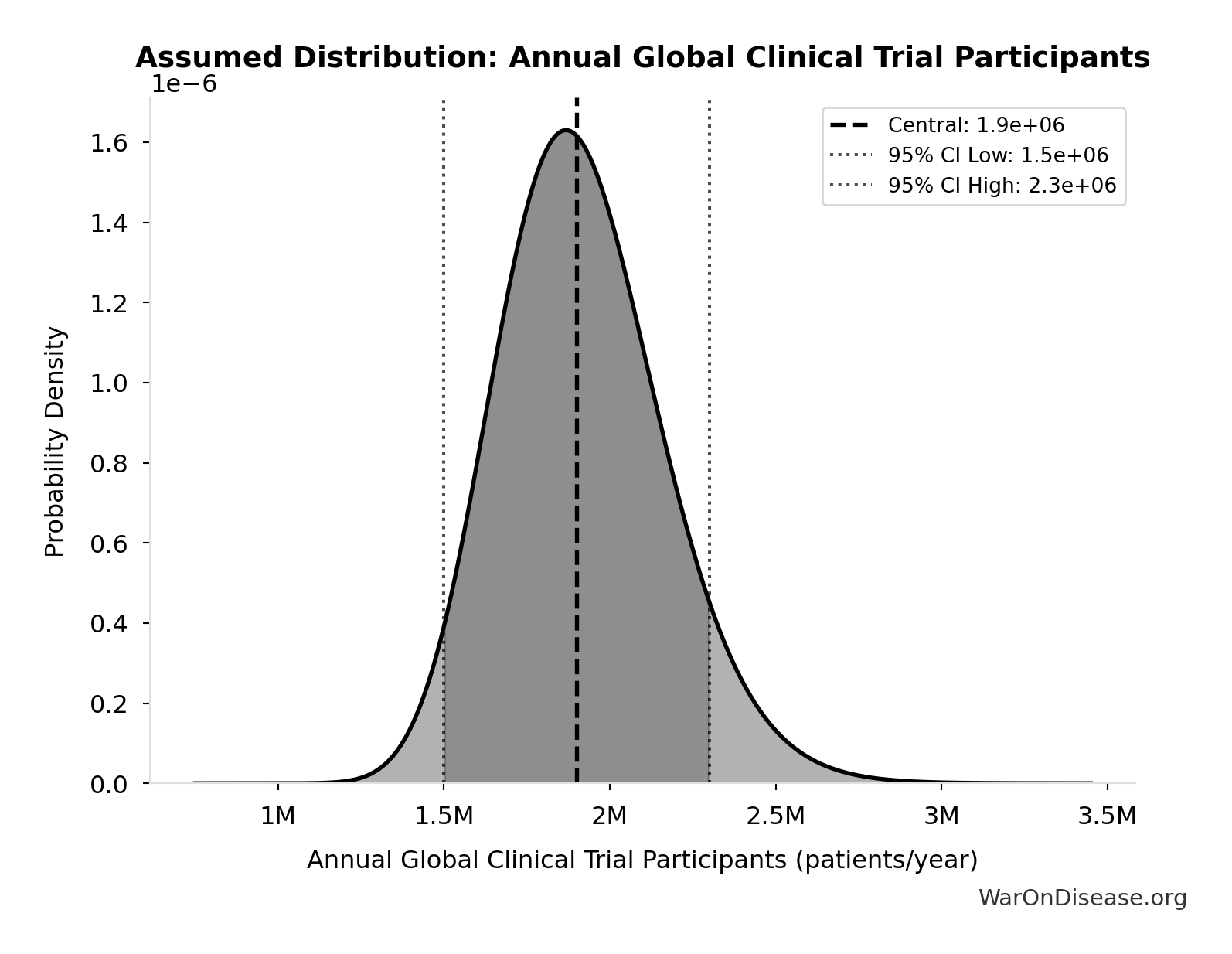
Inputs:
- Annual Global Clinical Trial Participants 📊: 1.9 million patients/year (95% CI: 1.5 million patients/year - 2.3 million patients/year)
- dFDA Patients Fundable Annually 🔢: 23.4 million patients/year
\[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ✓ High confidence
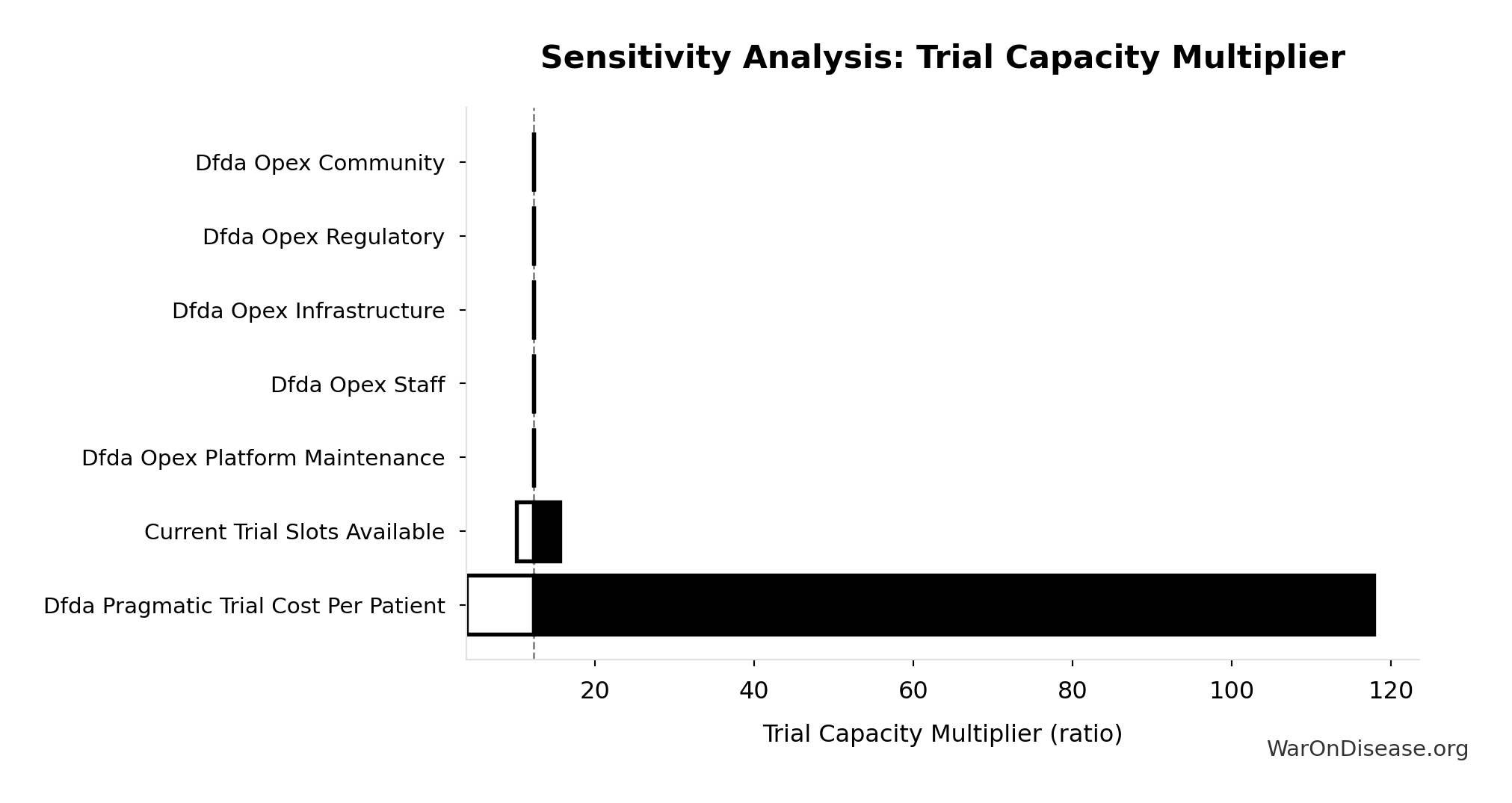
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Trial Capacity Multiplier
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| dFDA Patients Fundable Annually (patients/year) | 1.0768 | Strong driver |
| Annual Global Clinical Trial Participants (patients/year) | 0.0910 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Trial Capacity Multiplier
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 12.3x |
| Mean (expected value) | 22.1x |
| Median (50th percentile) | 16x |
| Standard Deviation | 20.2x |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [4.2x, 61.4x] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Trial Capacity Multiplier across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Trial Capacity Multiplier will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
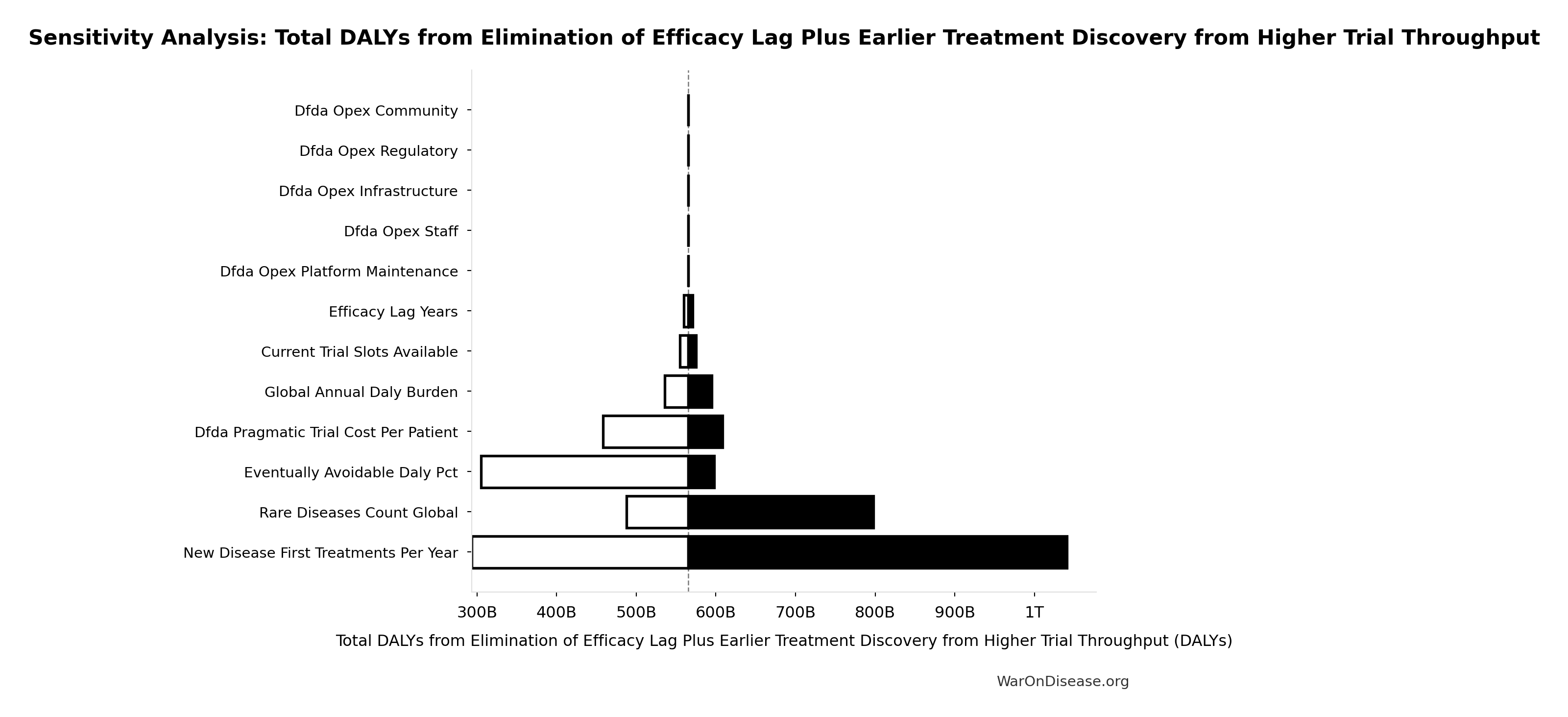
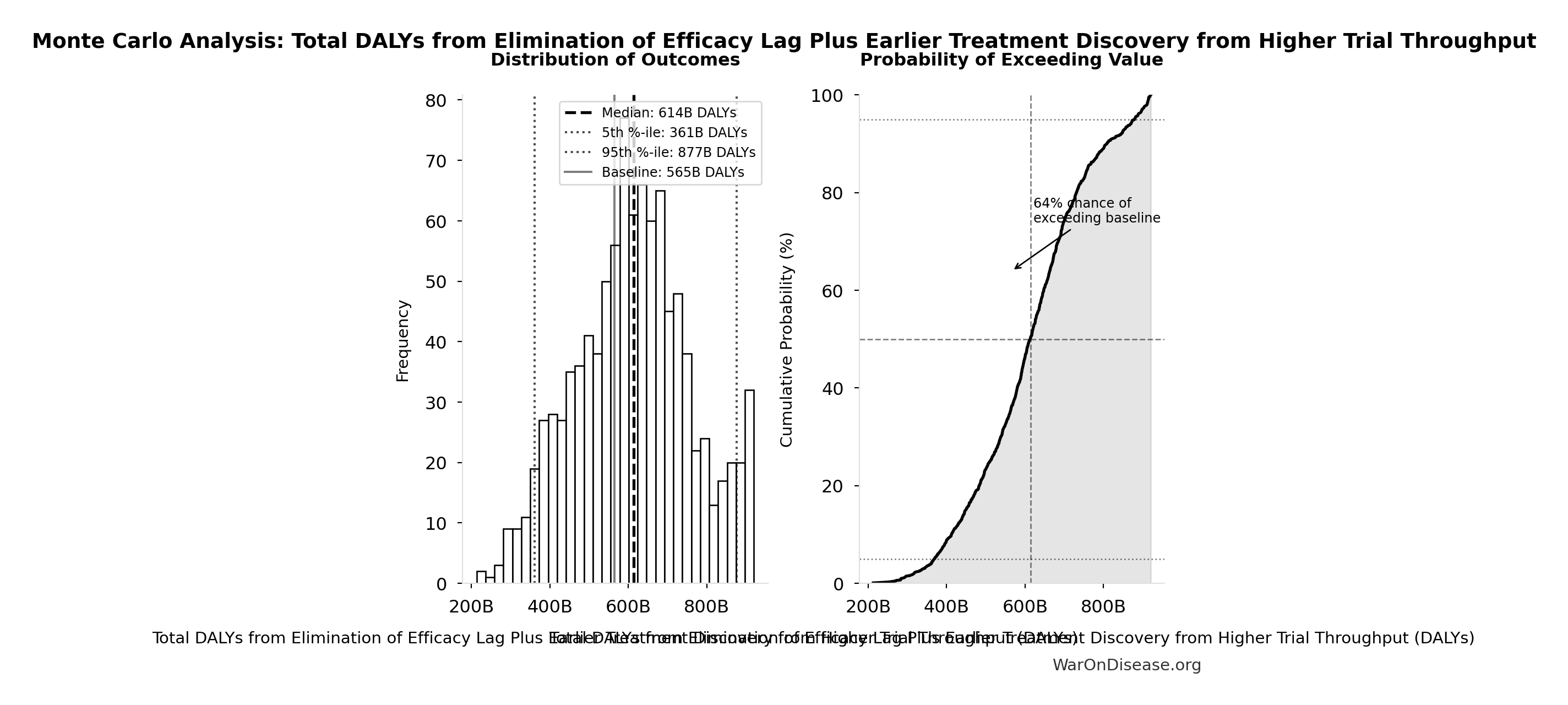
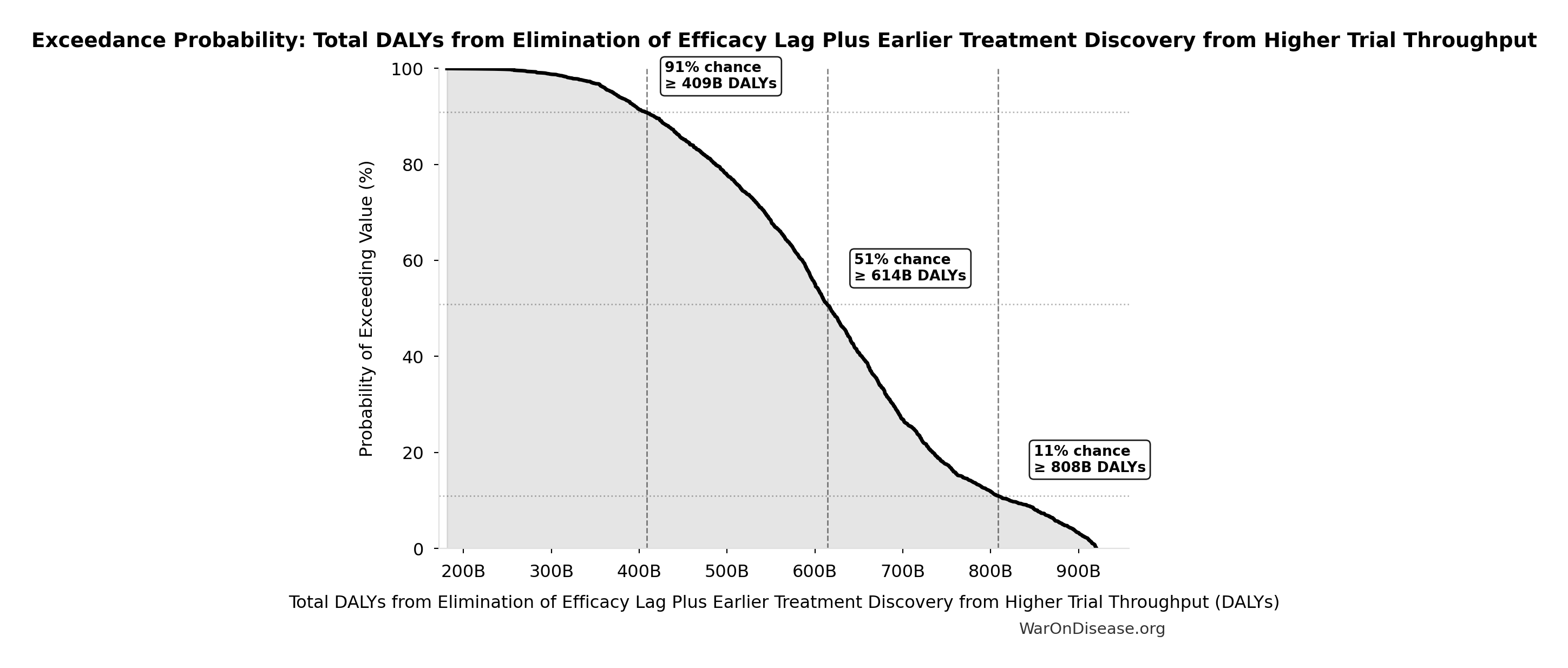
Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput: 565 billion DALYs
Total DALYs averted from the combined dFDA timeline shift. Calculated as annual global DALY burden × eventually avoidable percentage × timeline shift years. Includes both fatal and non-fatal diseases (WHO GBD methodology).
Inputs:
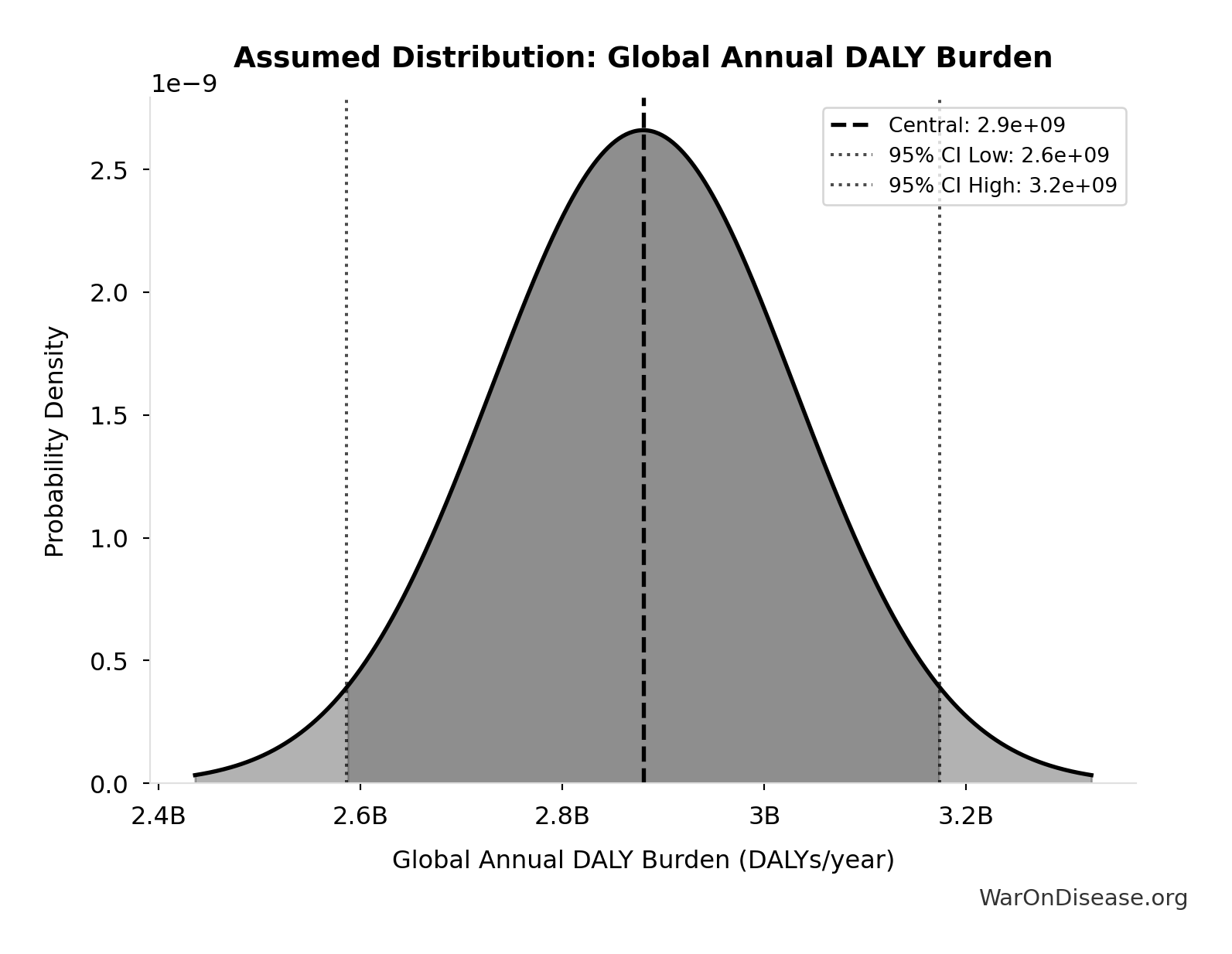
- Global Annual DALY Burden 📊: 2.88 billion DALYs/year (SE: ±150 million DALYs/year)
- Eventually Avoidable DALY Percentage: 92.6% (95% CI: 50% - 98%)
- dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift 🔢: 212 years
\[ \begin{gathered} DALYs_{max} \\ = DALYs_{global,ann} \times Pct_{avoid,DALY} \times T_{accel,max} \\ = 2.88B \times 92.6\% \times 212 \\ = 565B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift (years) | 0.8999 | Strong driver |
| Eventually Avoidable DALY Percentage (percentage) | 0.4866 | Moderate driver |
| Global Annual DALY Burden (DALYs/year) | 0.0432 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 565 billion |
| Mean (expected value) | 610 billion |
| Median (50th percentile) | 614 billion |
| Standard Deviation | 148 billion |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [361 billion, 877 billion] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
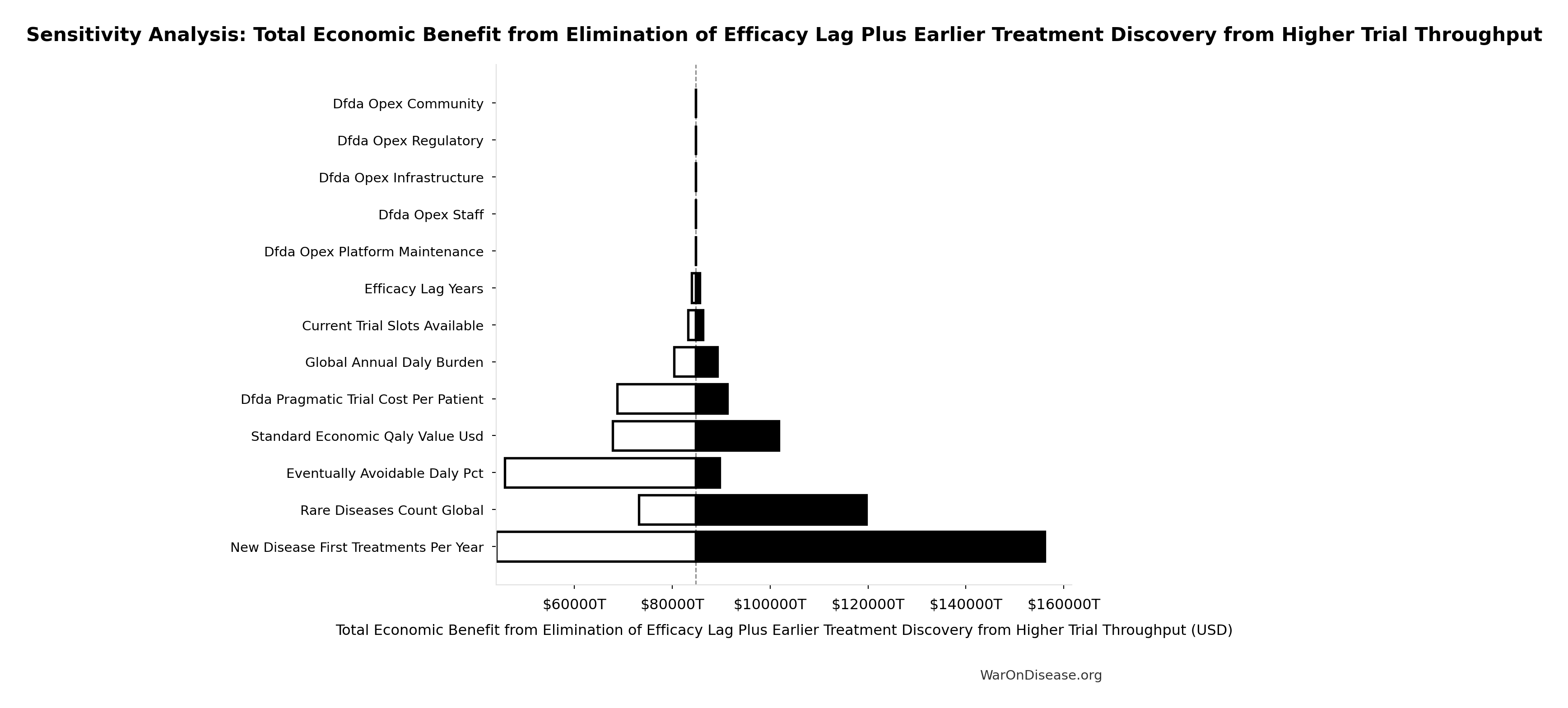
Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput: $84.8 quadrillion
Total economic value from the combined dFDA timeline shift. DALYs valued at standard economic rate.
Inputs:
- Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput 🔢: 565 billion DALYs
- Standard Economic Value per QALY 📊: $150K (SE: ±$30K)
\[ \begin{gathered} Value_{max} \\ = DALYs_{max} \times Value_{QALY} \\ = 565B \times \$150K \\ = \$84800T \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} DALYs_{max} \\ = DALYs_{global,ann} \times Pct_{avoid,DALY} \times T_{accel,max} \\ = 2.88B \times 92.6\% \times 212 \\ = 565B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput (DALYs) | 1.7788 | Strong driver |
| Standard Economic Value per QALY (USD/QALY) | 1.3381 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
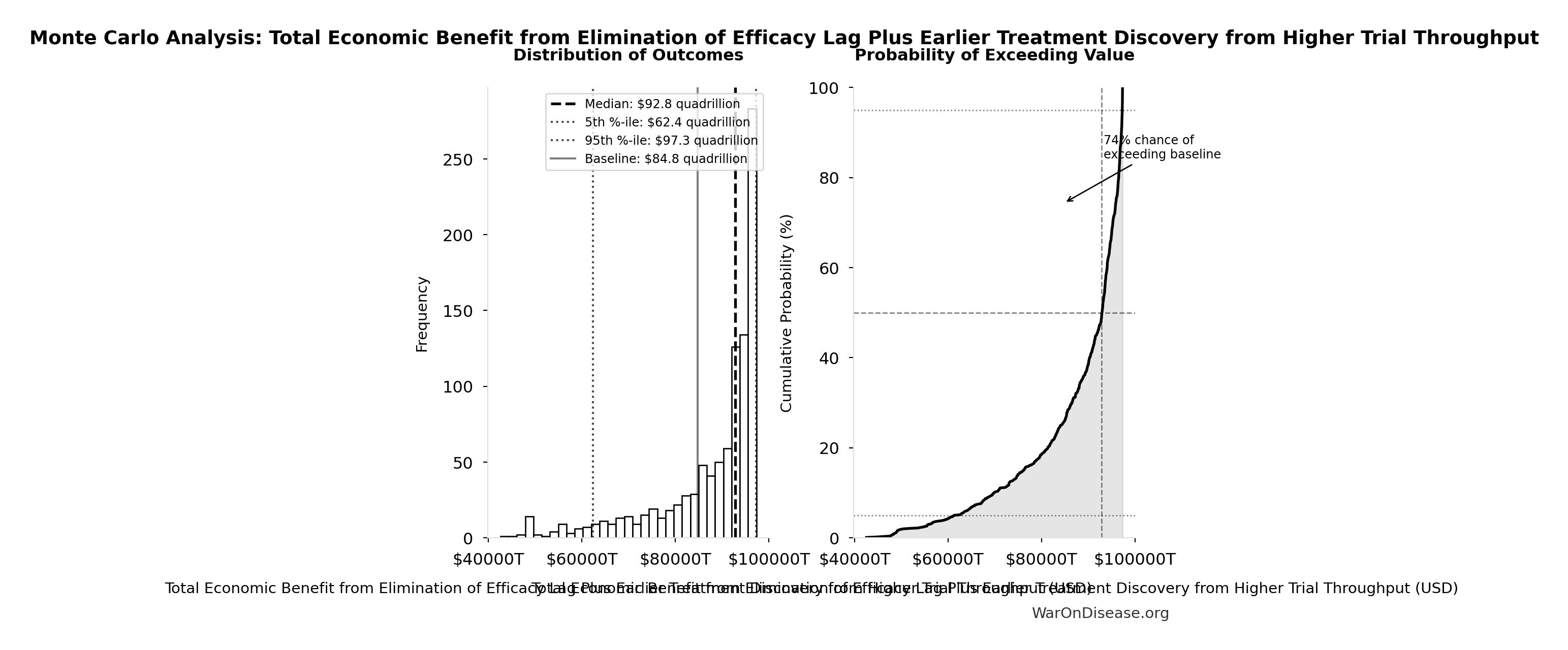
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $84.8 quadrillion |
| Mean (expected value) | $87.8 quadrillion |
| Median (50th percentile) | $92.9 quadrillion |
| Standard Deviation | $11.5 quadrillion |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$62.4 quadrillion, $97.3 quadrillion] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
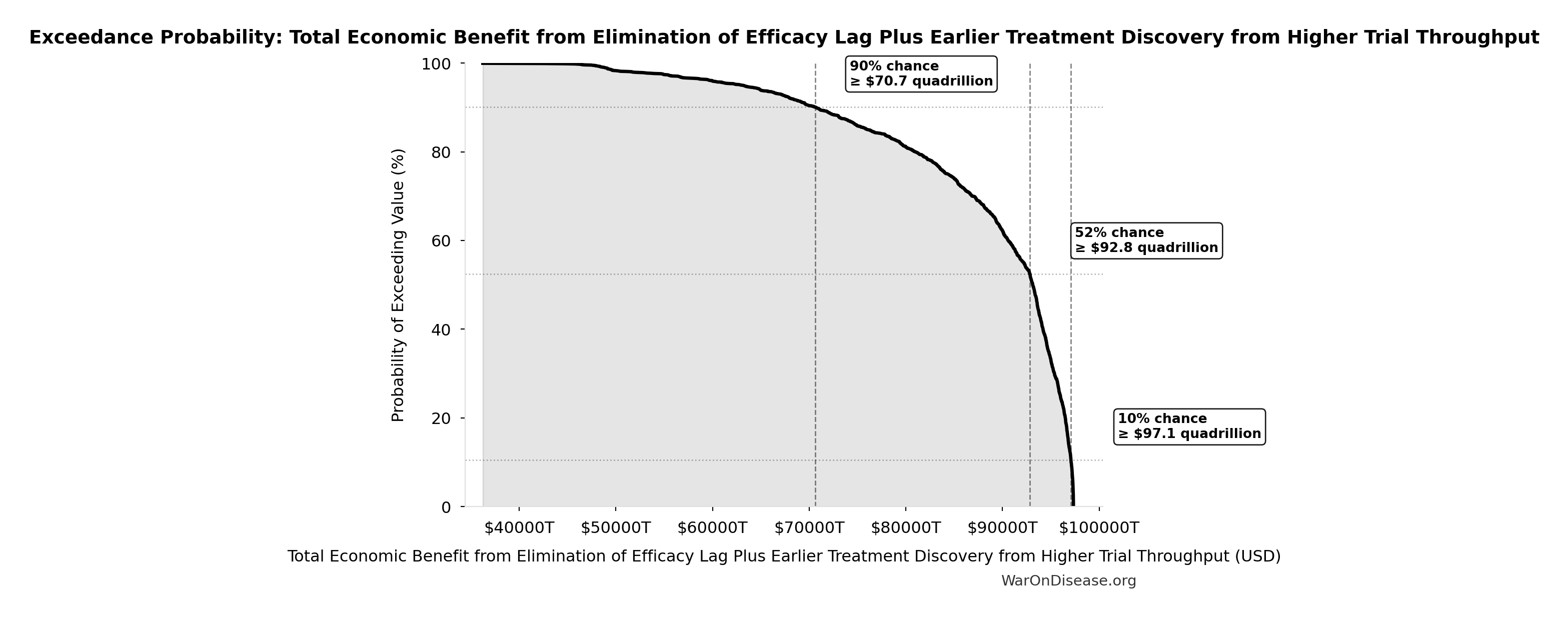
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
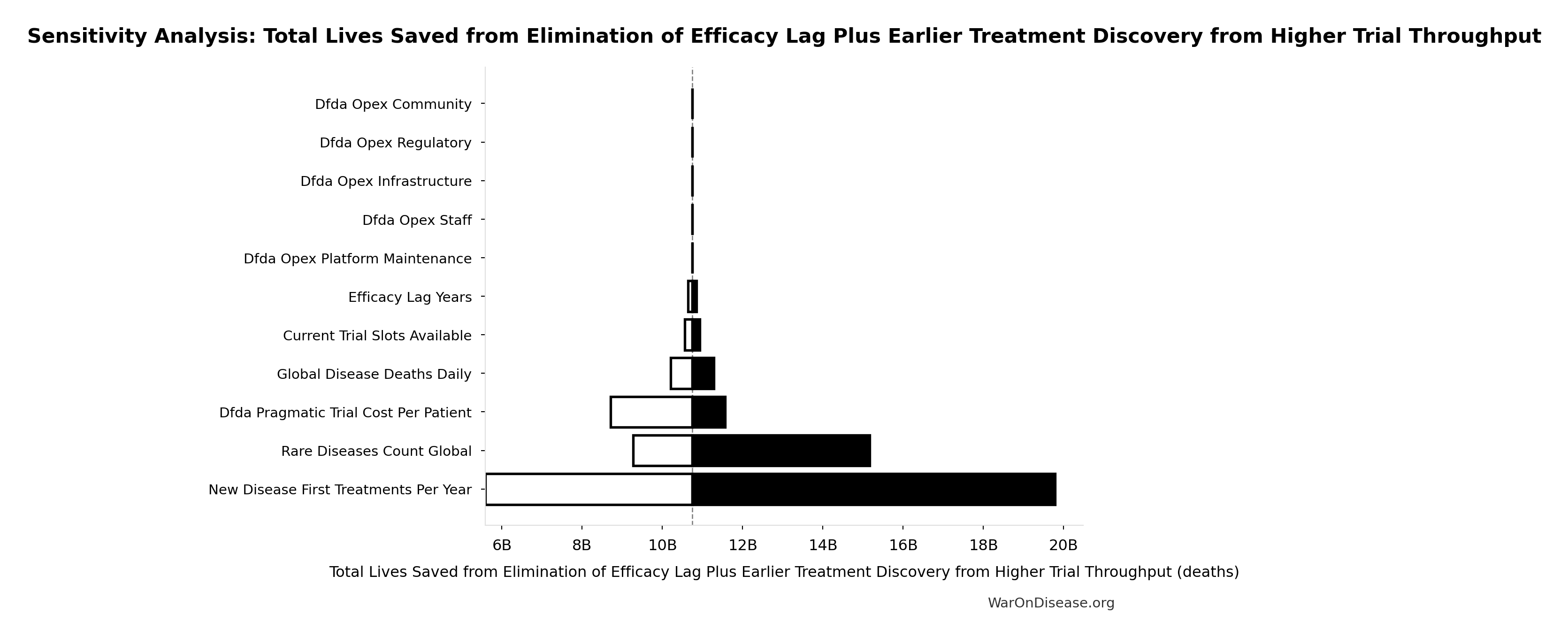
Total Lives Saved from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput: 10.7 billion deaths
Total eventually avoidable deaths from the combined dFDA timeline shift. Represents deaths prevented when cures arrive earlier due to both increased trial capacity and eliminated efficacy lag.
Inputs:
- Global Daily Deaths from Disease and Aging 📊: 150 thousand deaths/day (SE: ±7.5 thousand deaths/day)
- dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift 🔢: 212 years
\[ \begin{gathered} Lives_{max} \\ = Deaths_{disease,daily} \times T_{accel,max} \times 338 \\ = 150{,}000 \times 212 \times 338 \\ = 10.7B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Total Lives Saved from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift (years) | 1.0374 | Strong driver |
| Global Daily Deaths from Disease and Aging (deaths/day) | 0.0406 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
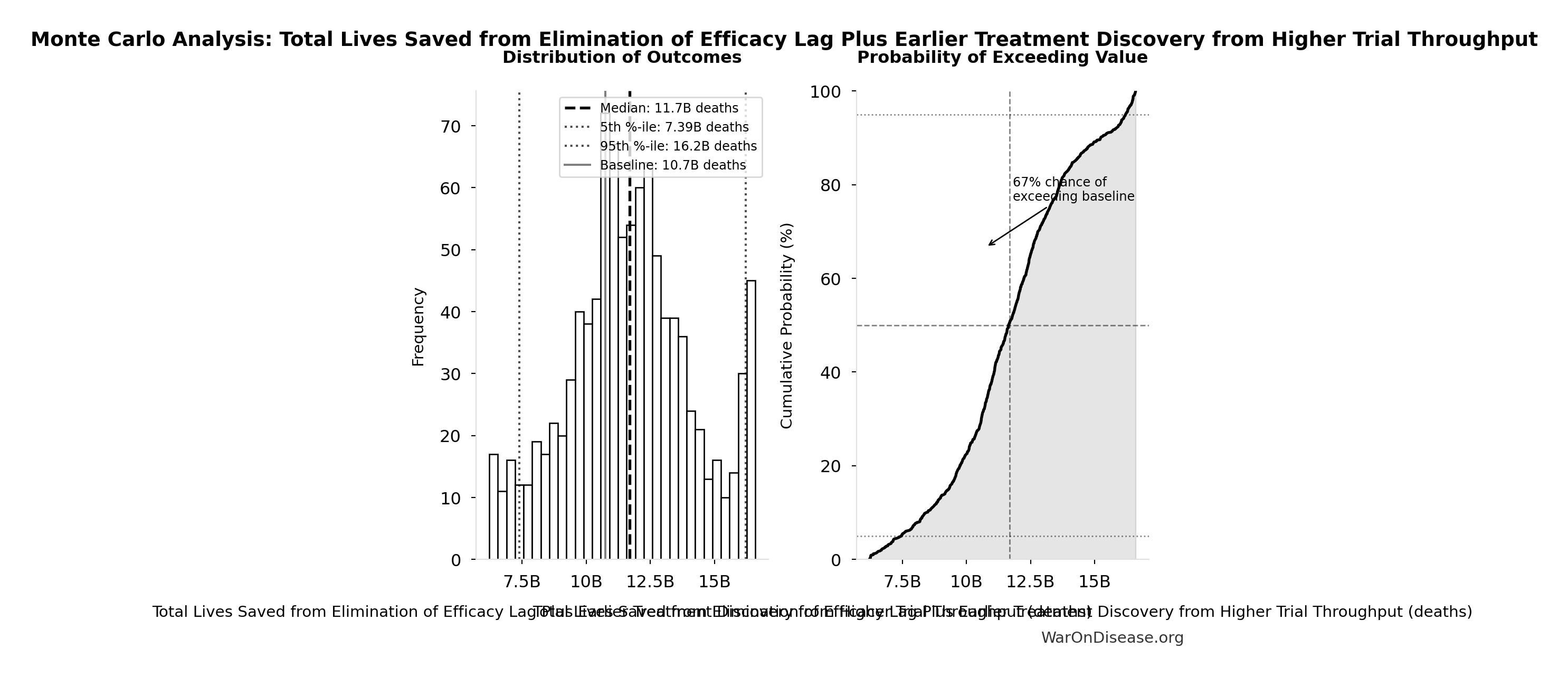
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Total Lives Saved from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 10.7 billion |
| Mean (expected value) | 11.7 billion |
| Median (50th percentile) | 11.7 billion |
| Standard Deviation | 2.45 billion |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [7.4 billion, 16.2 billion] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Total Lives Saved from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
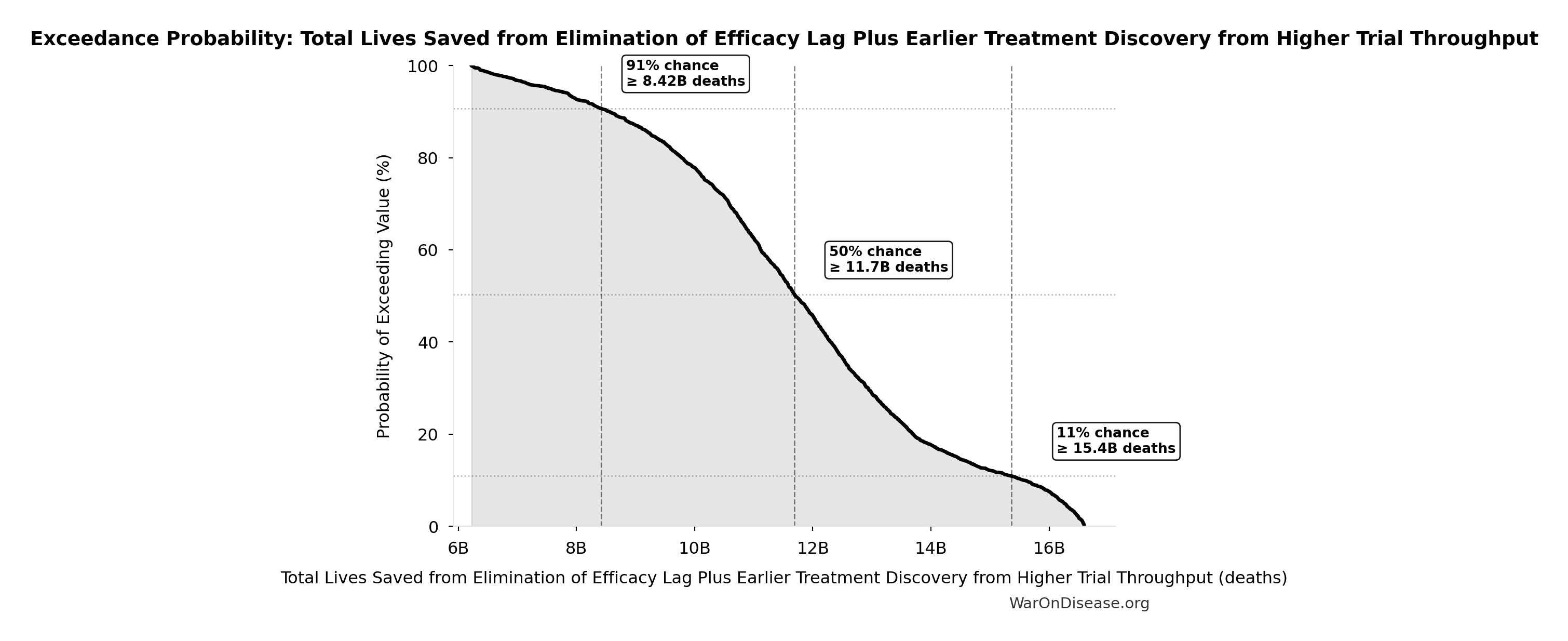
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Total Lives Saved from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
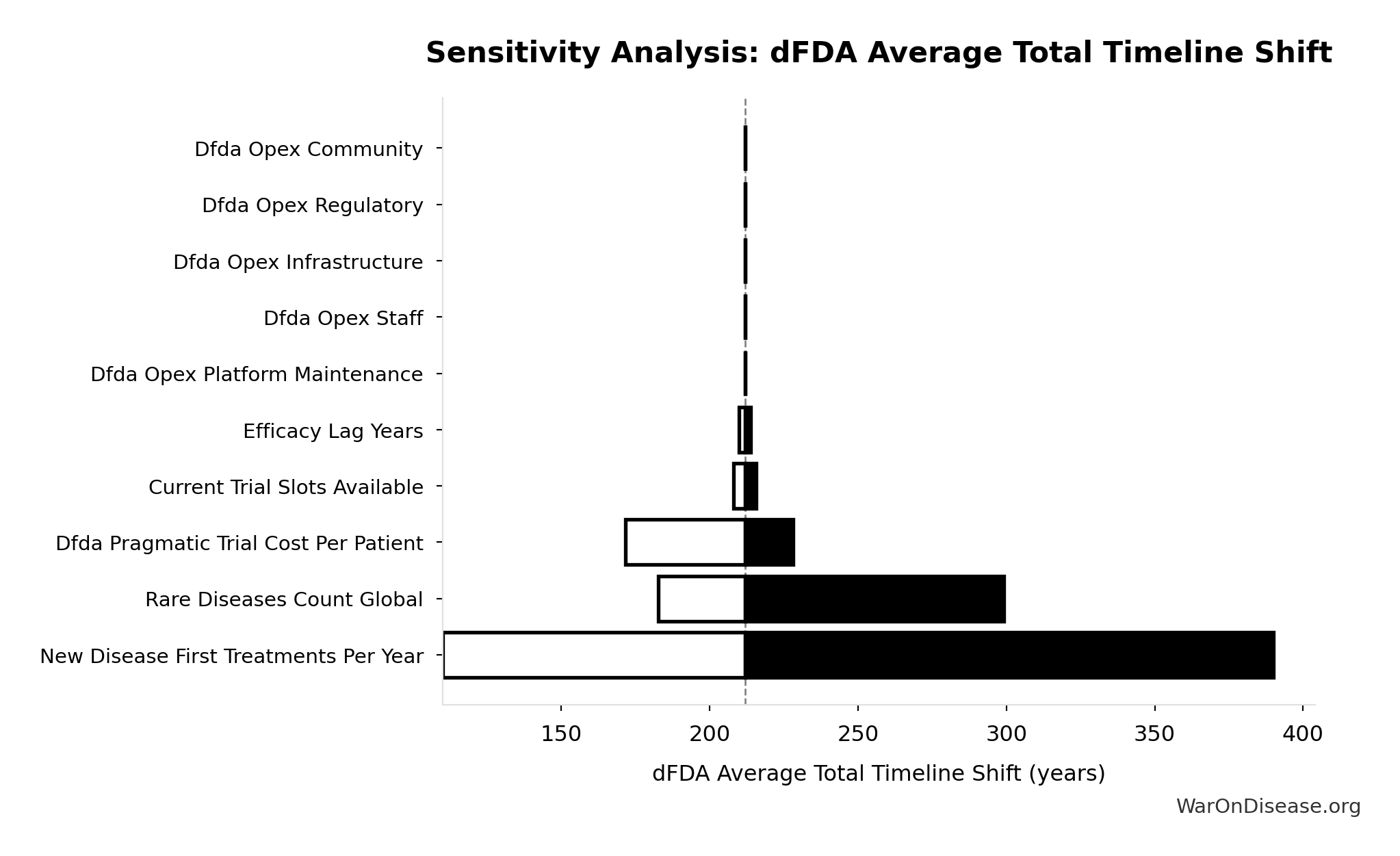
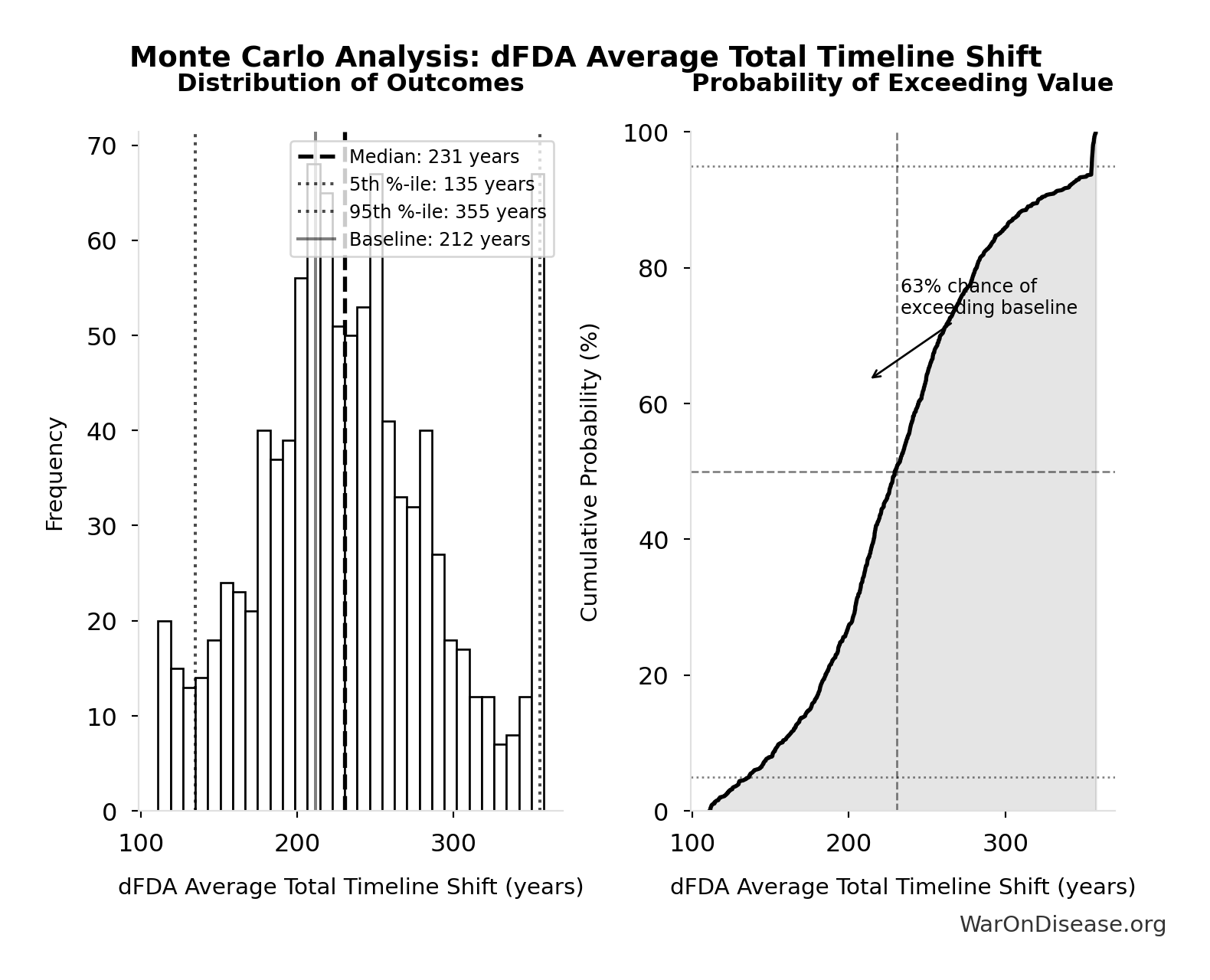
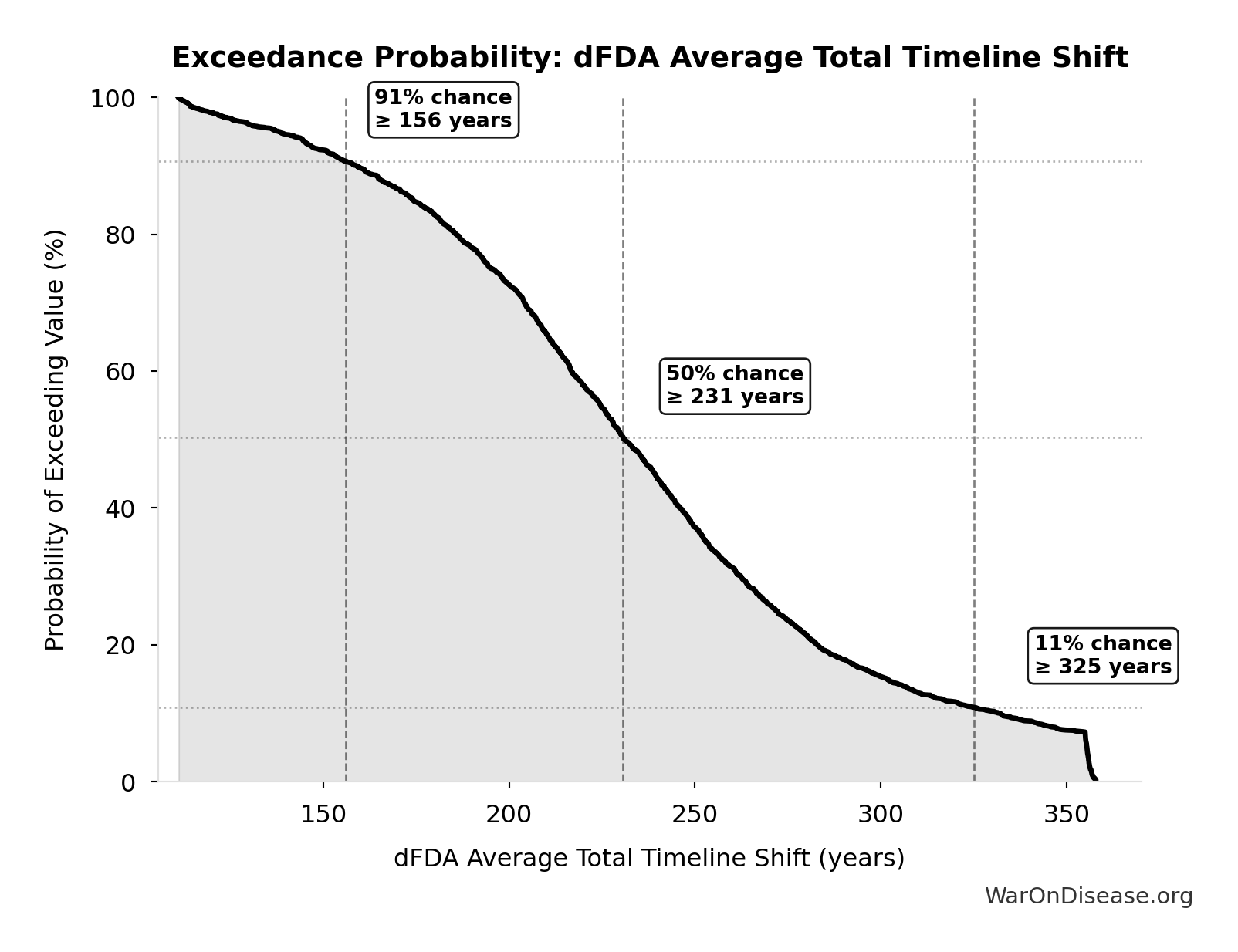
dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift: 212 years
Average years earlier patients receive treatments due to dFDA. Combines treatment timeline acceleration from increased trial capacity with efficacy lag elimination for treatments already discovered.
Inputs:
- dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration 🔢: 204 years
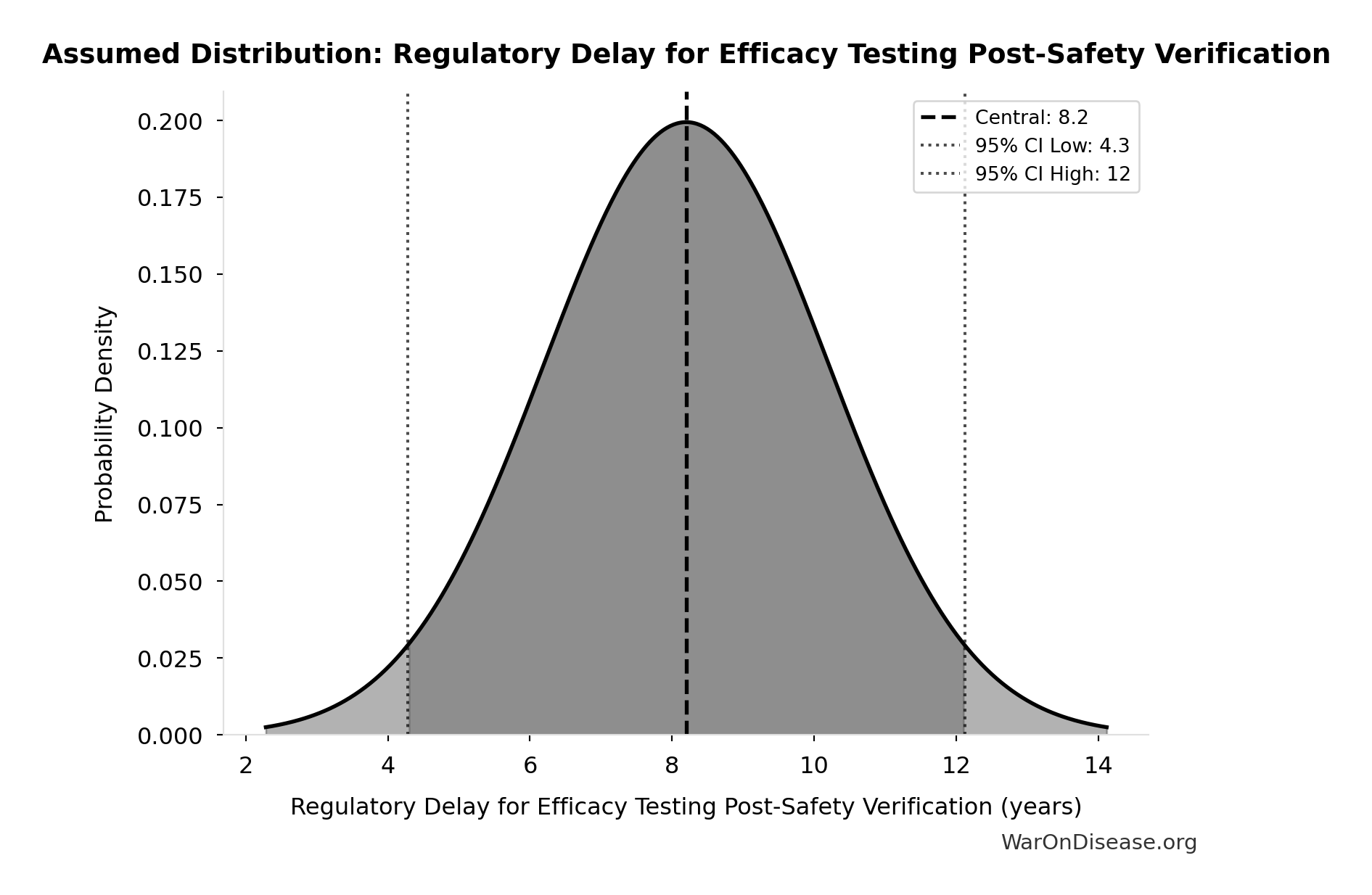
- Regulatory Delay for Efficacy Testing Post-Safety Verification 📊: 8.2 years (SE: ±2 years)
\[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration (years) | 1.0325 | Strong driver |
| Regulatory Delay for Efficacy Testing Post-Safety Verification (years) | 0.0328 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 212 |
| Mean (expected value) | 233 |
| Median (50th percentile) | 231 |
| Standard Deviation | 60.3 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [135, 355] |
The histogram shows the distribution of dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
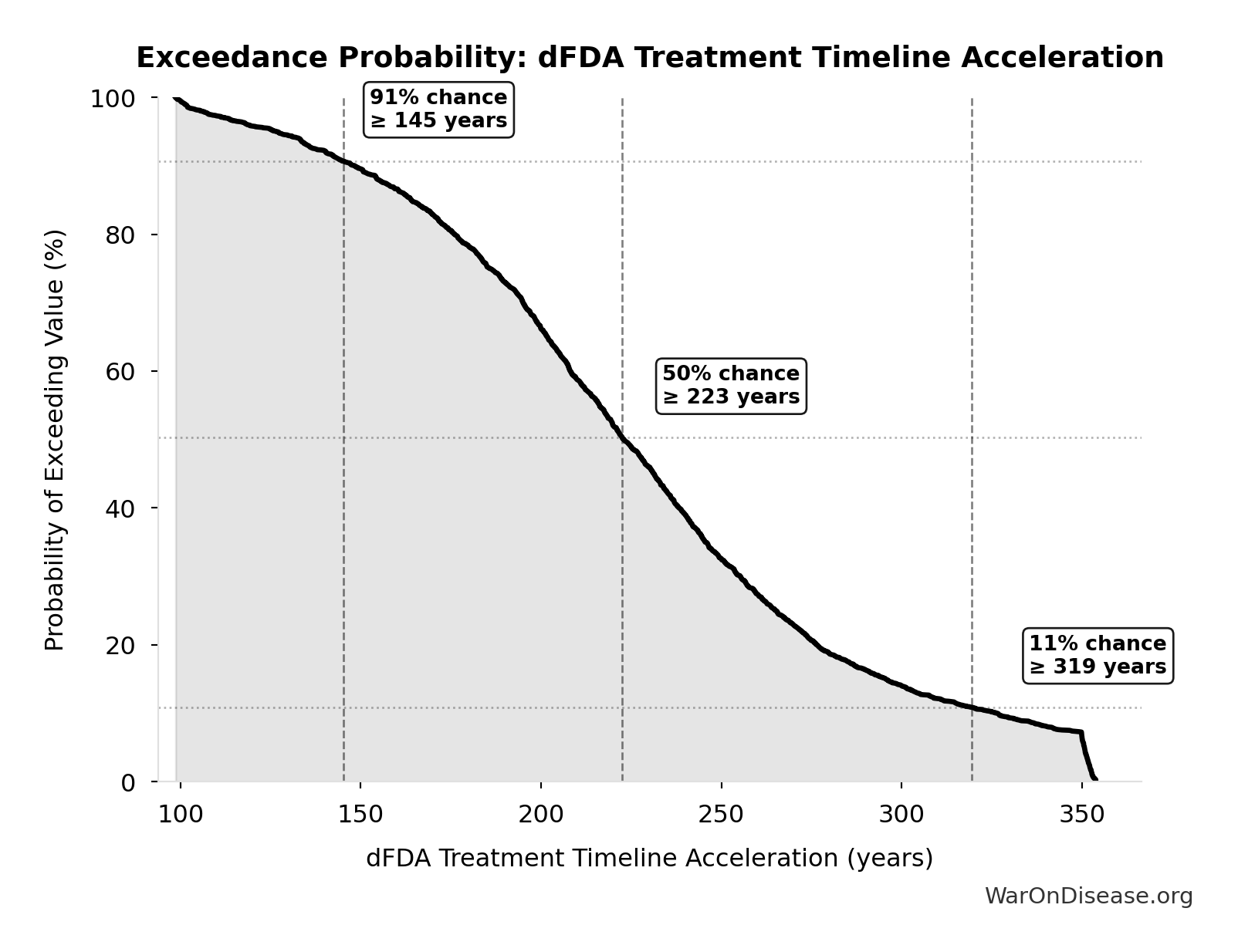
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that dFDA Average Total Timeline Shift will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
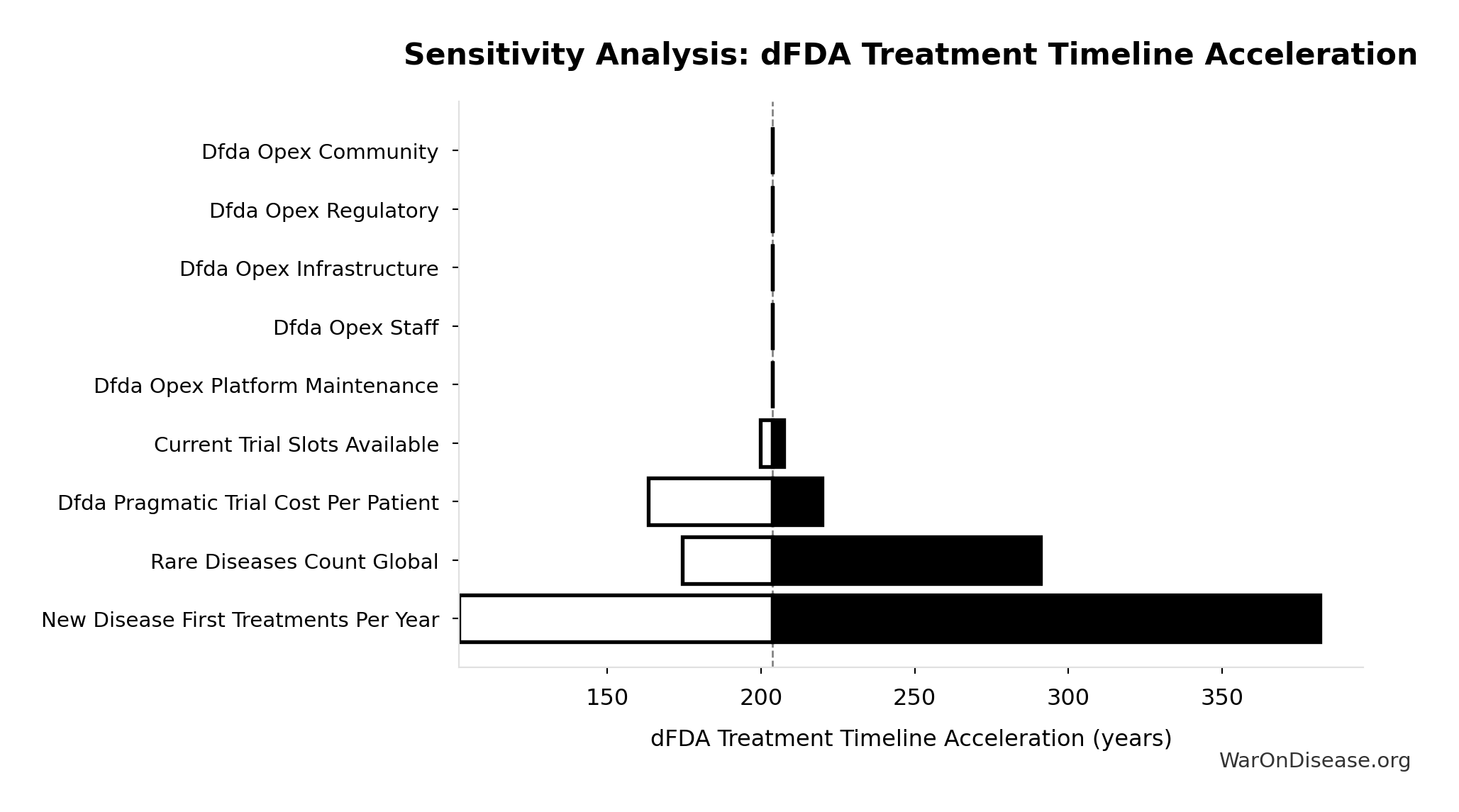
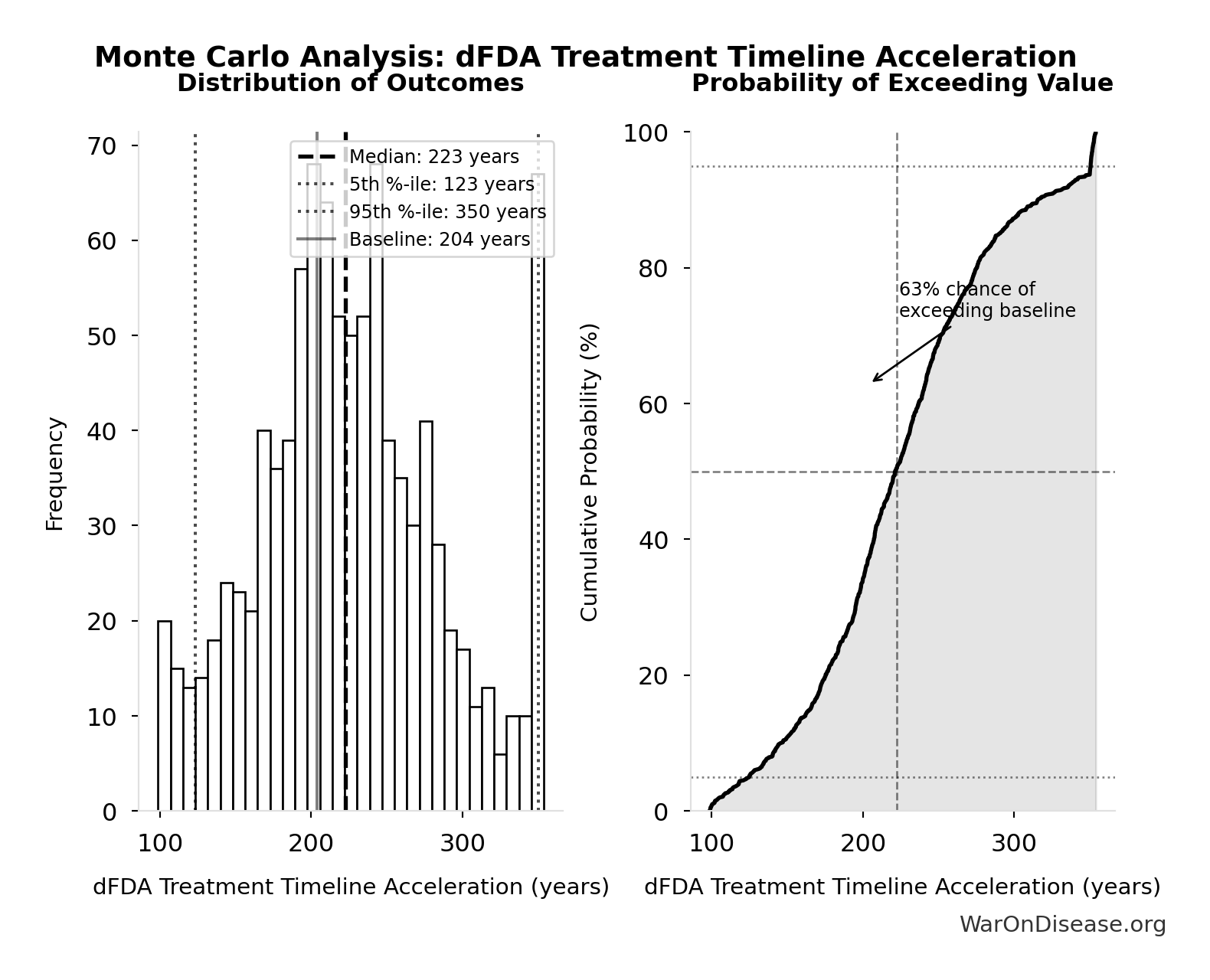
dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration: 204 years
Years earlier the average first treatment arrives due to dFDA’s trial capacity increase. Calculated as the status quo timeline reduced by the inverse of the capacity multiplier. Uses only trial capacity multiplier (not combined with valley of death rescue) because additional candidates don’t directly speed therapeutic space exploration.
Inputs:
- Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment 🔢: 222 years
- Trial Capacity Multiplier 🔢: 12.3x
\[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment (years) | 1.0664 | Strong driver |
| Trial Capacity Multiplier (x) | -0.0777 | Minimal effect |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 204 |
| Mean (expected value) | 225 |
| Median (50th percentile) | 223 |
| Standard Deviation | 62.3 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [123, 350] |
The histogram shows the distribution of dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that dFDA Treatment Timeline Acceleration will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
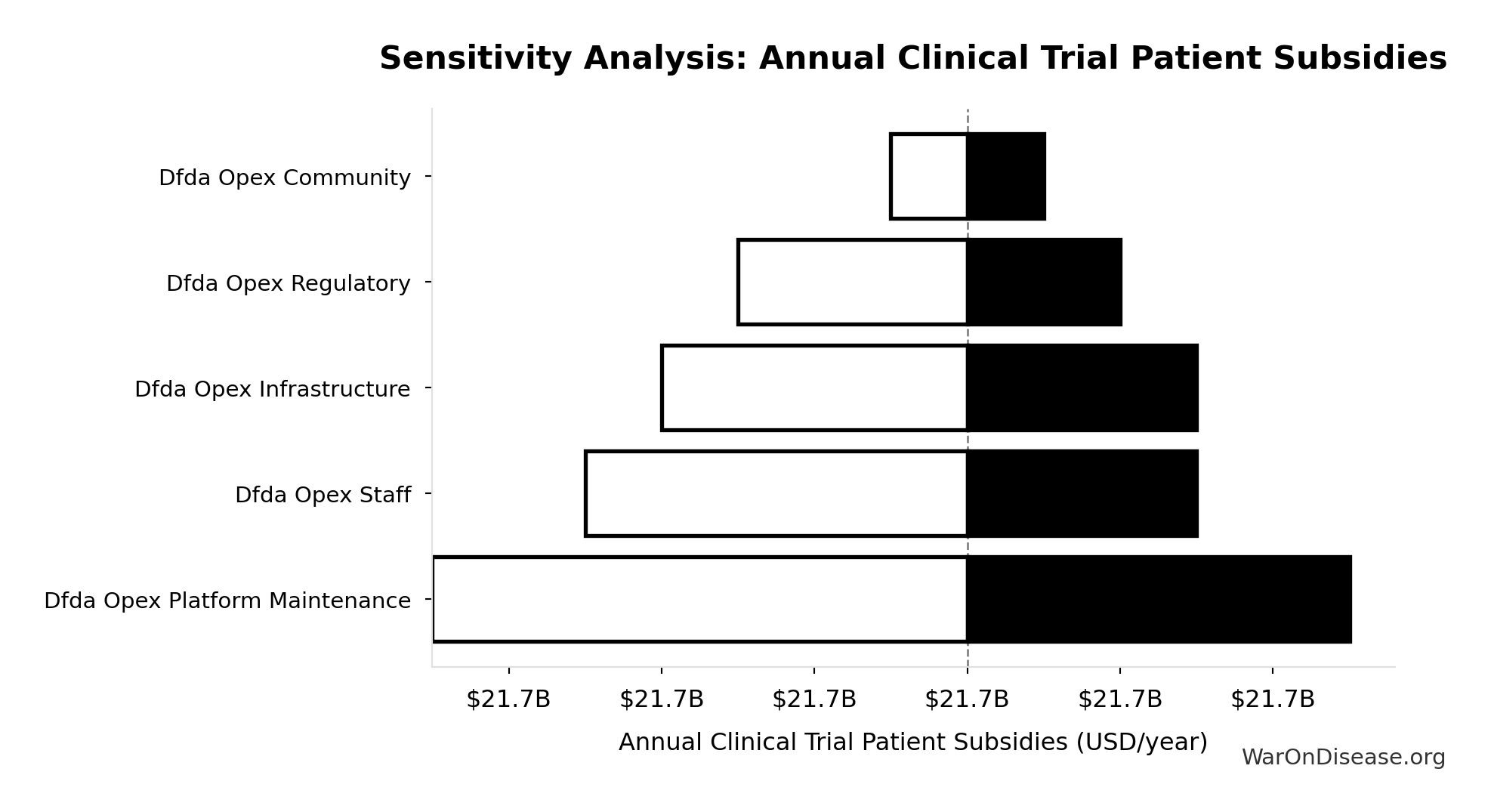
dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies: $21.8B
Annual clinical trial patient subsidies from dFDA funding (total funding minus operational costs)
Inputs:
- dFDA Annual Trial Funding: $21.8B
- Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs 🔢: $40M
\[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ✓ High confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total Annual Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Operational Costs (USD/year) | -1.0000 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
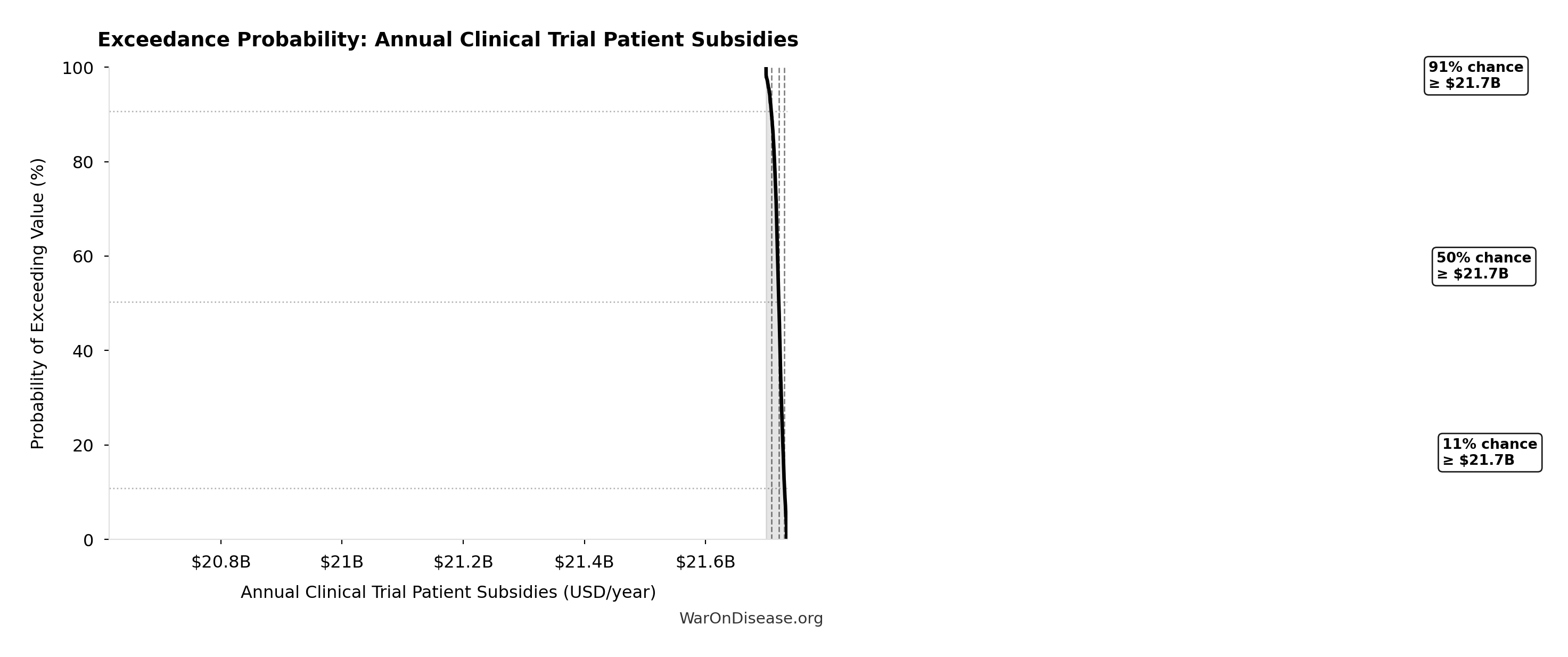
Simulation Results Summary: dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $21.8B |
| Mean (expected value) | $21.8B |
| Median (50th percentile) | $21.8B |
| Standard Deviation | $8.21M |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$21.7B, $21.8B] |
The histogram shows the distribution of dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that dFDA Annual Trial Subsidies will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
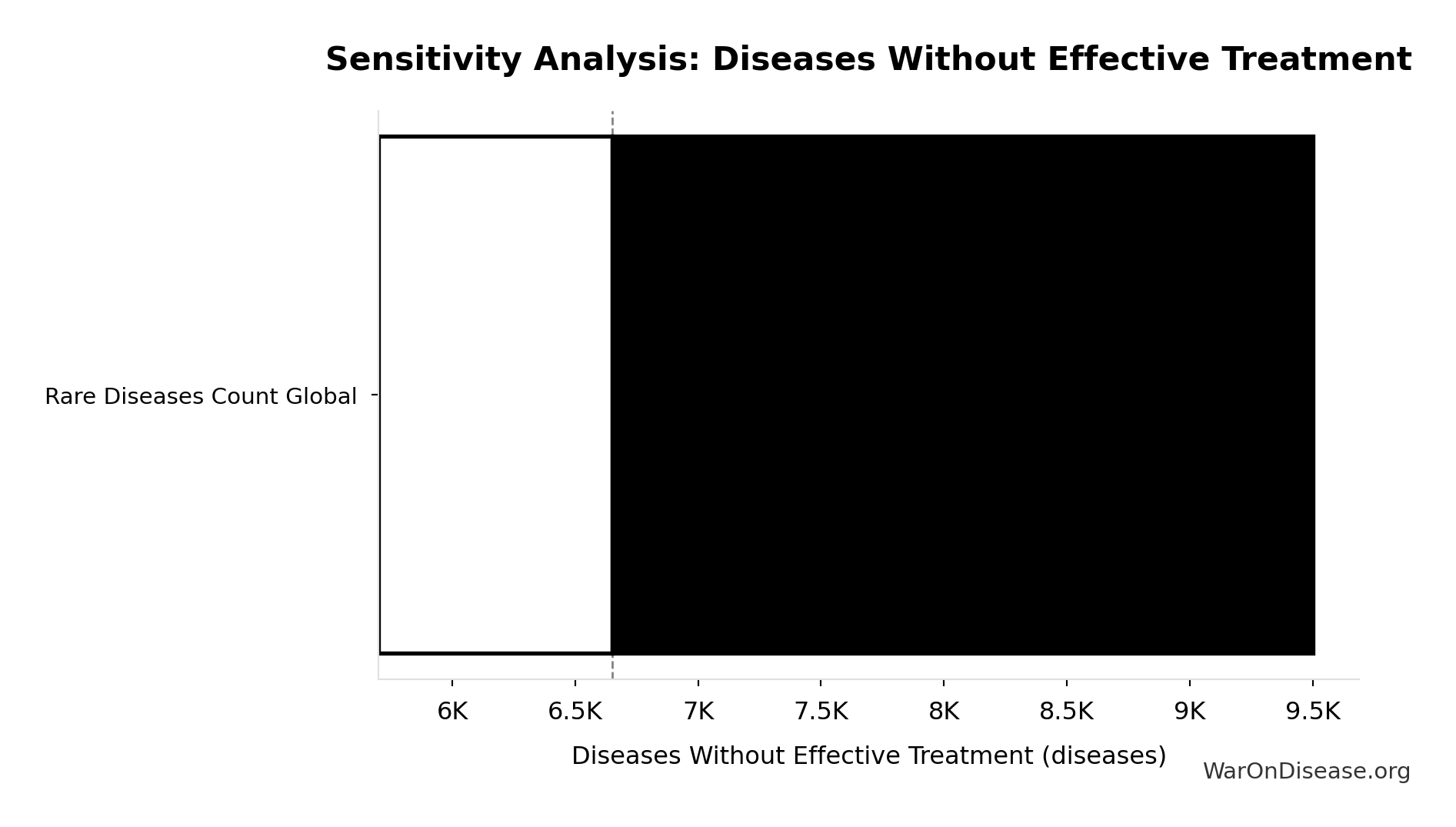
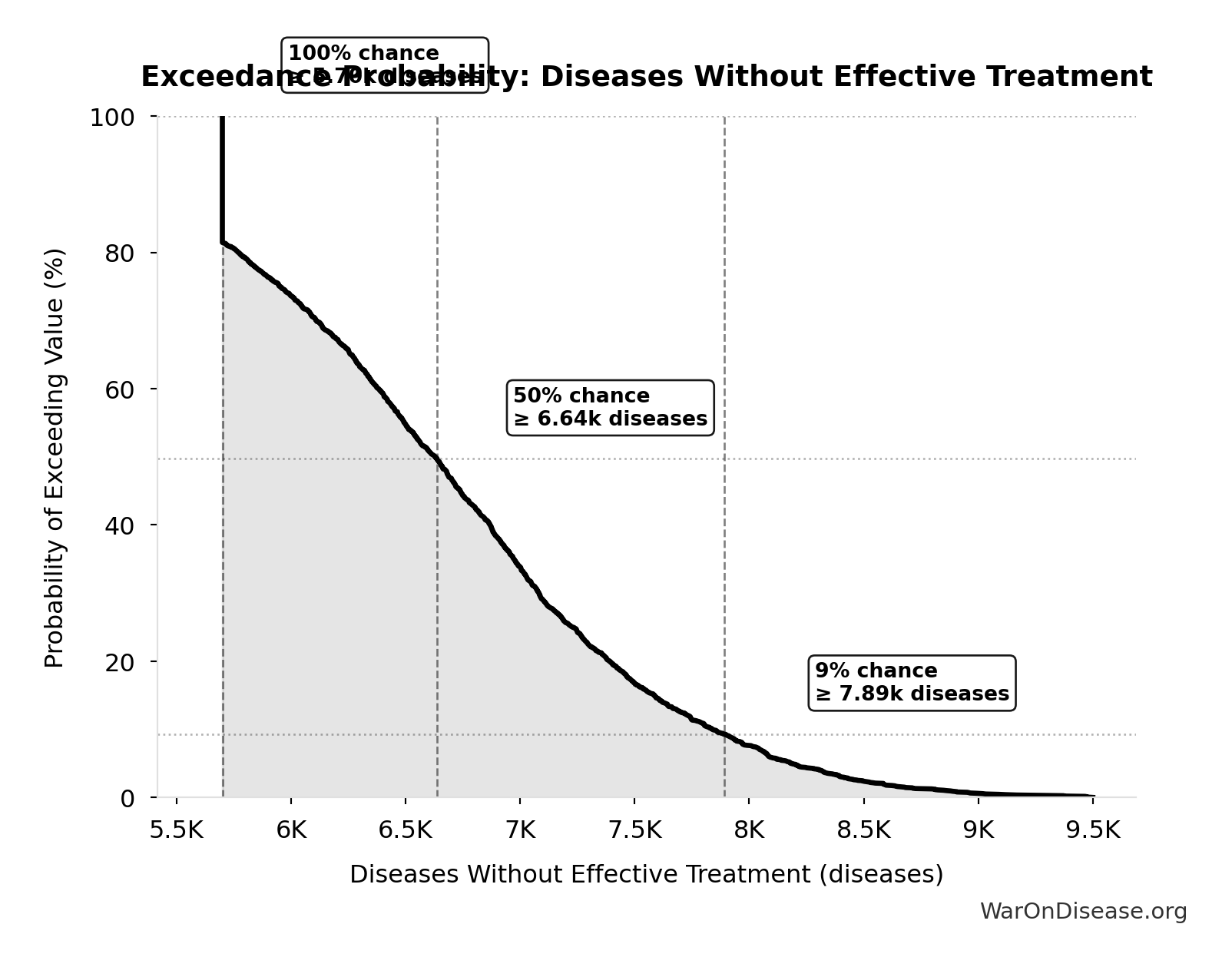
Diseases Without Effective Treatment: 6.65 thousand diseases
Number of diseases without effective treatment. 95% of 7,000 rare diseases lack FDA-approved treatment (per Orphanet 2024). This represents the therapeutic search space that remains unexplored.
Inputs:
- Total Number of Rare Diseases Globally 📊: 7 thousand diseases (95% CI: 6 thousand diseases - 10 thousand diseases)
\[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \]
Methodology:133
~ Medium confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Diseases Without Effective Treatment
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Rare Diseases Globally (diseases) | 1.0000 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
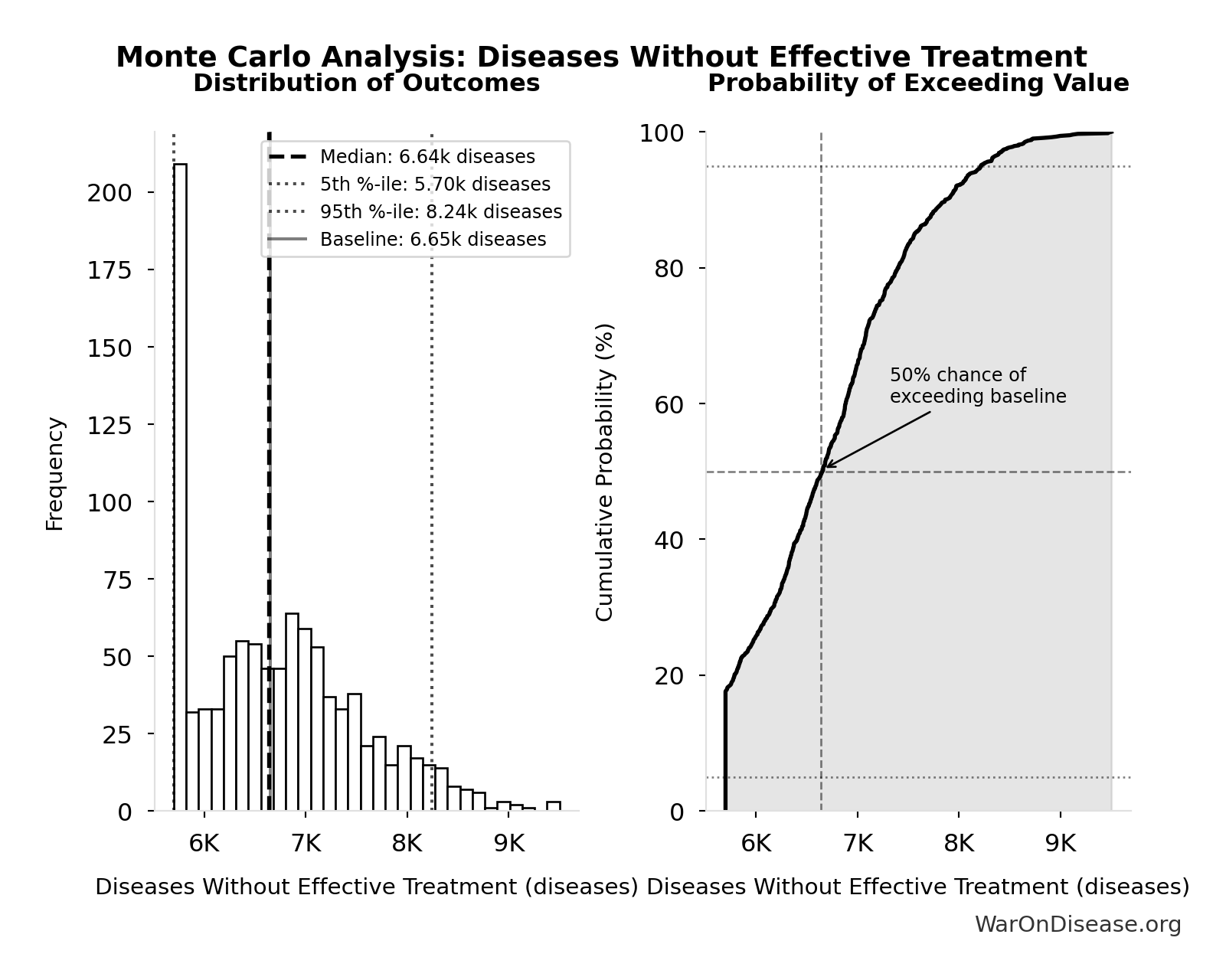
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Diseases Without Effective Treatment
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 6.65 thousand |
| Mean (expected value) | 6.73 thousand |
| Median (50th percentile) | 6.64 thousand |
| Standard Deviation | 835 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [5.7 thousand, 8.24 thousand] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Diseases Without Effective Treatment across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Diseases Without Effective Treatment will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
Global Political Reform Investment: $128B
Estimated global advocacy investment for policy reform. Calculated as US costs × global ratio (based on discretionary spending). Upper bound representing full democratic engagement at scale.
Inputs:
- US Political Reform Investment (Total) 🔢: $25.5B
- Global-to-US Political Cost Ratio: 5:1 (95% CI: 3:1 - 8:1)
\[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{global,reform} \\ = Cost_{US,total} \times \rho_{global/US} \\ = \$25.5B \times 5 \\ = \$128B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{US,total} \\ = (Cost_{campaign} \\ + Cost_{lobby} \times 2) \times \mu_{effort} + Cost_{career} \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{US,congress} \\ = N_{congress} \times V_{post-office} \\ = 535 \times \$10M \\ = \$5.35B \end{gathered} \] ? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Global Political Reform Investment
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| US Political Reform Investment (Total) (USD) | 4.7165 | Strong driver |
| Global-to-US Political Cost Ratio (ratio) | -3.7249 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Global Political Reform Investment
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $128B |
| Mean (expected value) | $133B |
| Median (50th percentile) | $119B |
| Standard Deviation | $62.7B |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$55.2B, $266B] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Global Political Reform Investment across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Global Political Reform Investment will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
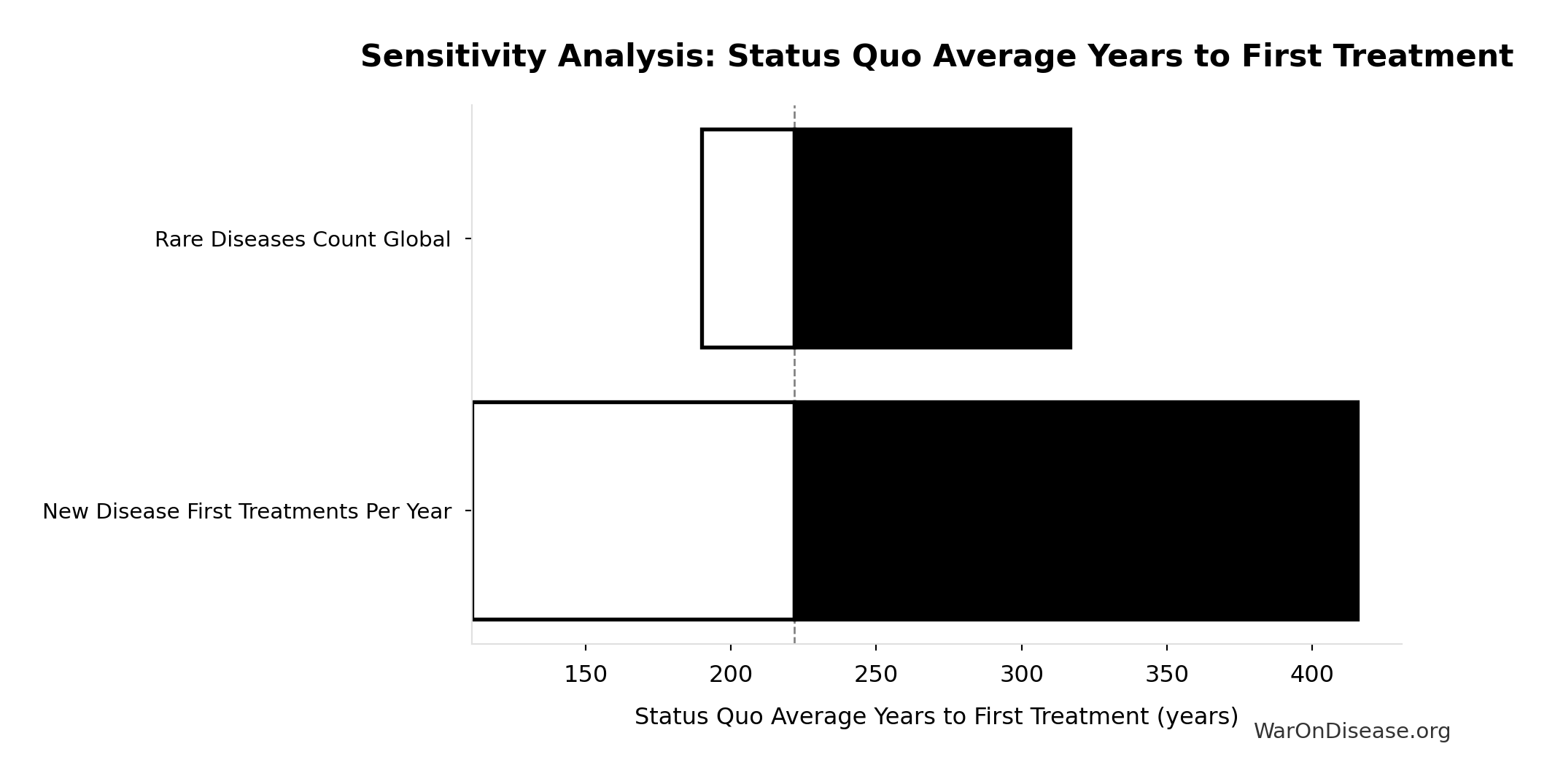
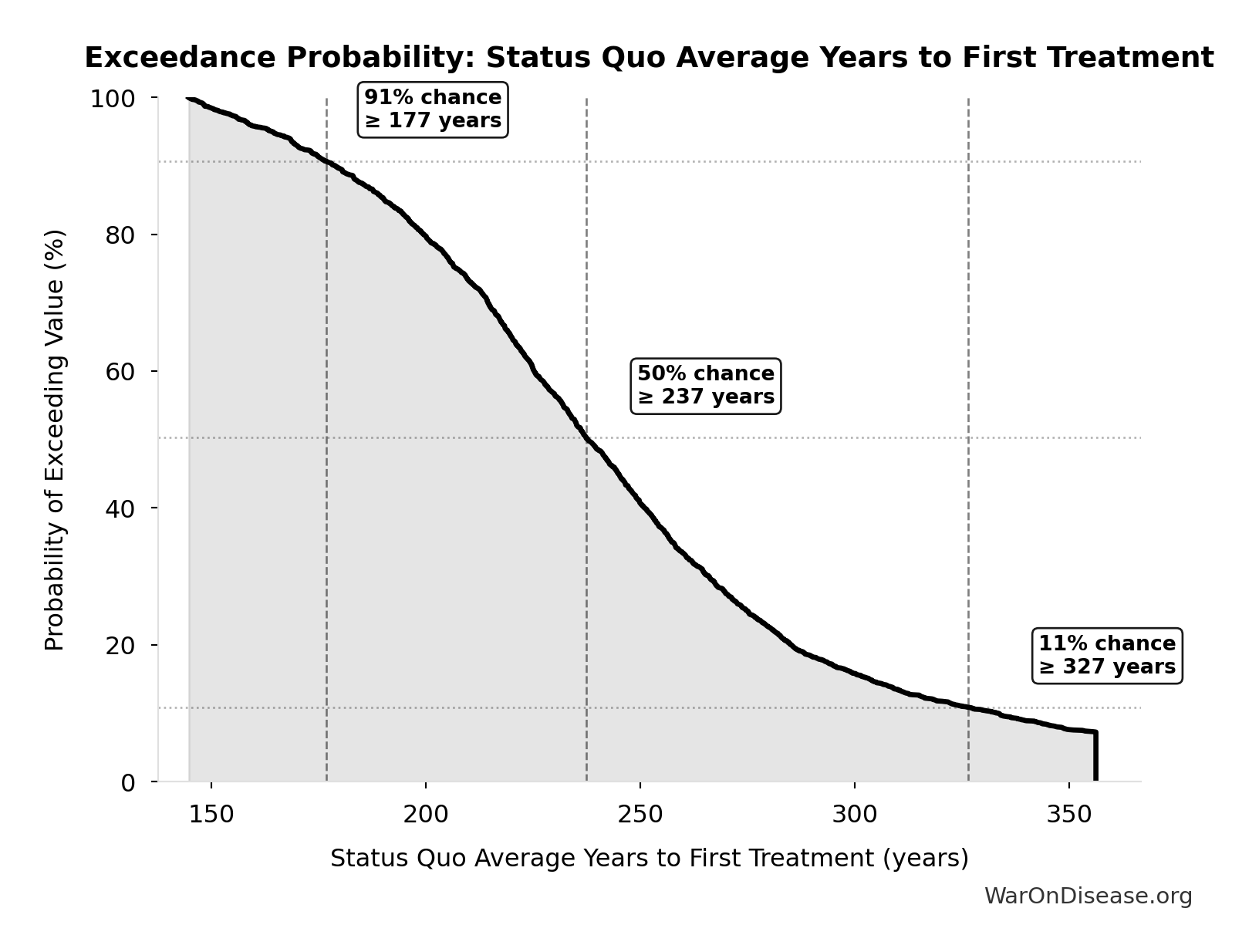
Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment: 222 years
Average years until first treatment discovered for a typical disease under current system. At current discovery rates, the average disease waits half the total exploration time (~443/2 = ~222 years).
Inputs:
- Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time 🔢: 443 years
\[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] Methodology:134
? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time (years) | 1.0000 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
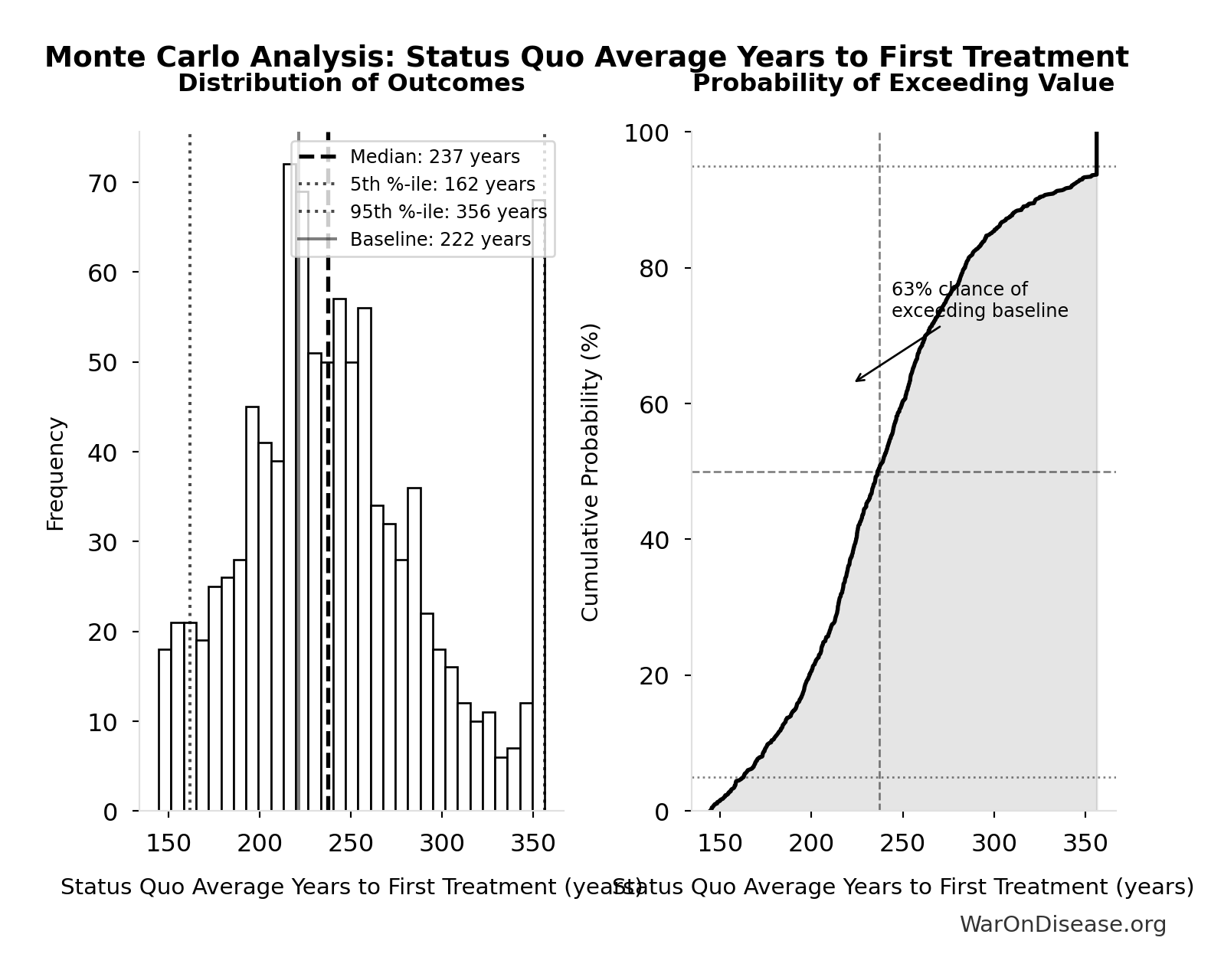
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 222 |
| Mean (expected value) | 242 |
| Median (50th percentile) | 237 |
| Standard Deviation | 53.2 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [162, 356] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Status Quo Average Years to First Treatment will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
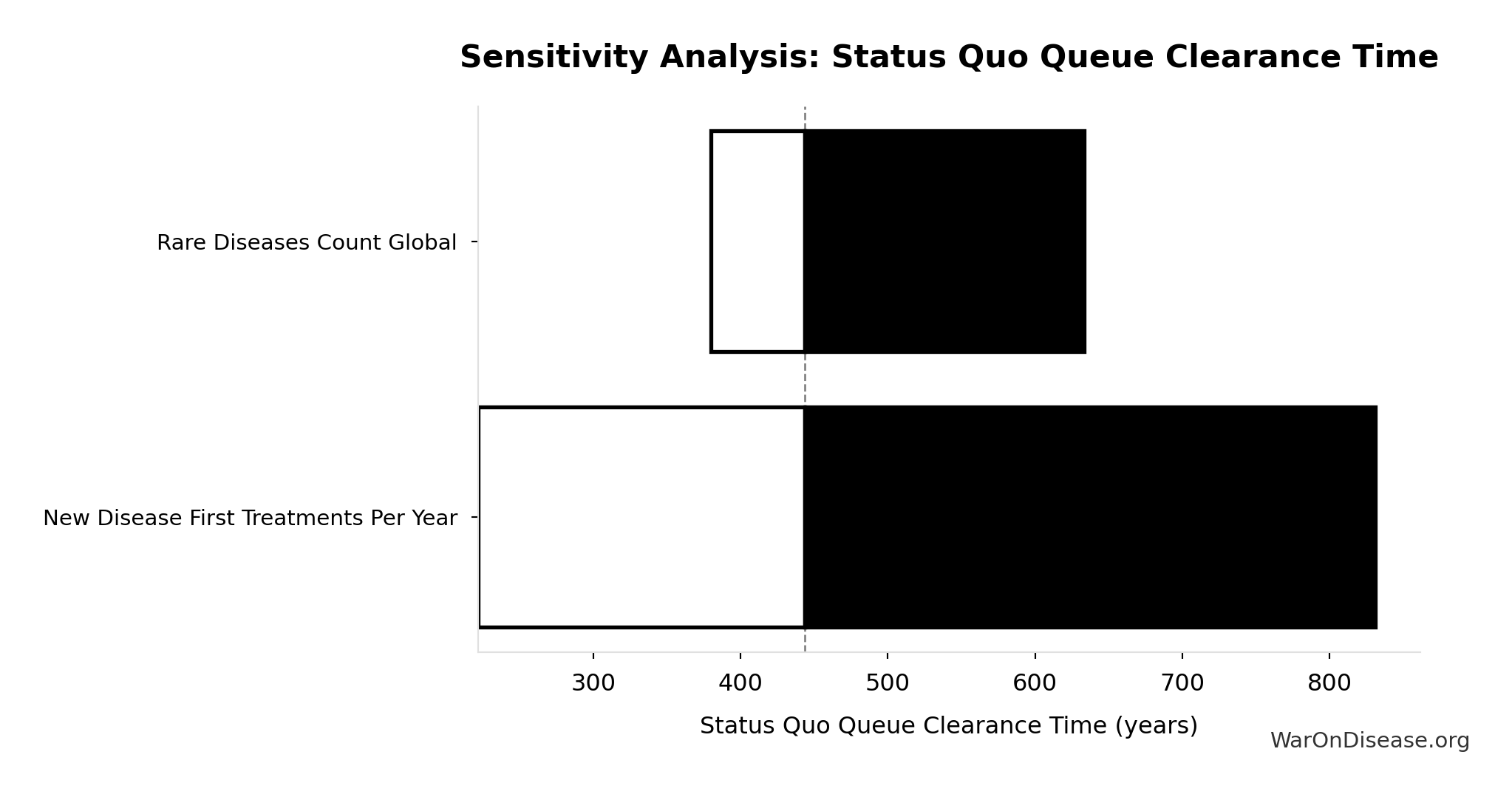
Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time: 443 years
Years to explore the entire therapeutic search space under current system. At current discovery rate of ~15 diseases/year getting first treatments, finding treatments for all ~6,650 untreated diseases would take ~443 years.
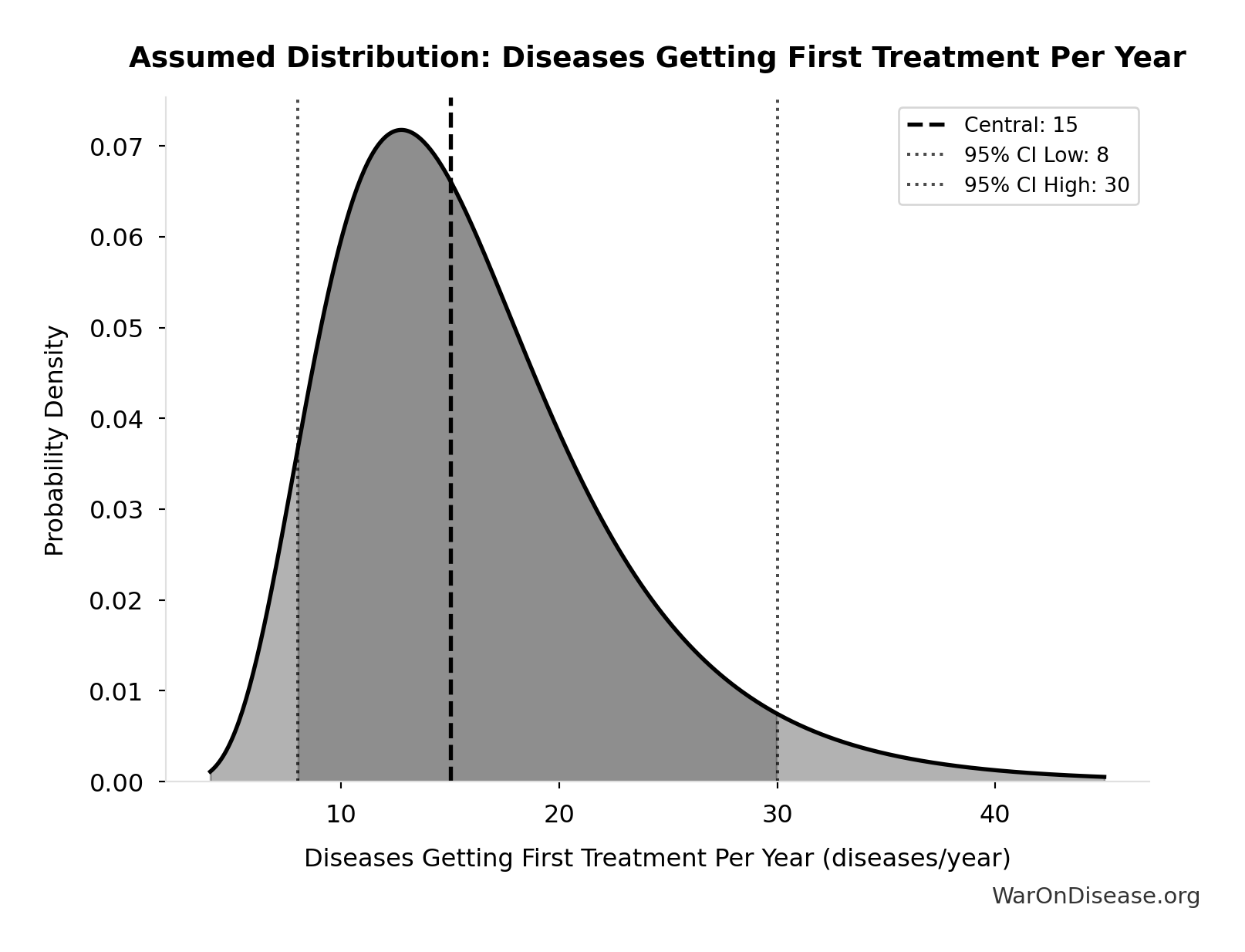
Inputs:
- Diseases Without Effective Treatment 🔢: 6.65 thousand diseases
- Diseases Getting First Treatment Per Year 📊: 15 diseases/year (95% CI: 8 diseases/year - 30 diseases/year)
\[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] Methodology:134
? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Diseases Without Effective Treatment (diseases) | -0.7011 | Strong driver |
| Diseases Getting First Treatment Per Year (diseases/year) | -0.2360 | Weak driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
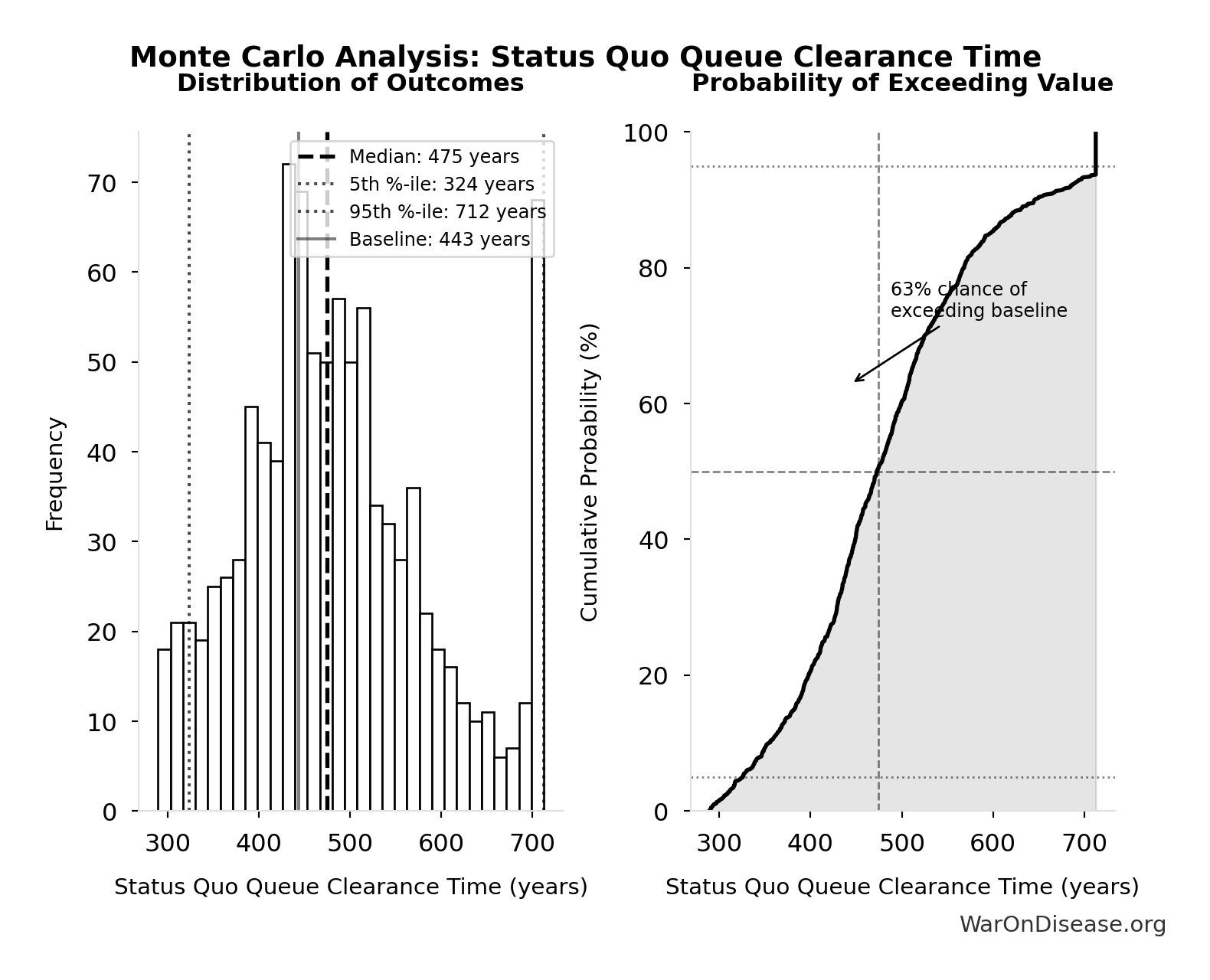
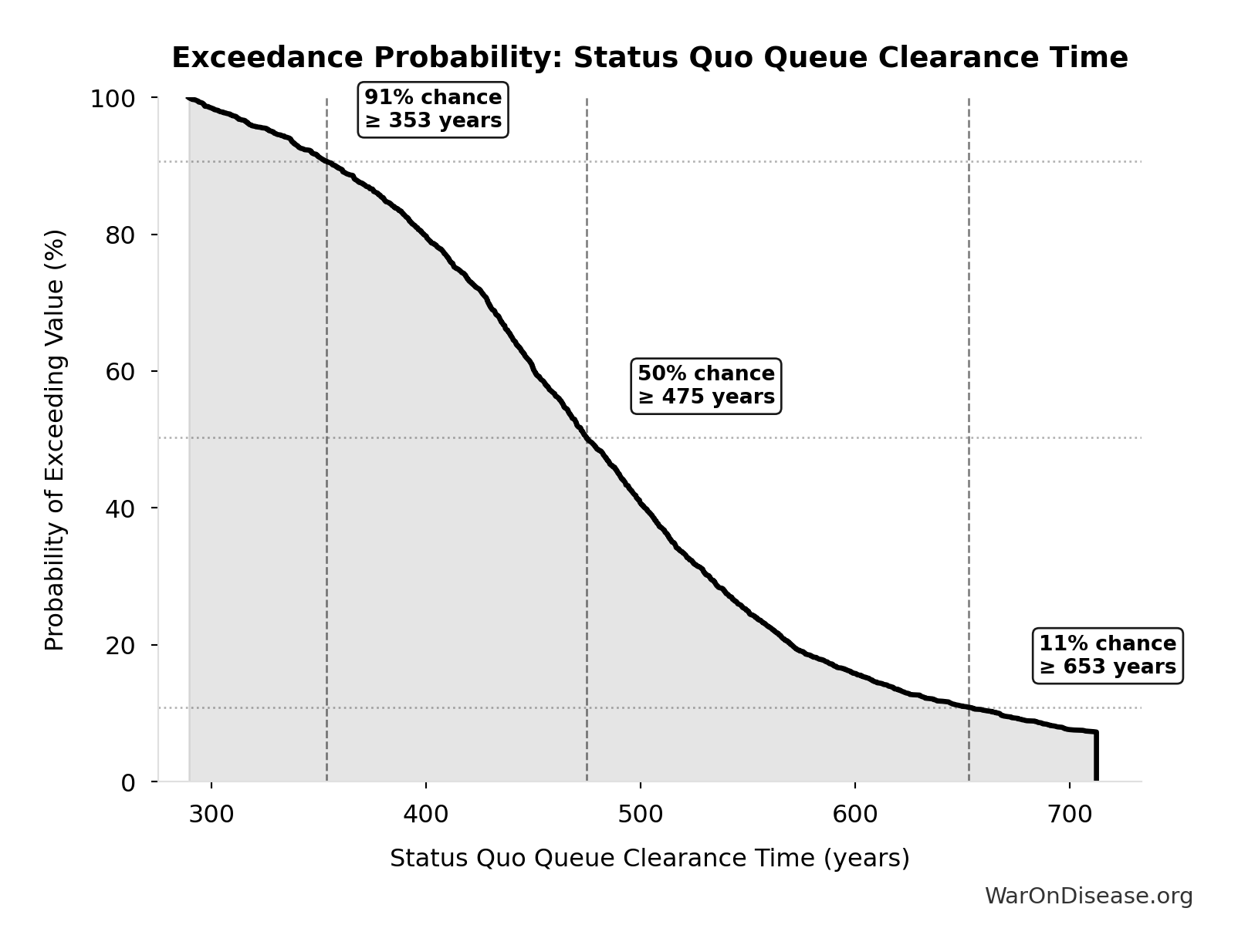
Simulation Results Summary: Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 443 |
| Mean (expected value) | 485 |
| Median (50th percentile) | 475 |
| Standard Deviation | 106 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [324, 712] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Status Quo Therapeutic Space Exploration Time will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
Annual Funding from 1% of Global Military Spending Redirected to DIH: $27.2B
Annual funding from 1% of global military spending redirected to DIH
Inputs:
- Global Military Spending in 2024 📊: $2.72T
- 1% Reduction in Military Spending/War Costs from Treaty: 1%
\[ \begin{gathered} Funding_{treaty} \\ = Spending_{mil} \times Reduce_{treaty} \\ = \$2.72T \times 1\% \\ = \$27.2B \end{gathered} \]
✓ High confidence
Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost: $1B
Total treaty campaign cost (100% VICTORY Incentive Alignment Bonds)
Inputs:
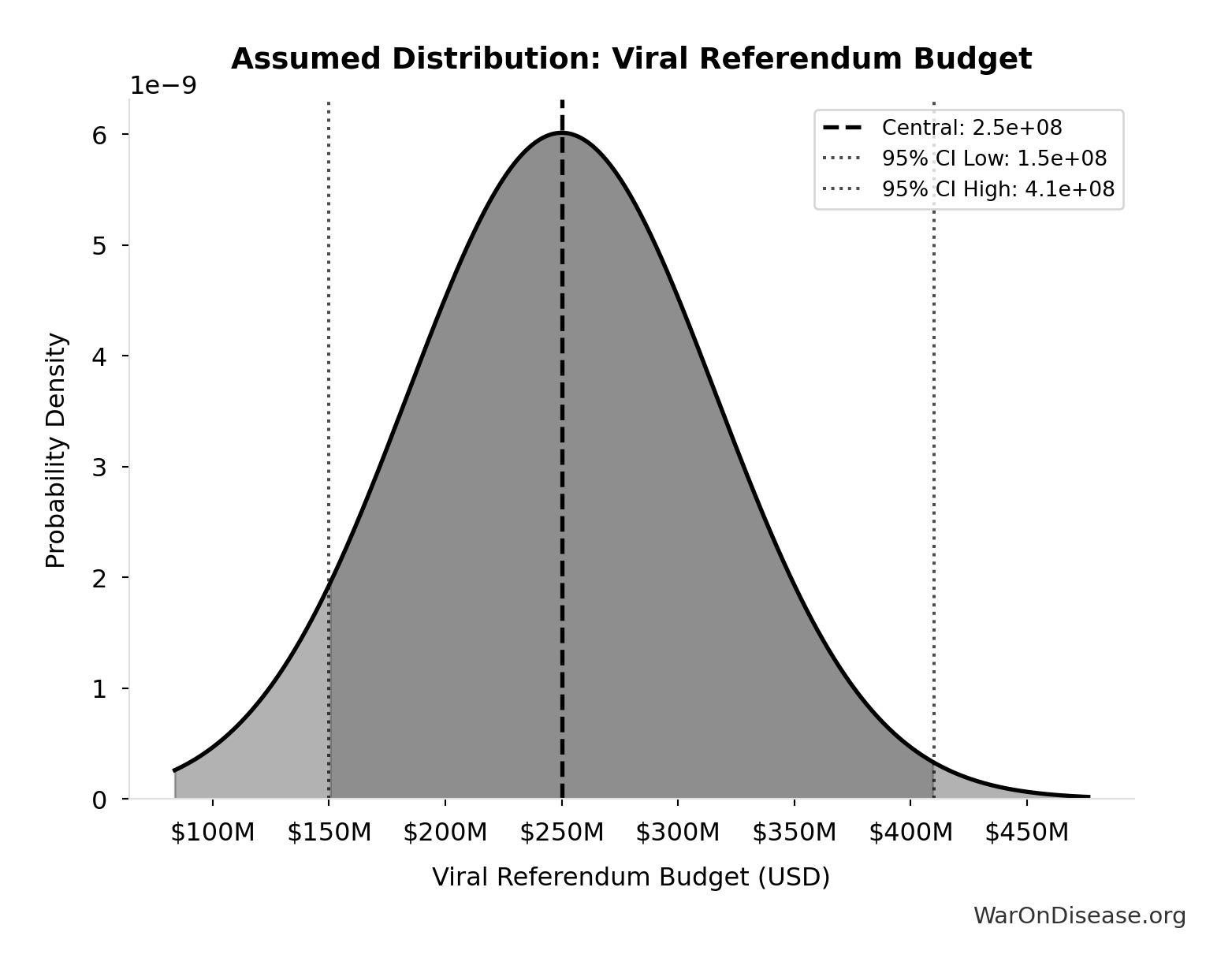
- Viral Referendum Budget: $250M (95% CI: $150M - $410M)
- Political Lobbying Campaign: Direct Lobbying, Super Pacs, Opposition Research, Staff, Legal/Compliance: $650M (95% CI: $325M - $1.3B)
- Reserve Fund / Contingency Buffer: $100M (95% CI: $20M - $150M)
\[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{campaign} \\ = Budget_{viral,base} + Budget_{lobby,treaty} \\ + Budget_{reserve} \\ = \$250M + \$650M + \$100M \\ = \$1B \end{gathered} \]
✓ High confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Political Lobbying Campaign: Direct Lobbying, Super Pacs, Opposition Research, Staff, Legal/Compliance (USD) | 0.9016 | Strong driver |
| Reserve Fund / Contingency Buffer (USD) | 0.1026 | Weak driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $1B |
| Mean (expected value) | $996M |
| Median (50th percentile) | $949M |
| Standard Deviation | $276M |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$632M, $1.51B] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
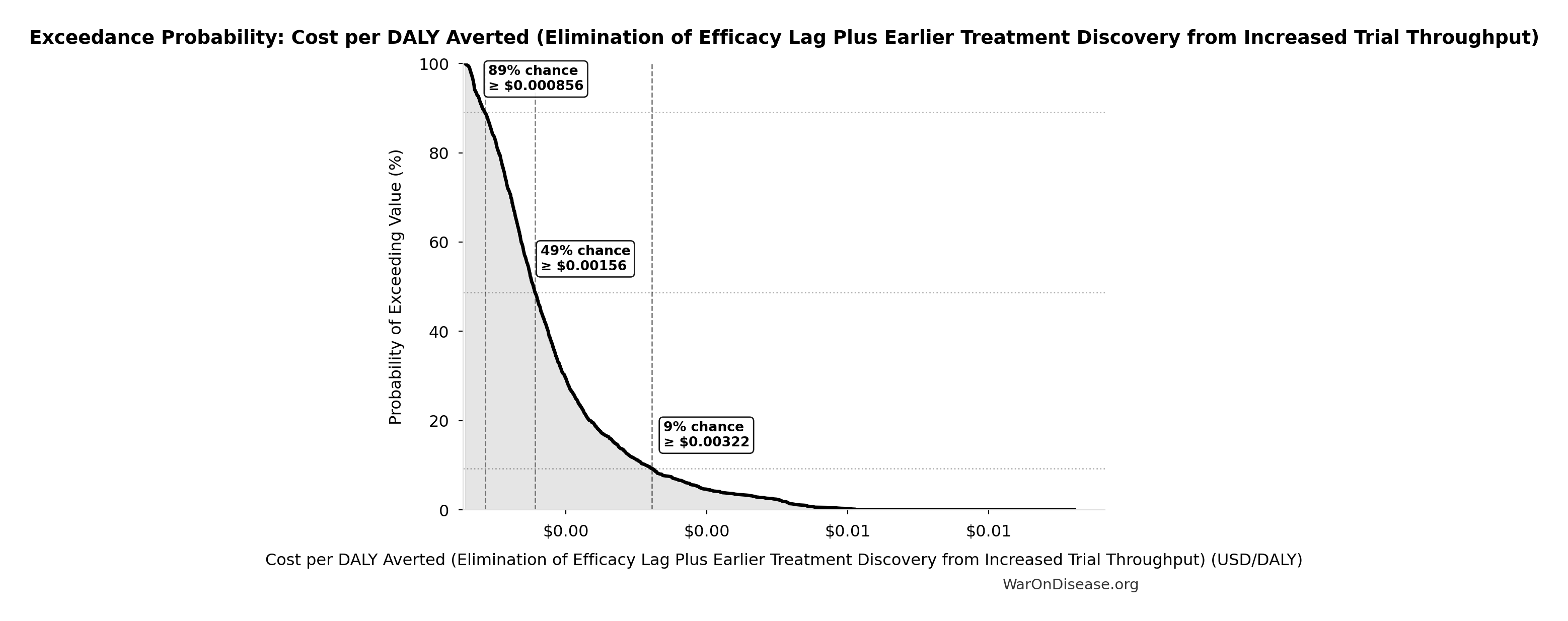
Cost per DALY Averted (Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput): $0.00177
Cost per DALY averted from elimination of efficacy lag plus earlier treatment discovery from increased trial throughput. Only counts campaign cost; ignores economic benefits from funding and R&D savings.
Inputs:
- Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost 🔢: $1B
- Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput 🔢: 565 billion DALYs
\[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{treaty,DALY} \\ = \frac{Cost_{campaign}}{DALYs_{max}} \\ = \frac{\$1B}{565B} \\ = \$0.00177 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{campaign} \\ = Budget_{viral,base} + Budget_{lobby,treaty} \\ + Budget_{reserve} \\ = \$250M + \$650M + \$100M \\ = \$1B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} DALYs_{max} \\ = DALYs_{global,ann} \times Pct_{avoid,DALY} \times T_{accel,max} \\ = 2.88B \times 92.6\% \times 212 \\ = 565B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] ✓ High confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Cost per DALY Averted (Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput)
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost (USD) | 0.6487 | Strong driver |
| Total DALYs from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput (DALYs) | -0.3322 | Moderate driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Cost per DALY Averted (Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput)
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $0.00177 |
| Mean (expected value) | $0.00186 |
| Median (50th percentile) | $0.00156 |
| Standard Deviation | $0.00109 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$0.000715, $0.00412] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Cost per DALY Averted (Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput) across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Cost per DALY Averted (Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput) will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
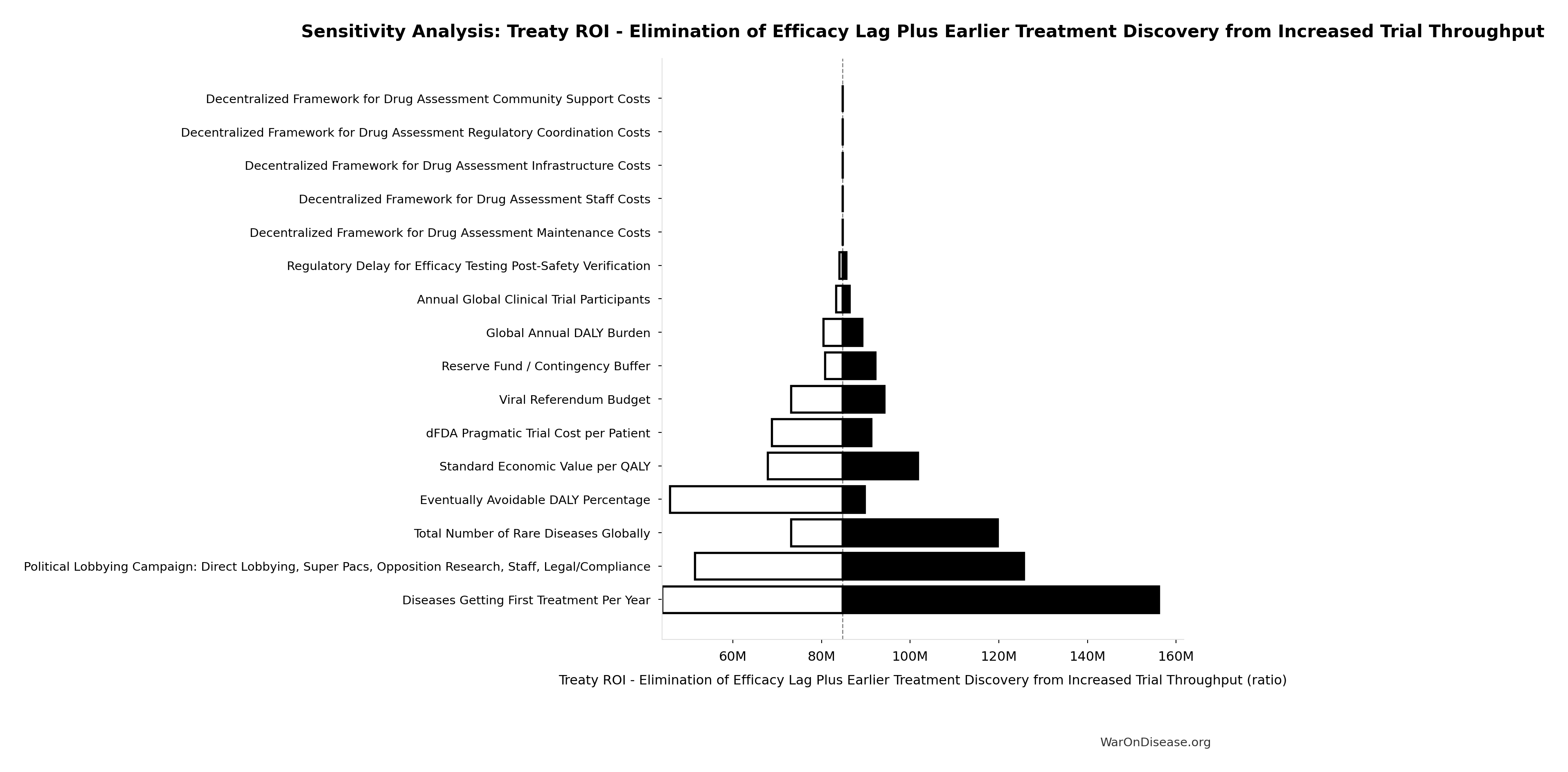
Treaty ROI - Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput: 84.8M:1
Treaty ROI from elimination of efficacy lag plus earlier treatment discovery from increased trial throughput. Total one-time benefit divided by campaign cost. This is the primary ROI estimate for total health benefits.
Inputs:
- Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput 🔢: $84.8 quadrillion
- Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost 🔢: $1B
\[ \begin{gathered} ROI_{max} \\ = \frac{Value_{max}}{Cost_{campaign}} \\ = \frac{\$84800T}{\$1B} \\ = 84.8M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Value_{max} \\ = DALYs_{max} \times Value_{QALY} \\ = 565B \times \$150K \\ = \$84800T \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} DALYs_{max} \\ = DALYs_{global,ann} \times Pct_{avoid,DALY} \times T_{accel,max} \\ = 2.88B \times 92.6\% \times 212 \\ = 565B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ T_{accel,max} = T_{accel} + T_{lag} = 204 + 8.2 = 212 \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{accel} \\ = T_{first,SQ} \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{k_{capacity}}\right) \\ = 222 \times \left(1 - \frac{1}{12.3}\right) \\ = 204 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{first,SQ} \\ = T_{queue,SQ} \times 0.5 \\ = 443 \times 0.5 \\ = 222 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} T_{queue,SQ} \\ = \frac{N_{untreated}}{Treatments_{new,ann}} \\ = \frac{6{,}650}{15} \\ = 443 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{untreated} \\ = N_{rare} \times 0.95 \\ = 7{,}000 \times 0.95 \\ = 6{,}650 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} k_{capacity} \\ = \frac{N_{fundable,dFDA}}{Slots_{curr}} \\ = \frac{23.4M}{1.9M} \\ = 12.3 \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} N_{fundable,dFDA} \\ = \frac{Subsidies_{dFDA,ann}}{Cost_{pragmatic,pt}} \\ = \frac{\$21.8B}{\$929} \\ = 23.4M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Subsidies_{dFDA,ann} \\ = Funding_{dFDA,ann} - OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = \$21.8B - \$40M \\ = \$21.8B \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} OPEX_{dFDA} \\ = Cost_{platform} + Cost_{staff} + Cost_{infra} \\ + Cost_{regulatory} + Cost_{community} \\ = \$15M + \$10M + \$8M + \$5M + \$2M \\ = \$40M \end{gathered} \] where: \[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{campaign} \\ = Budget_{viral,base} + Budget_{lobby,treaty} \\ + Budget_{reserve} \\ = \$250M + \$650M + \$100M \\ = \$1B \end{gathered} \] ~ Medium confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for Treaty ROI - Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Total 1% Treaty Campaign Cost (USD) | -0.7930 | Strong driver |
| Total Economic Benefit from Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Higher Trial Throughput (USD) | 0.3364 | Moderate driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
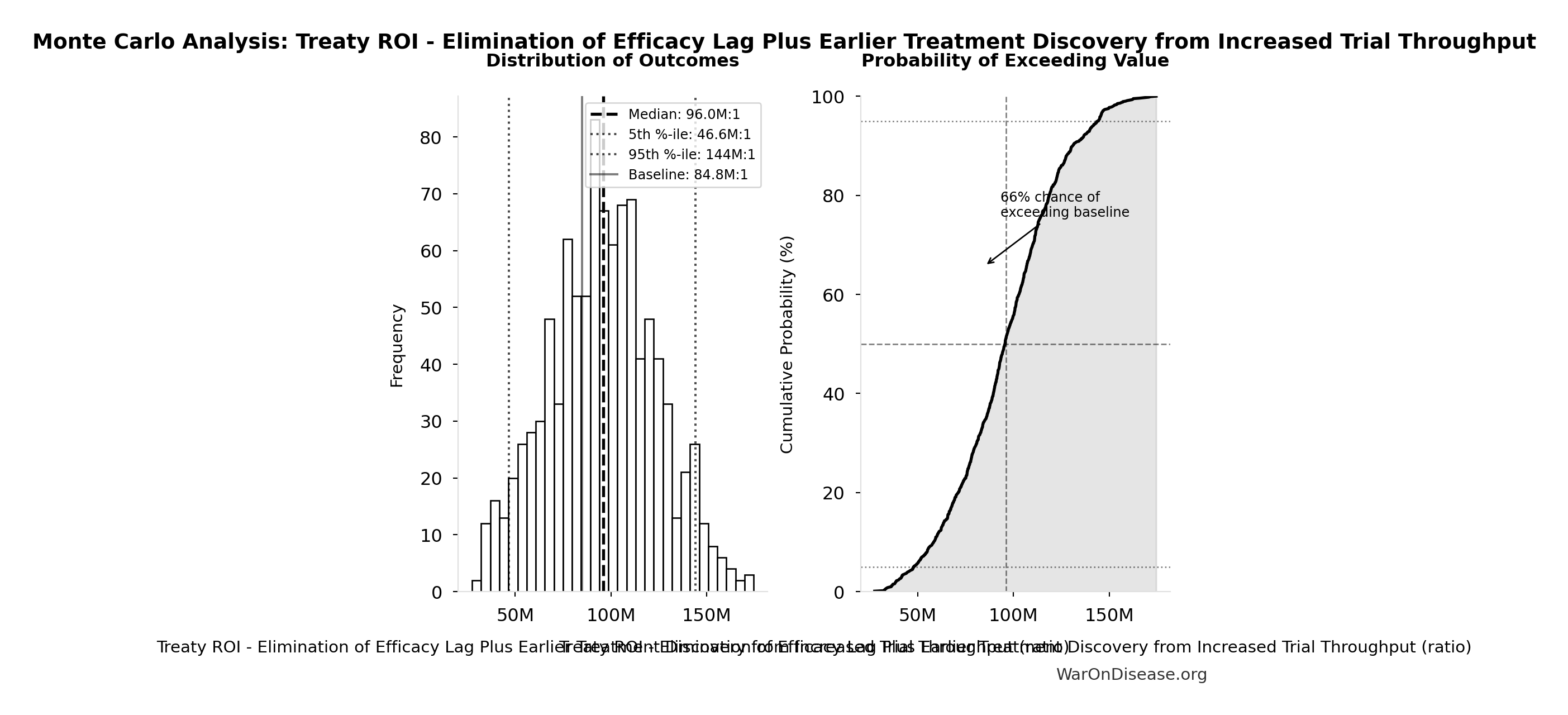
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: Treaty ROI - Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | 84.8M:1 |
| Mean (expected value) | 95.1M:1 |
| Median (50th percentile) | 96.0M:1 |
| Standard Deviation | 28.1M:1 |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [46.6M:1, 144M:1] |
The histogram shows the distribution of Treaty ROI - Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
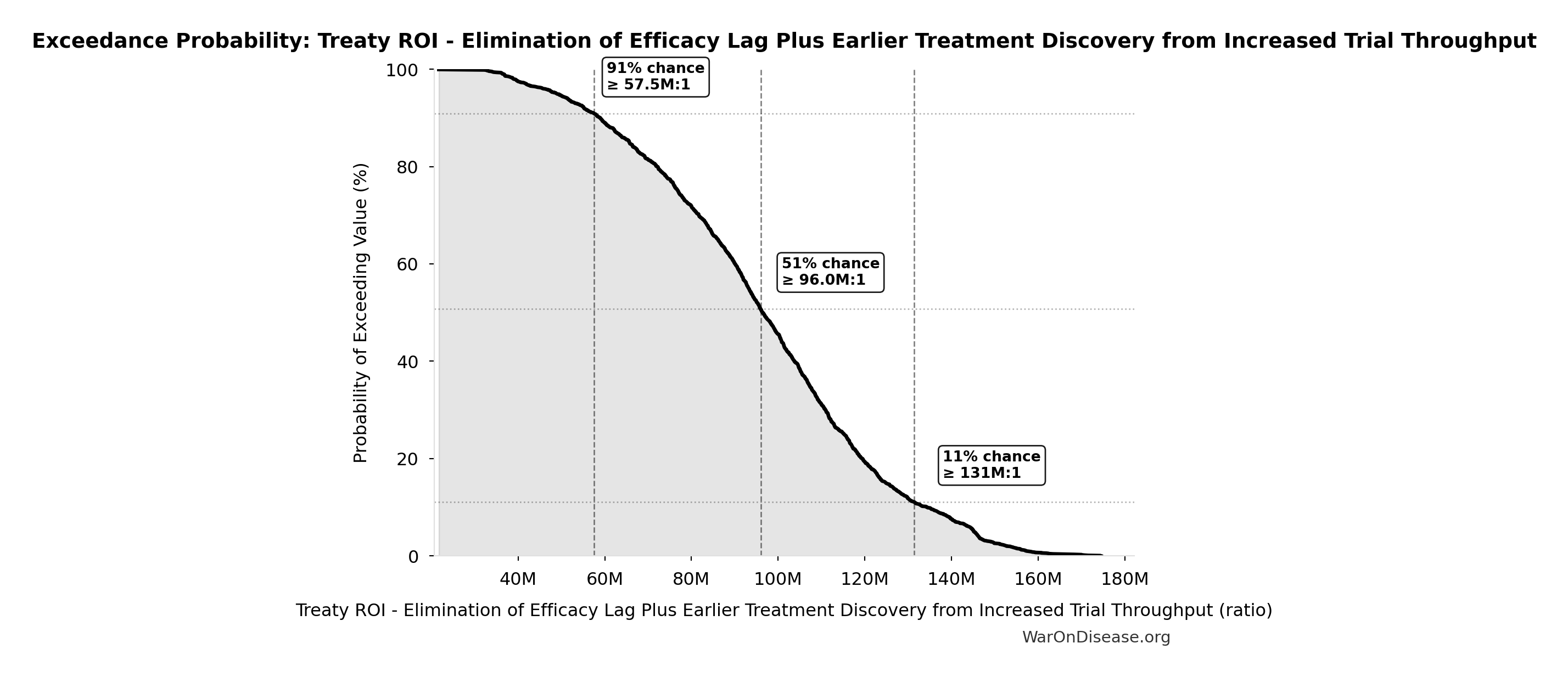
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that Treaty ROI - Elimination of Efficacy Lag Plus Earlier Treatment Discovery from Increased Trial Throughput will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
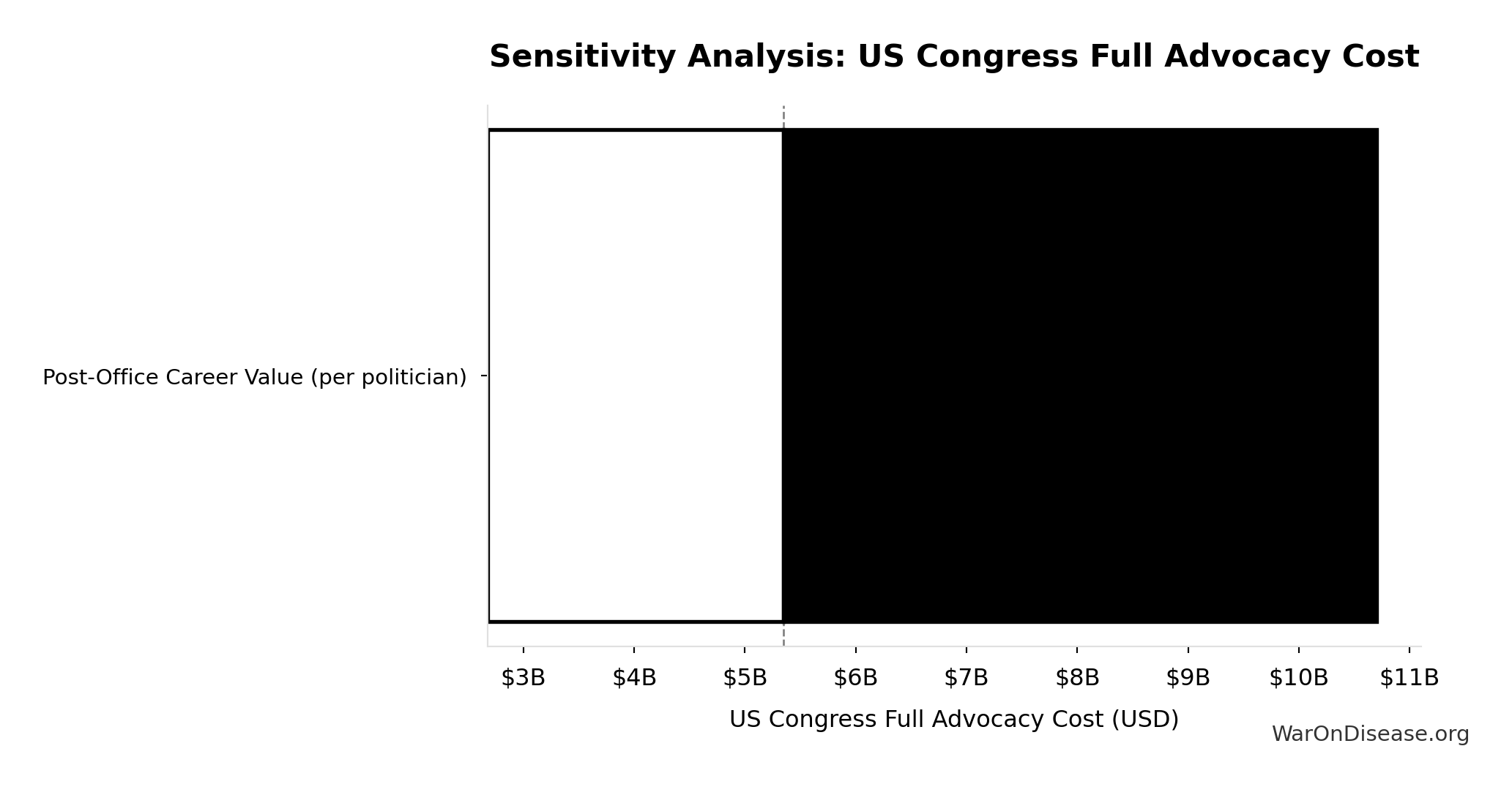
US Congress Full Advocacy Cost: $5.35B
Upper-bound advocacy cost to match career incentives for all 535 members of Congress
Inputs:
- US Congress Members: 535 members
- Post-Office Career Value (per politician) 📊: $10M (95% CI: $5M - $20M)
\[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{US,congress} \\ = N_{congress} \times V_{post-office} \\ = 535 \times \$10M \\ = \$5.35B \end{gathered} \]
~ Medium confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
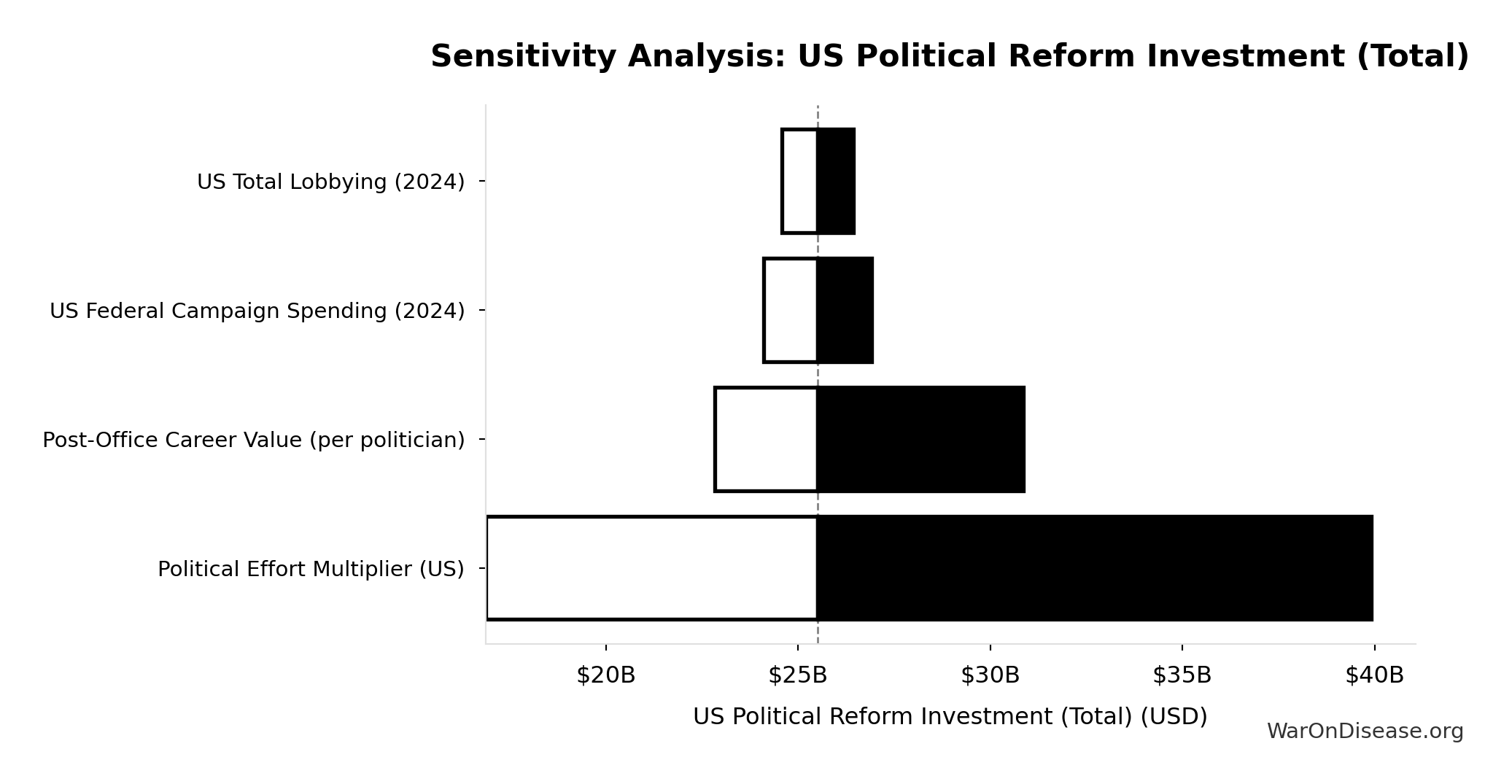
US Political Reform Investment (Total): $25.5B
Total upper-bound investment for US political reform: (campaign spending + 2 years lobbying) × effort multiplier + Congress career advocacy. Represents cost to achieve democratic parity with incumbent interests.
Inputs:
- US Federal Campaign Spending (2024) 📊: $20B (95% CI: $18B - $22B)
- US Total Lobbying (2024) 📊: $4.4B (95% CI: $3.74B - $5.06B)
- Political Effort Multiplier (US): 0.7x (95% CI: 0.4x - 1.2x)
- US Congress Full Advocacy Cost 🔢: $5.35B
\[ \begin{gathered} Cost_{US,total} \\ = (Cost_{campaign} \\ + Cost_{lobby} \times 2) \times \mu_{effort} + Cost_{career} \end{gathered} \]
? Low confidence
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Indices for US Political Reform Investment (Total)
Regression-based sensitivity showing which inputs explain the most variance in the output.
| Input Parameter | Sensitivity Coefficient | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Political Effort Multiplier (US) (multiplier) | 1.0000 | Strong driver |
Interpretation: Standardized coefficients show the change in output (in SD units) per 1 SD change in input. Values near ±1 indicate strong influence; values exceeding ±1 may occur with correlated inputs.
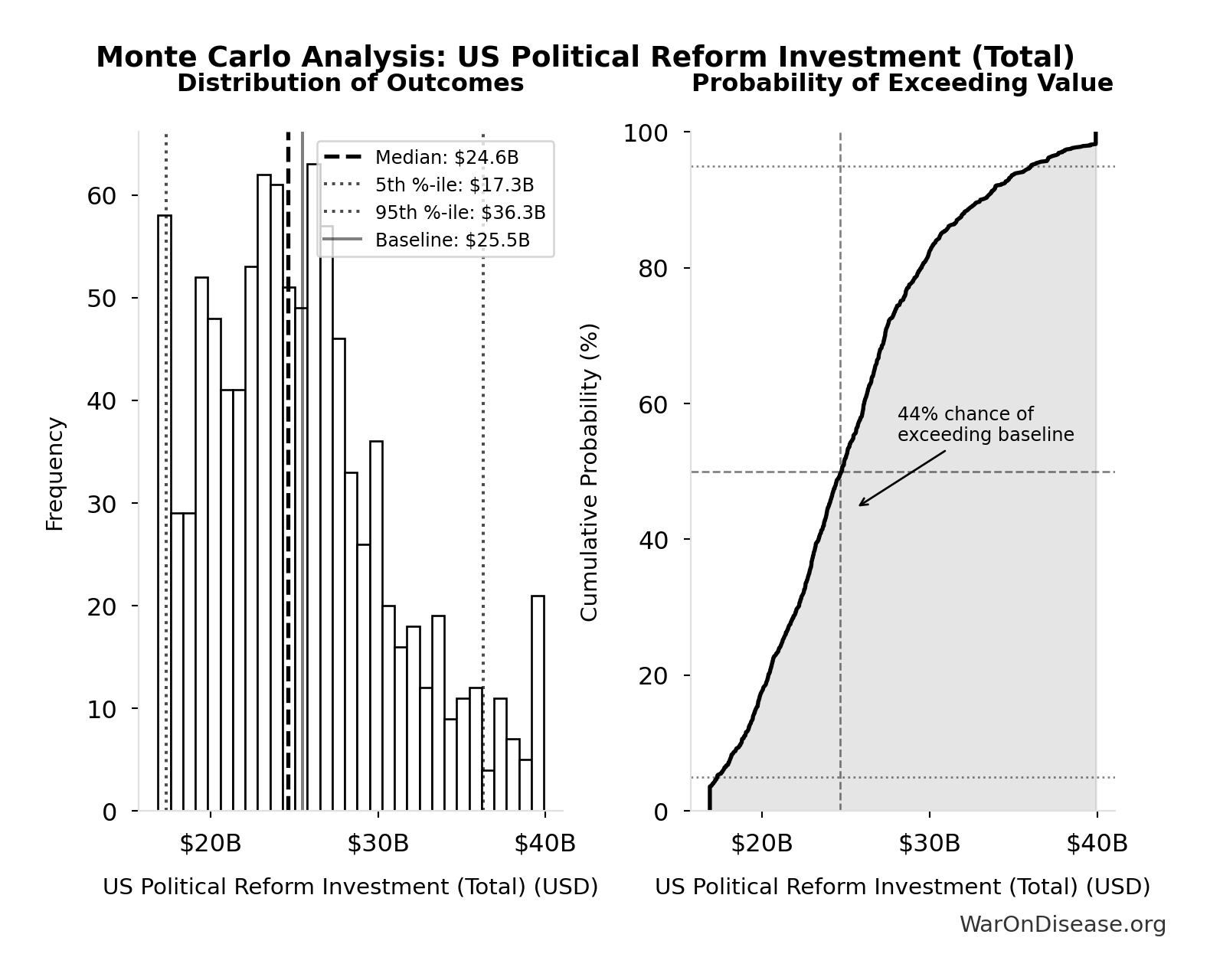
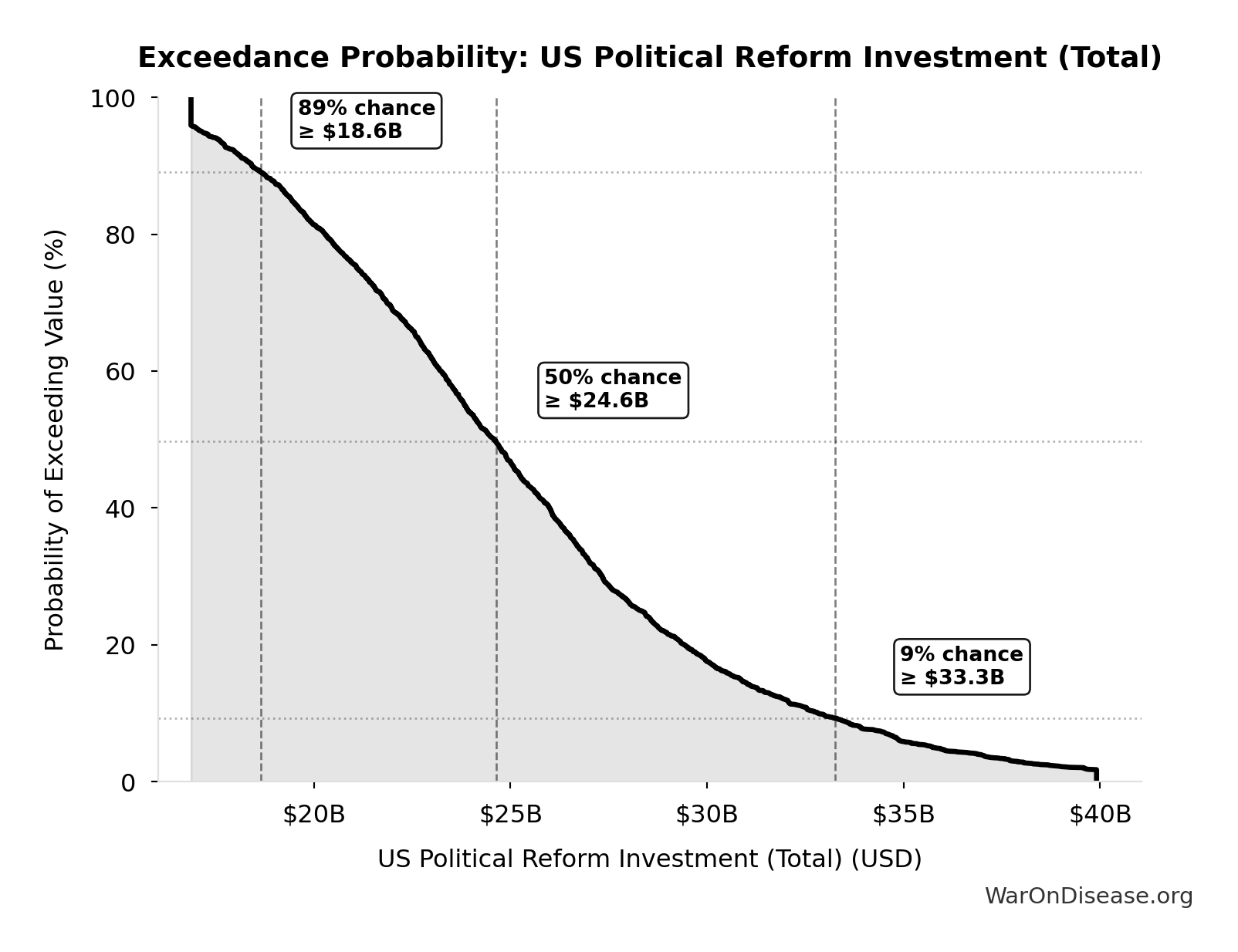
Monte Carlo Distribution
Simulation Results Summary: US Political Reform Investment (Total)
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Baseline (deterministic) | $25.5B |
| Mean (expected value) | $25.4B |
| Median (50th percentile) | $24.6B |
| Standard Deviation | $5.54B |
| 90% Range (5th-95th percentile) | [$17.3B, $36.3B] |
The histogram shows the distribution of US Political Reform Investment (Total) across 10,000 Monte Carlo simulations. The CDF (right) shows the probability of the outcome exceeding any given value, which is useful for risk assessment.
Exceedance Probability
This exceedance probability chart shows the likelihood that US Political Reform Investment (Total) will exceed any given threshold. Higher curves indicate more favorable outcomes with greater certainty.
External Data Sources
Parameters sourced from peer-reviewed publications, institutional databases, and authoritative reports.
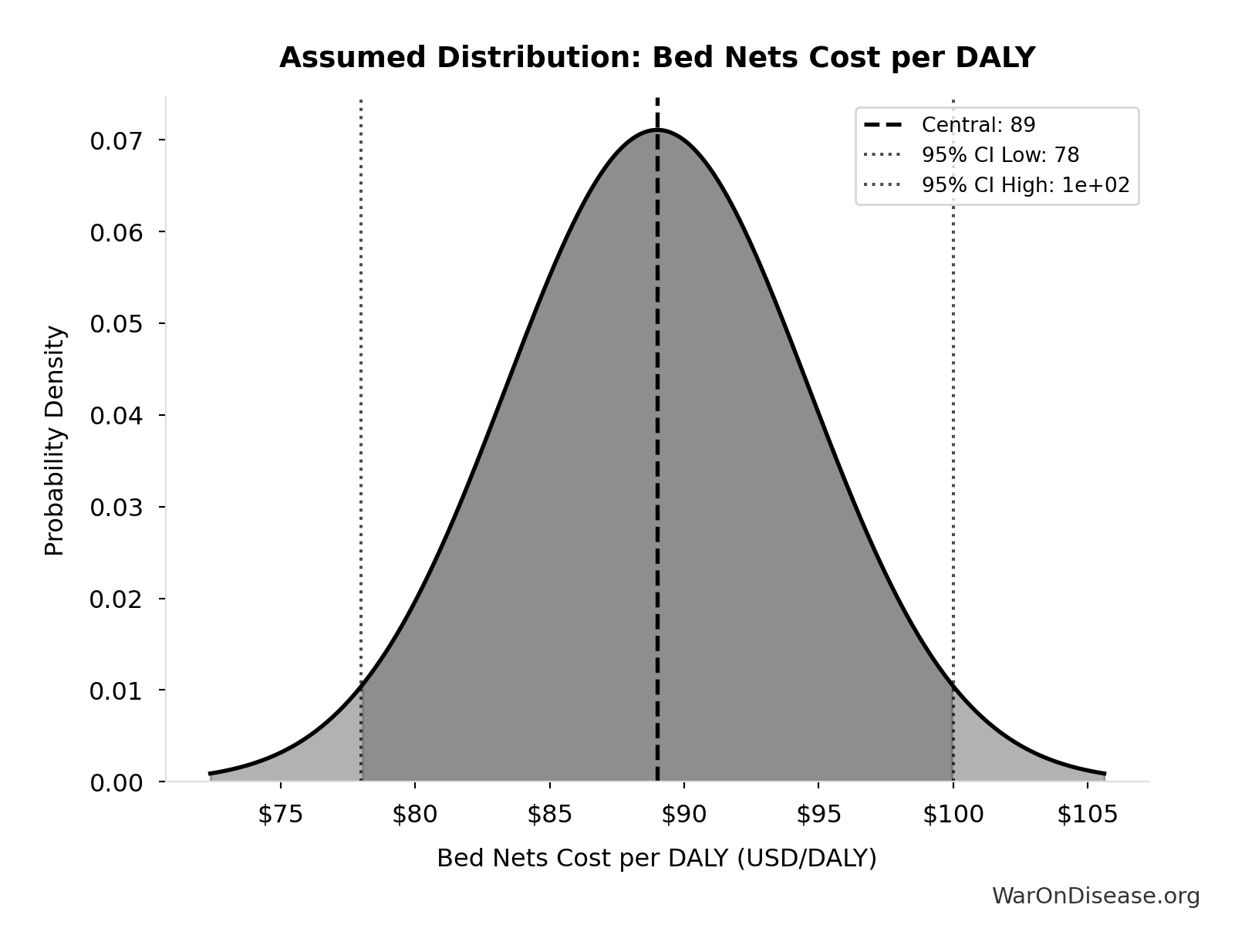
Bed Nets Cost per DALY: $89
GiveWell cost per DALY for insecticide-treated bed nets (midpoint estimate, range $78-100). DALYs (Disability-Adjusted Life Years) measure disease burden by combining years of life lost and years lived with disability. Bed nets prevent malaria deaths and are considered a gold standard benchmark for cost-effective global health interventions - if an intervention costs less per DALY than bed nets, it’s exceptionally cost-effective. GiveWell synthesizes peer-reviewed academic research with transparent, rigorous methodology and extensive external expert review.
Source:5
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$78, $100] • Distribution: Normal
What this means: This estimate has moderate uncertainty. The true value likely falls between $78 and $100 (±12%). This represents a reasonable range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The normal distribution means values cluster around the center with equal chances of being higher or lower.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence • 📊 Peer-reviewed
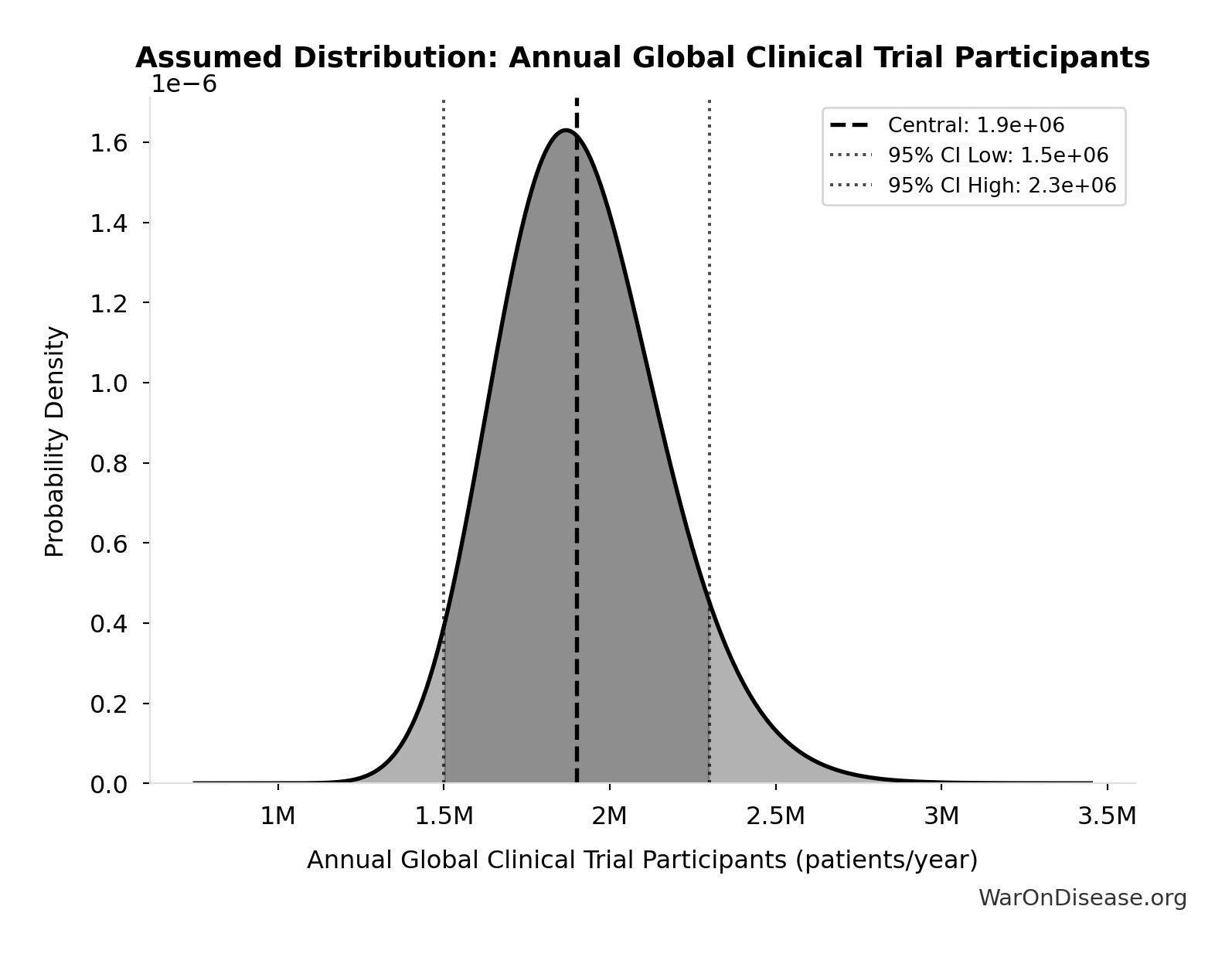
Annual Global Clinical Trial Participants: 1.9 million patients/year
Annual global clinical trial participants (IQVIA 2022: 1.9M post-COVID normalization)
Source:15
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [1.5 million patients/year, 2.3 million patients/year] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate has moderate uncertainty. The true value likely falls between 1.5 million patients/year and 2.3 million patients/year (±21%). This represents a reasonable range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence
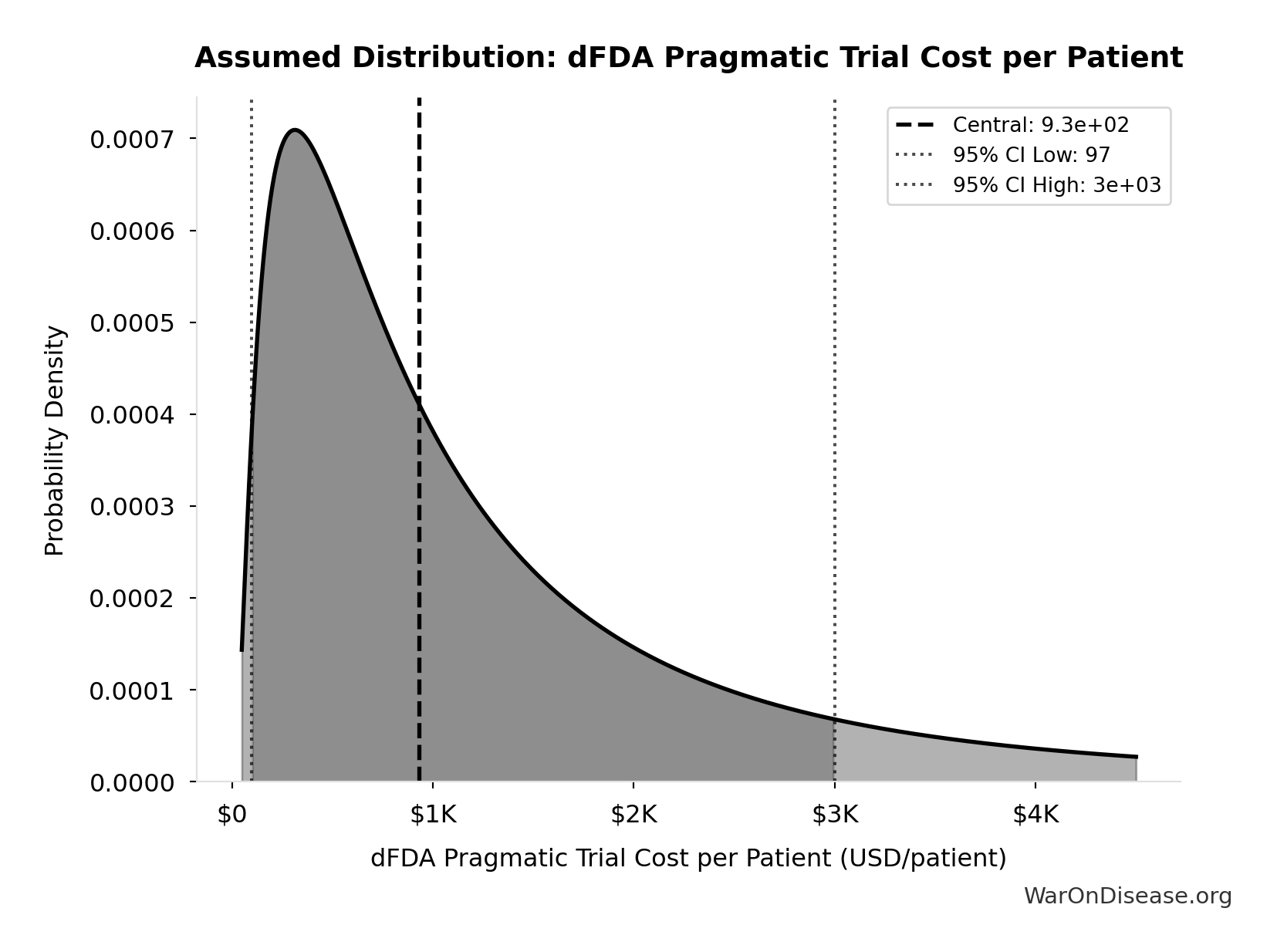
dFDA Pragmatic Trial Cost per Patient: $929
dFDA pragmatic trial cost per patient. Uses ADAPTABLE trial ($929) as DELIBERATELY CONSERVATIVE central estimate. Ramsberg & Platt (2018) reviewed 108 embedded pragmatic trials; 64 with cost data had median of only $97/patient - our estimate may overstate costs by 10x. Confidence interval spans meta-analysis median to complex chronic disease trials.
Source:1
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$97, $3K] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between $97 and $3K (±156%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
~ Medium confidence
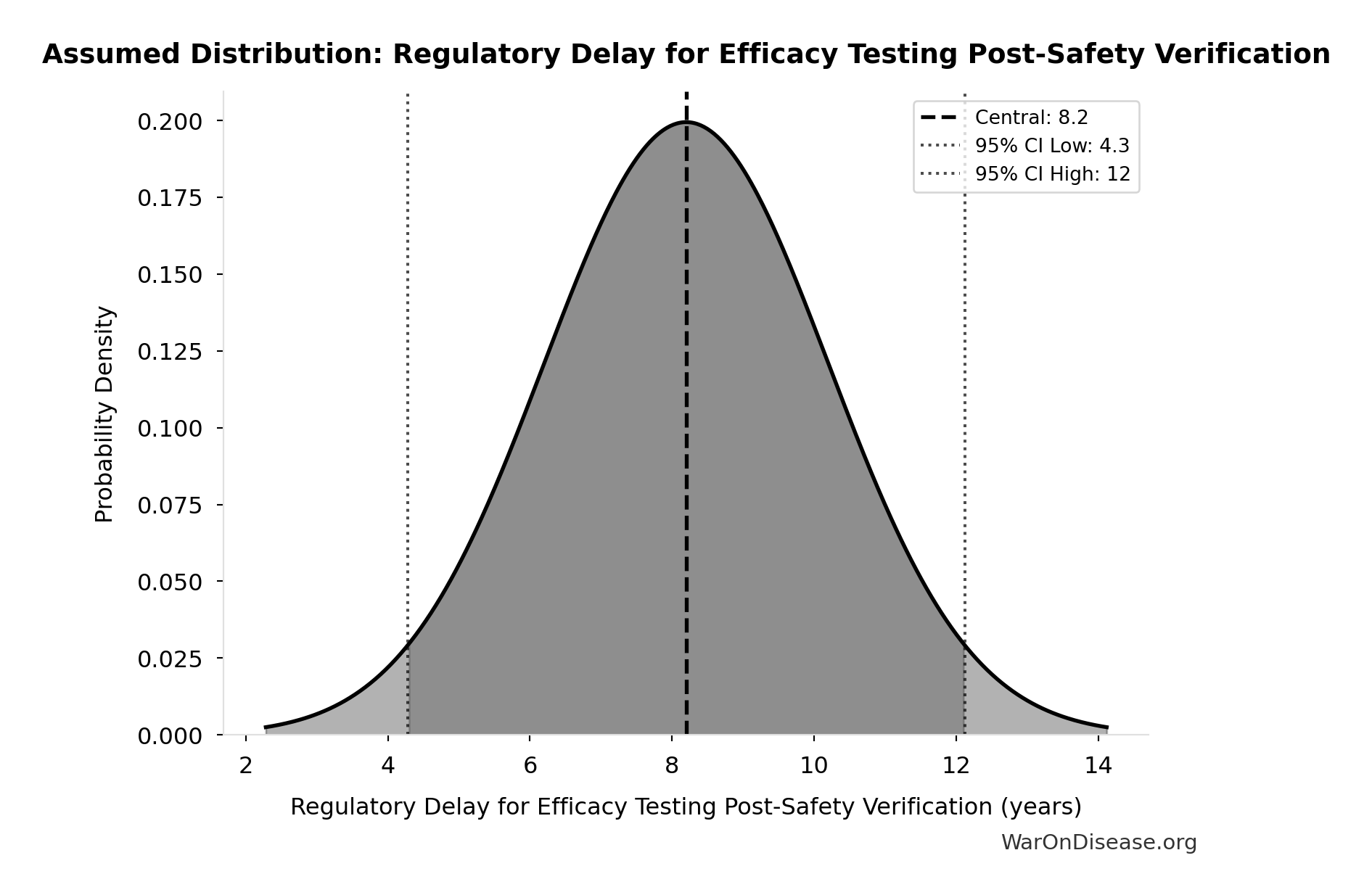
Regulatory Delay for Efficacy Testing Post-Safety Verification: 8.2 years
Regulatory delay for efficacy testing (Phase II/III) post-safety verification. Based on BIO 2021 industry survey. Note: This is for drugs that COMPLETE the pipeline - survivor bias means actual delay for any given disease may be longer if candidates fail and must restart.
Source:22
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Normal (SE: 2 years)
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
~ Medium confidence • 📊 Peer-reviewed • Updated 2021
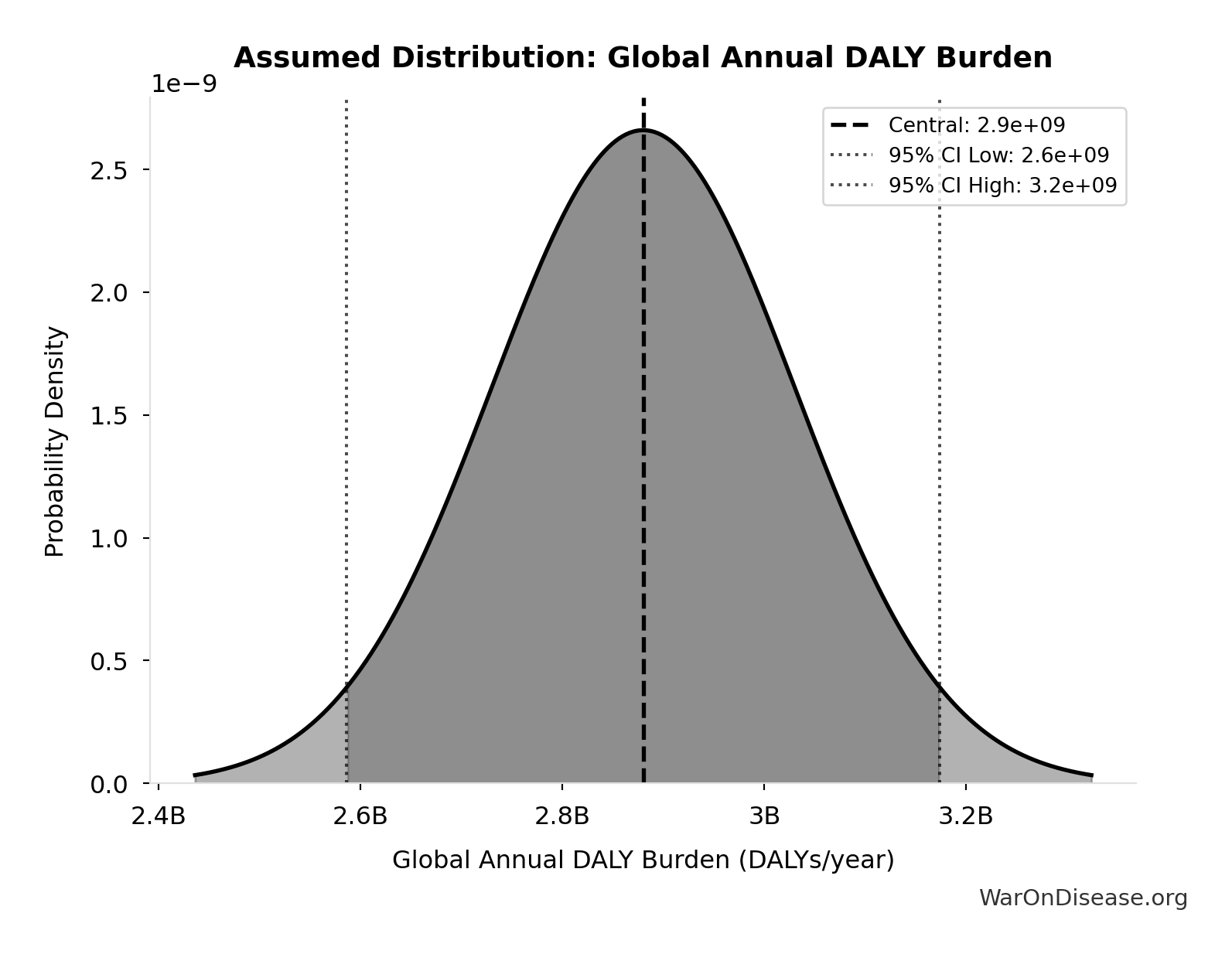
Global Annual DALY Burden: 2.88 billion DALYs/year
Global annual DALY burden from all diseases and injuries (WHO/IHME Global Burden of Disease 2021). Includes both YLL (years of life lost) and YLD (years lived with disability) from all causes.
Source:33
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Normal (SE: 150 million DALYs/year)
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence • 📊 Peer-reviewed
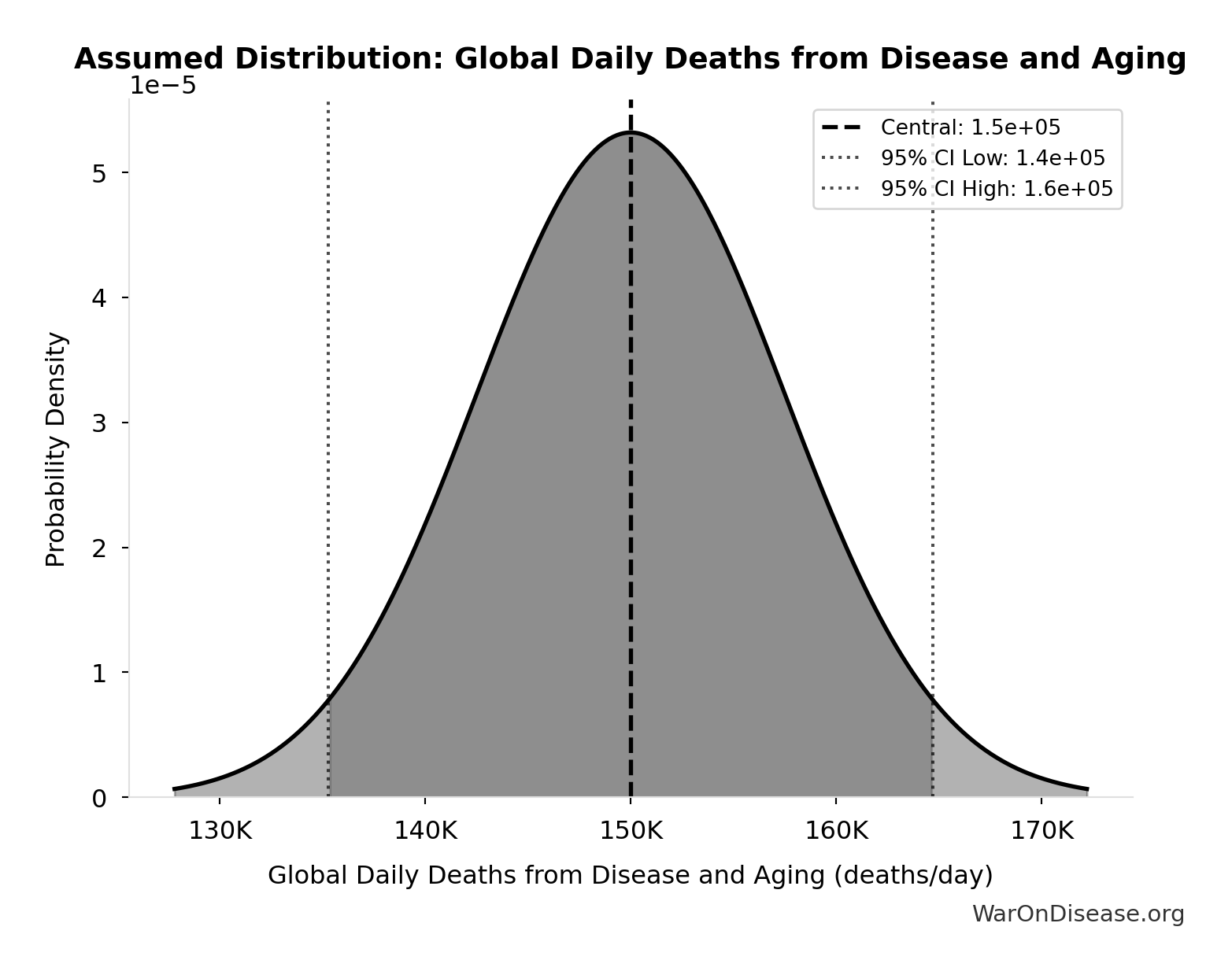
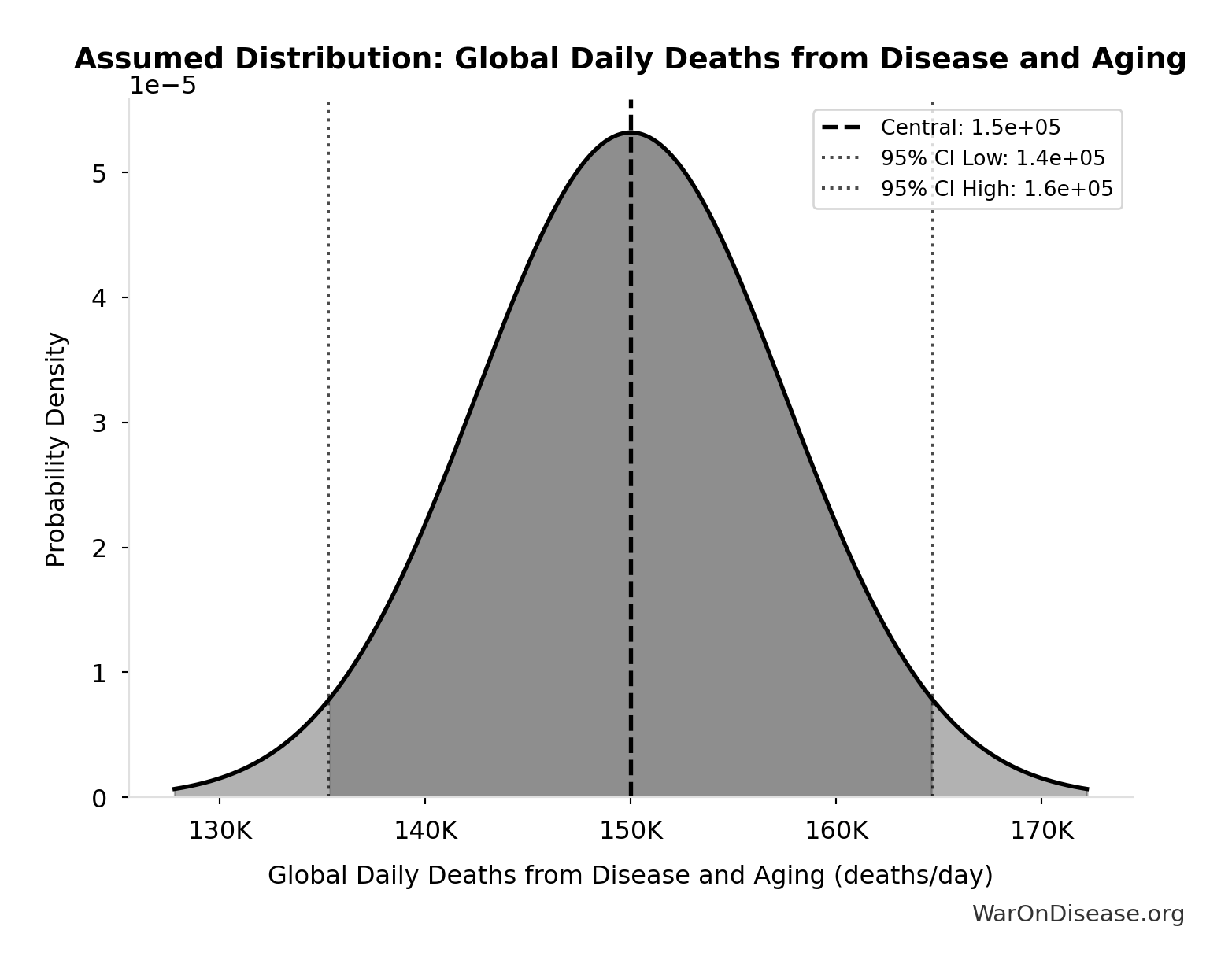
Global Daily Deaths from Disease and Aging: 150 thousand deaths/day
Total global deaths per day from all disease and aging (WHO Global Burden of Disease 2024)
Source:4
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Normal (SE: 7.5 thousand deaths/day)
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence • 📊 Peer-reviewed
Global Military Spending in 2024: $2.72T
Global military spending in 2024
Source:48
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Fixed
✓ High confidence
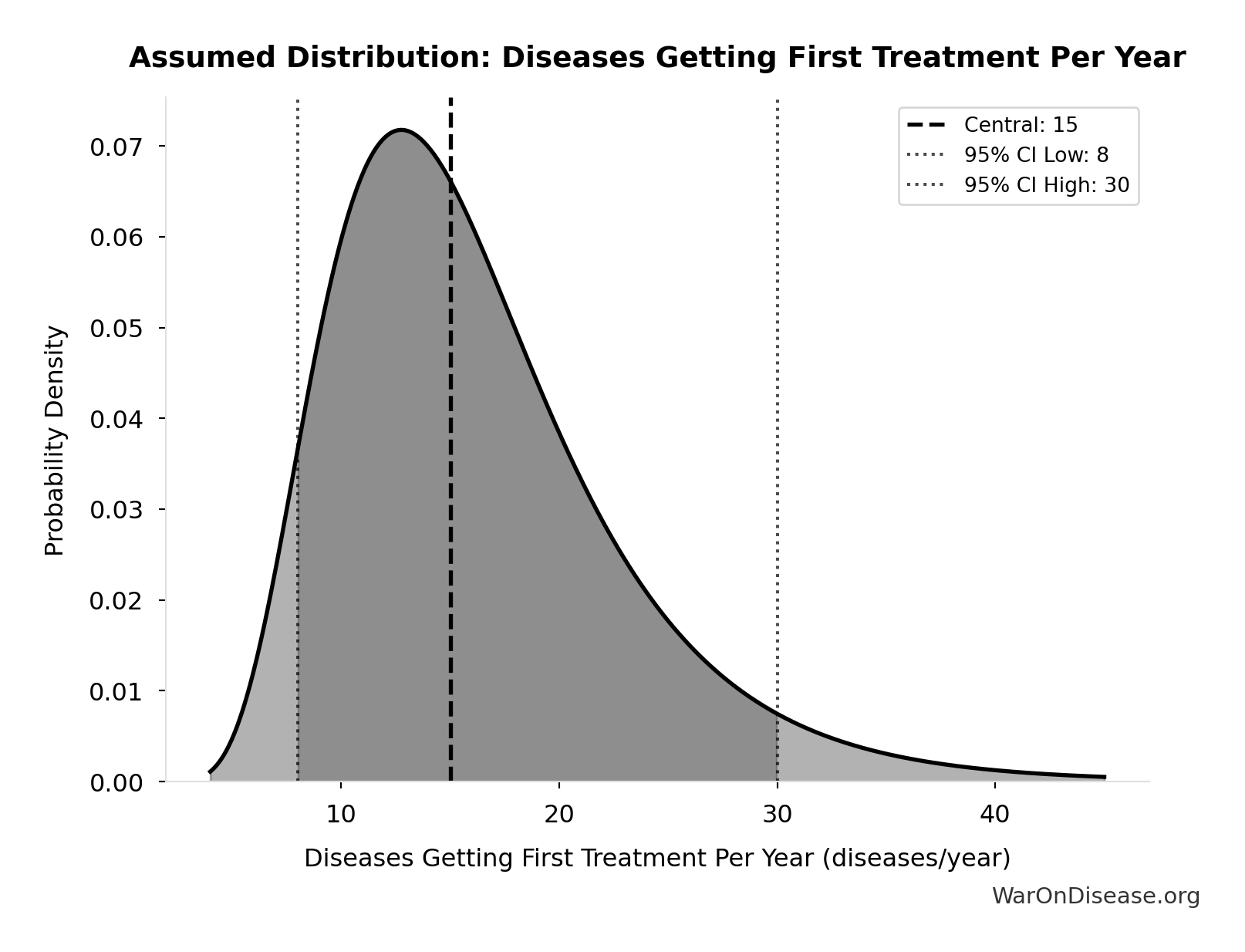
Diseases Getting First Treatment Per Year: 15 diseases/year
Number of diseases that receive their FIRST effective treatment each year under current system. ~9 rare diseases/year (based on 40 years of ODA: 350 with treatment ÷ 40 years), plus ~5-10 common diseases. Note: FDA approves ~50 drugs/year, but most are for diseases that already have treatments.
Source:62
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [8 diseases/year, 30 diseases/year] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between 8 diseases/year and 30 diseases/year (±73%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
? Low confidence
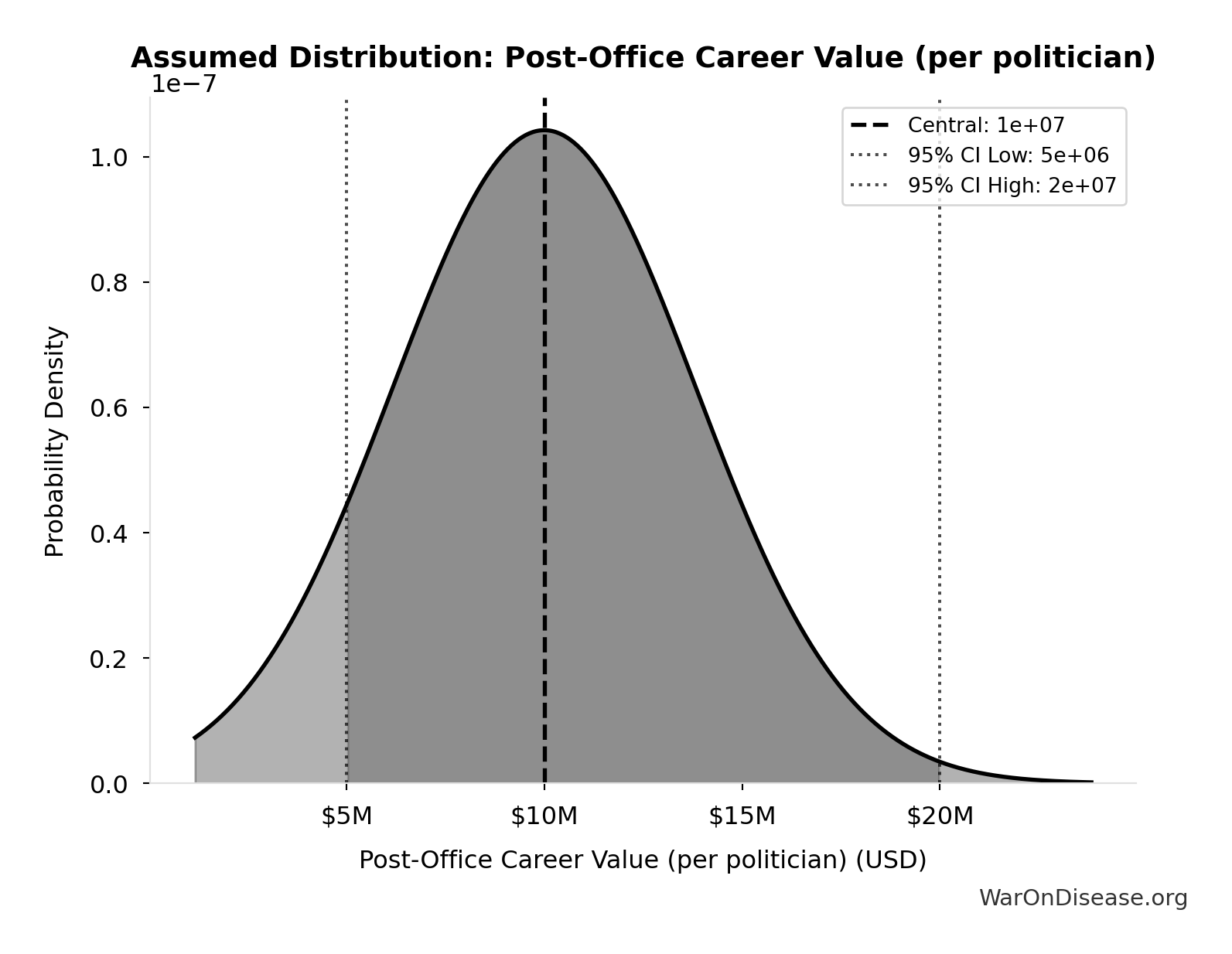
Post-Office Career Value (per politician): $10M
Net present value of post-office career premium for average congressperson (10 years x $1M/year premium). Based on documented cases: Gephardt $7M/year, Daschle $2M+/year.
Source:77
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$5M, $20M]
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between $5M and $20M (±75%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
~ Medium confidence
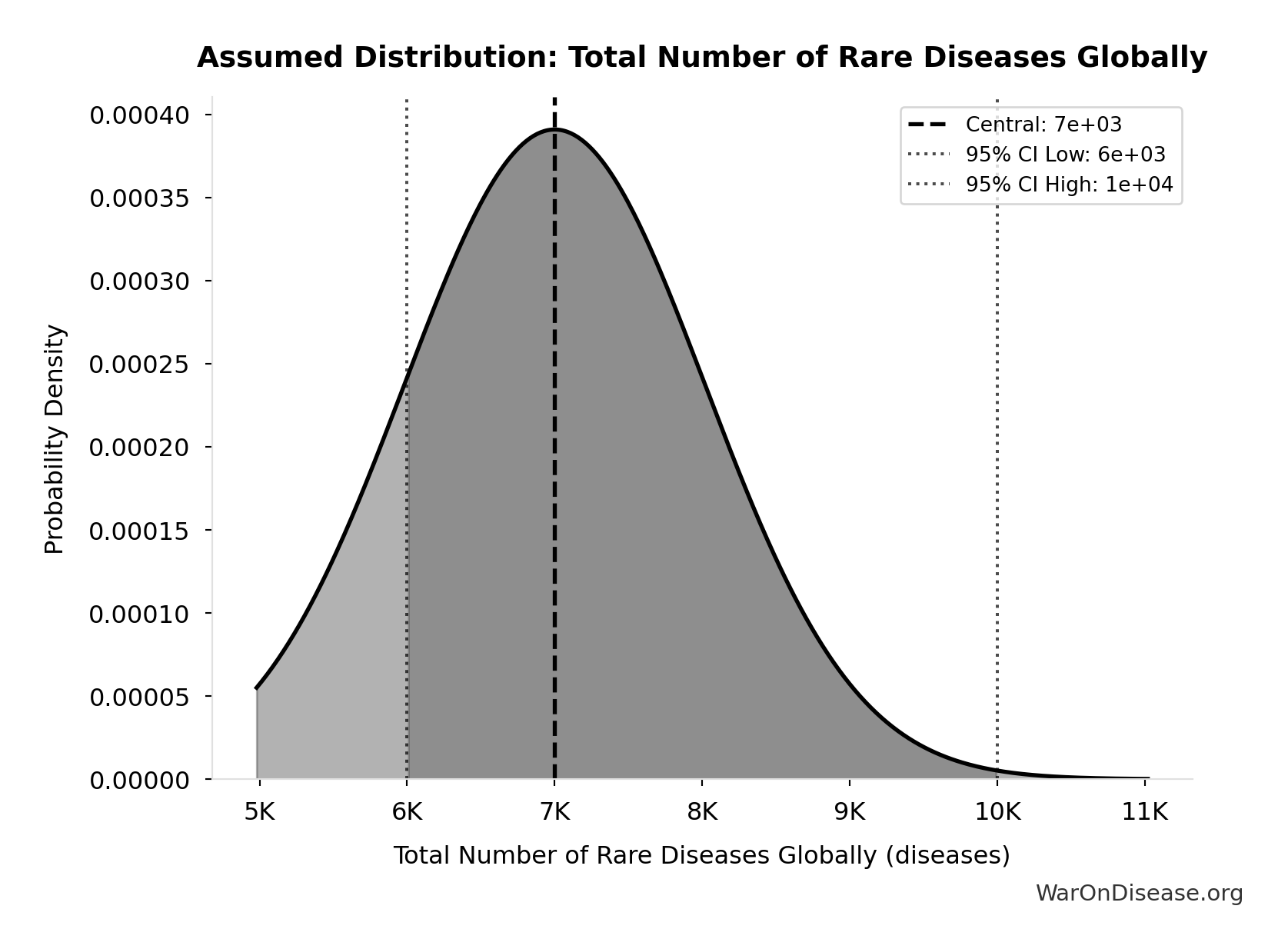
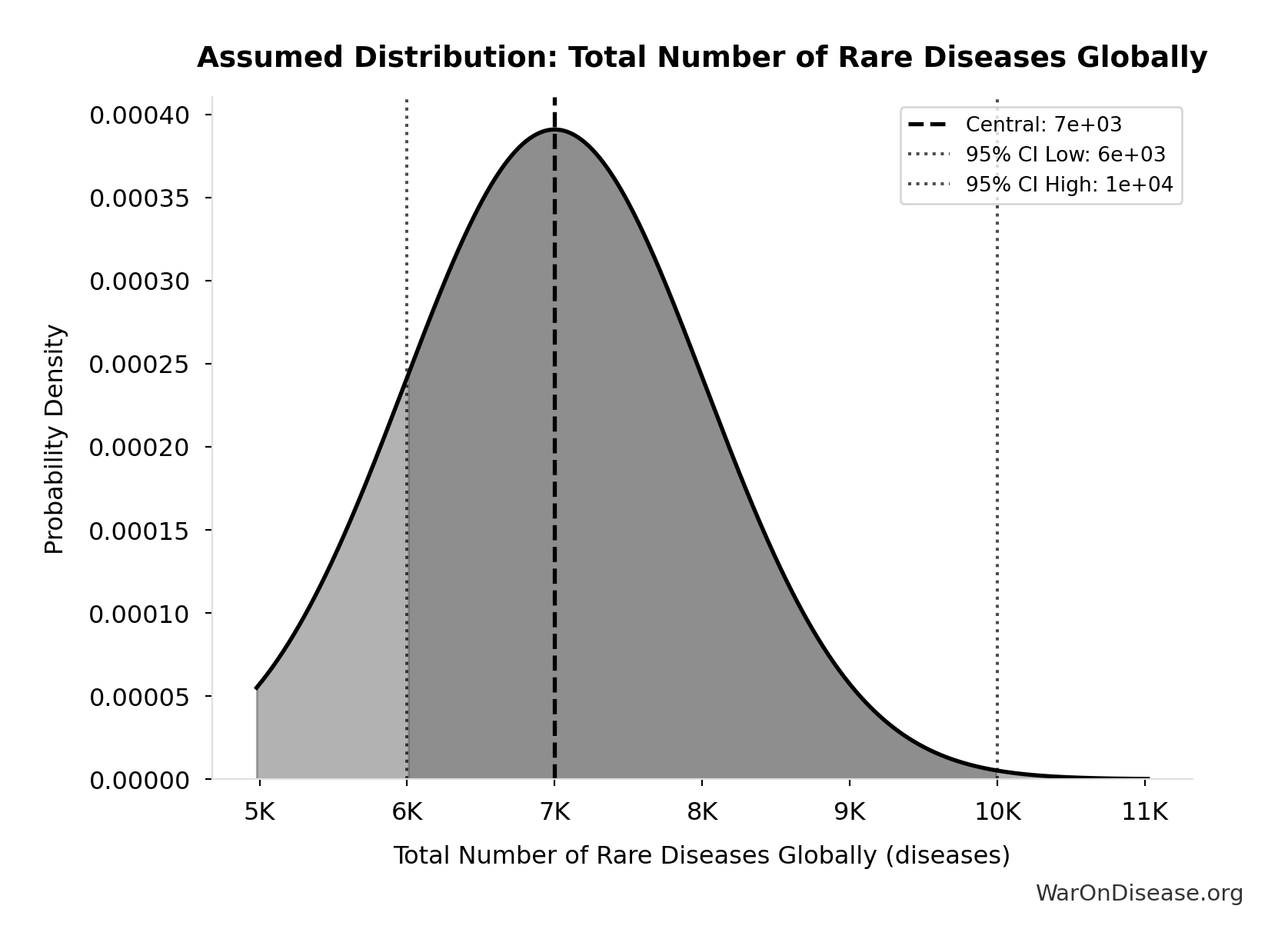
Total Number of Rare Diseases Globally: 7 thousand diseases
Total number of rare diseases globally
Source:81
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [6 thousand diseases, 10 thousand diseases] • Distribution: Normal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between 6 thousand diseases and 10 thousand diseases (±29%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The normal distribution means values cluster around the center with equal chances of being higher or lower.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence
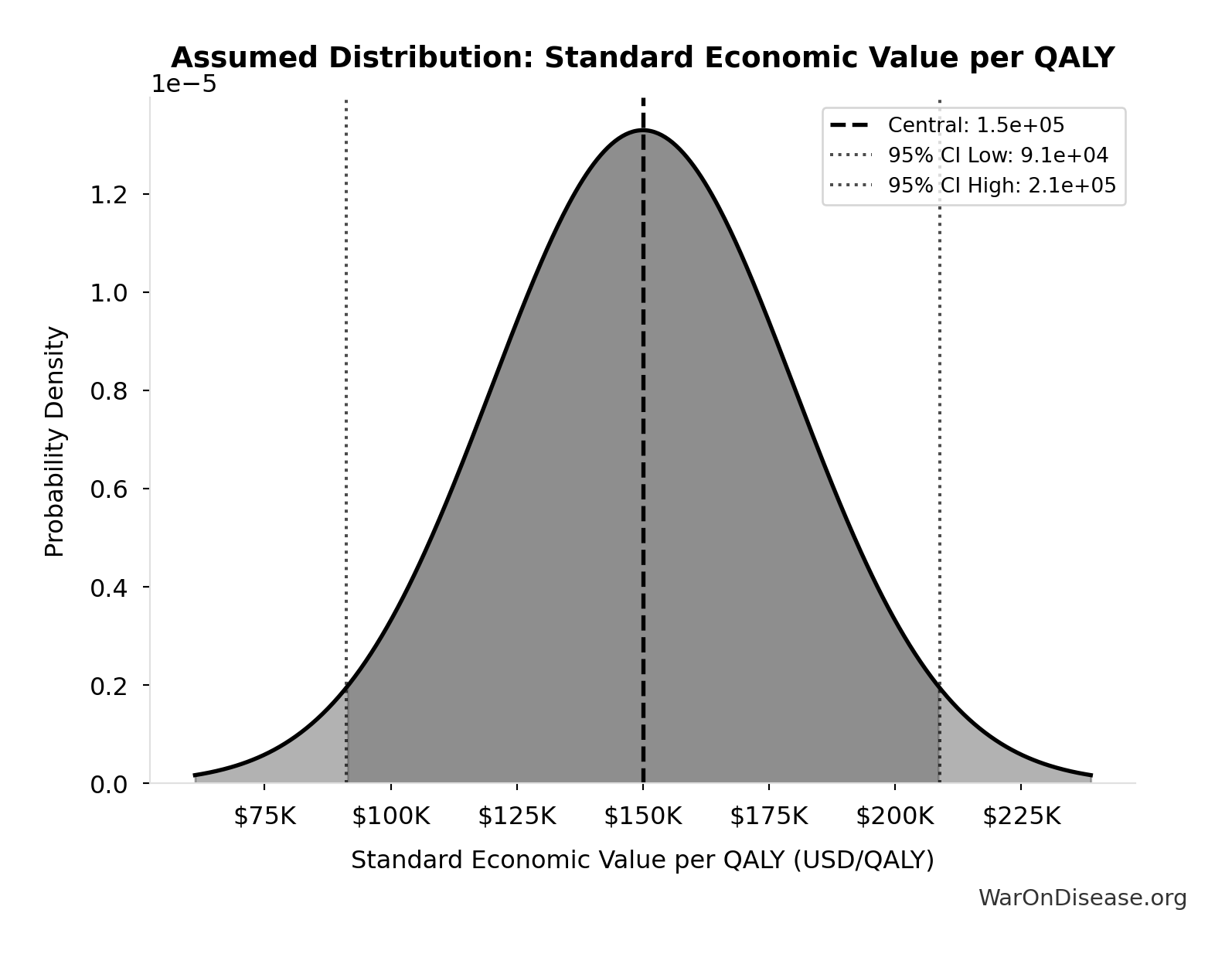
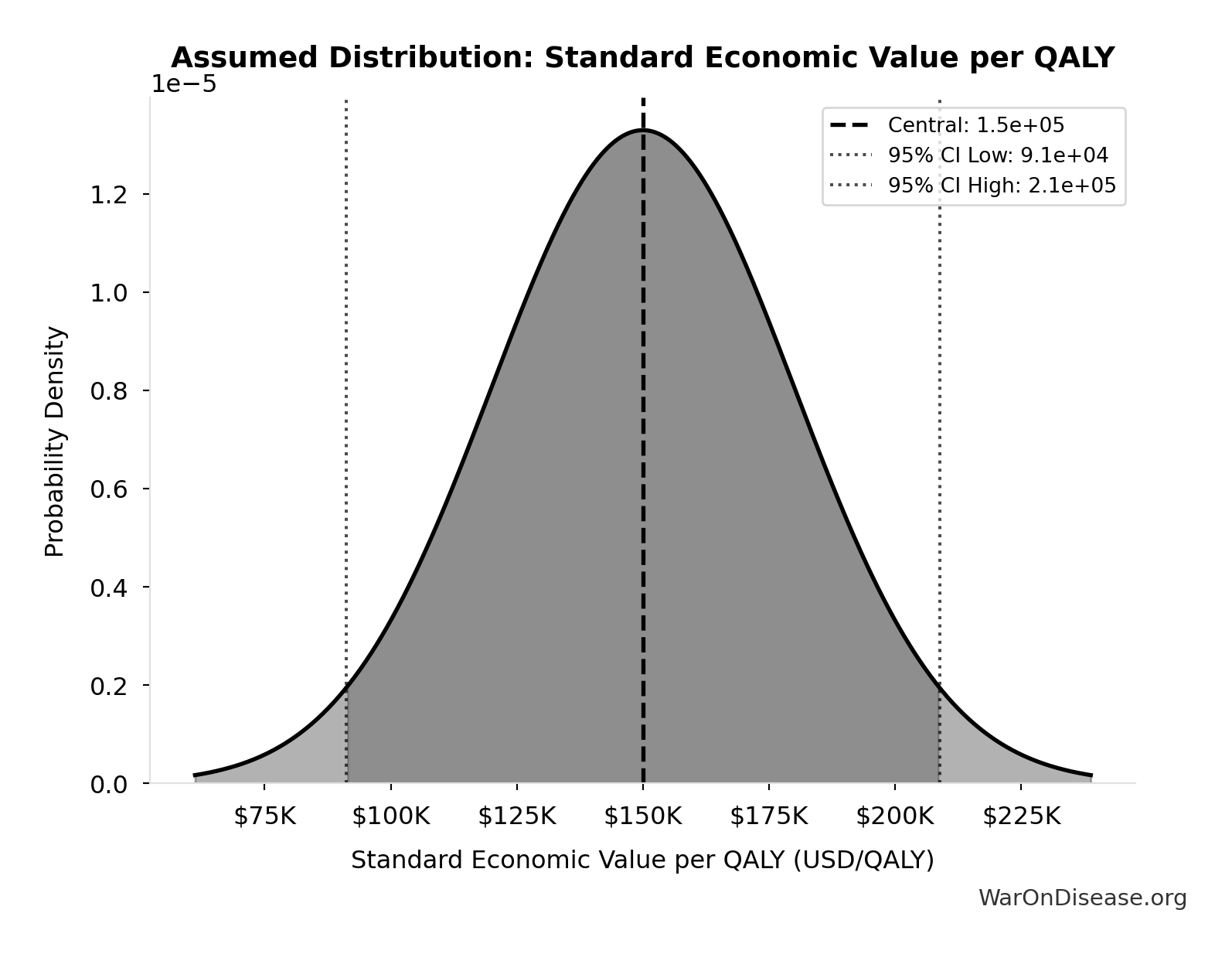
Standard Economic Value per QALY: $150K
Standard economic value per QALY
Source:90
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Normal (SE: $30K)
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence
Senators for Treaty Ratification: 67 senators
Senators needed for treaty ratification (2/3 majority per Article II, Section 2)
Source:123
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Fixed
✓ High confidence
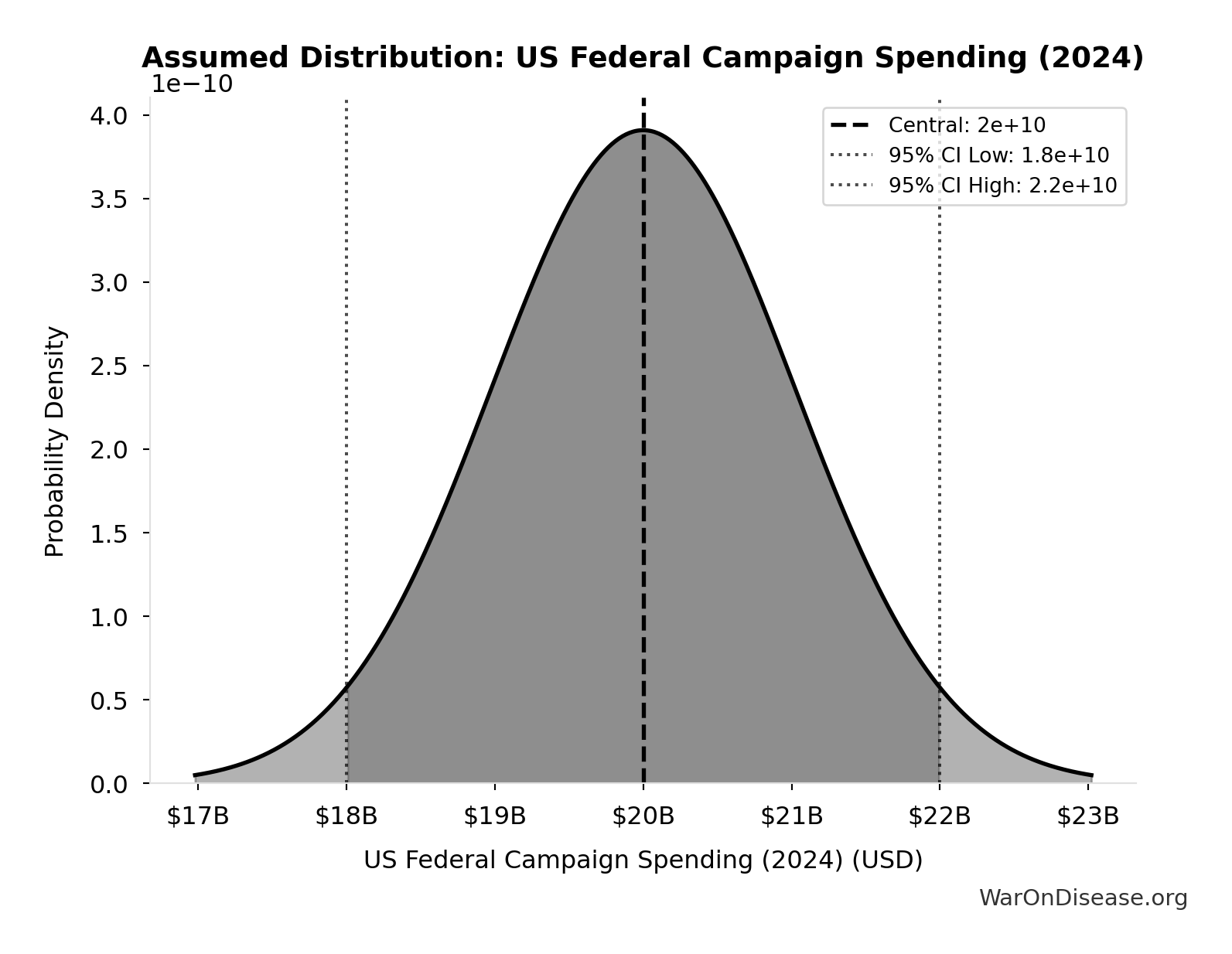
US Federal Campaign Spending (2024): $20B
Total US federal election spending in 2024 cycle including presidential, congressional, party committees, and PACs. Source: FEC Statistical Summary 2024.
Source:124
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$18B, $22B]
What this means: We’re quite confident in this estimate. The true value likely falls between $18B and $22B (±10%). This represents a narrow range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence
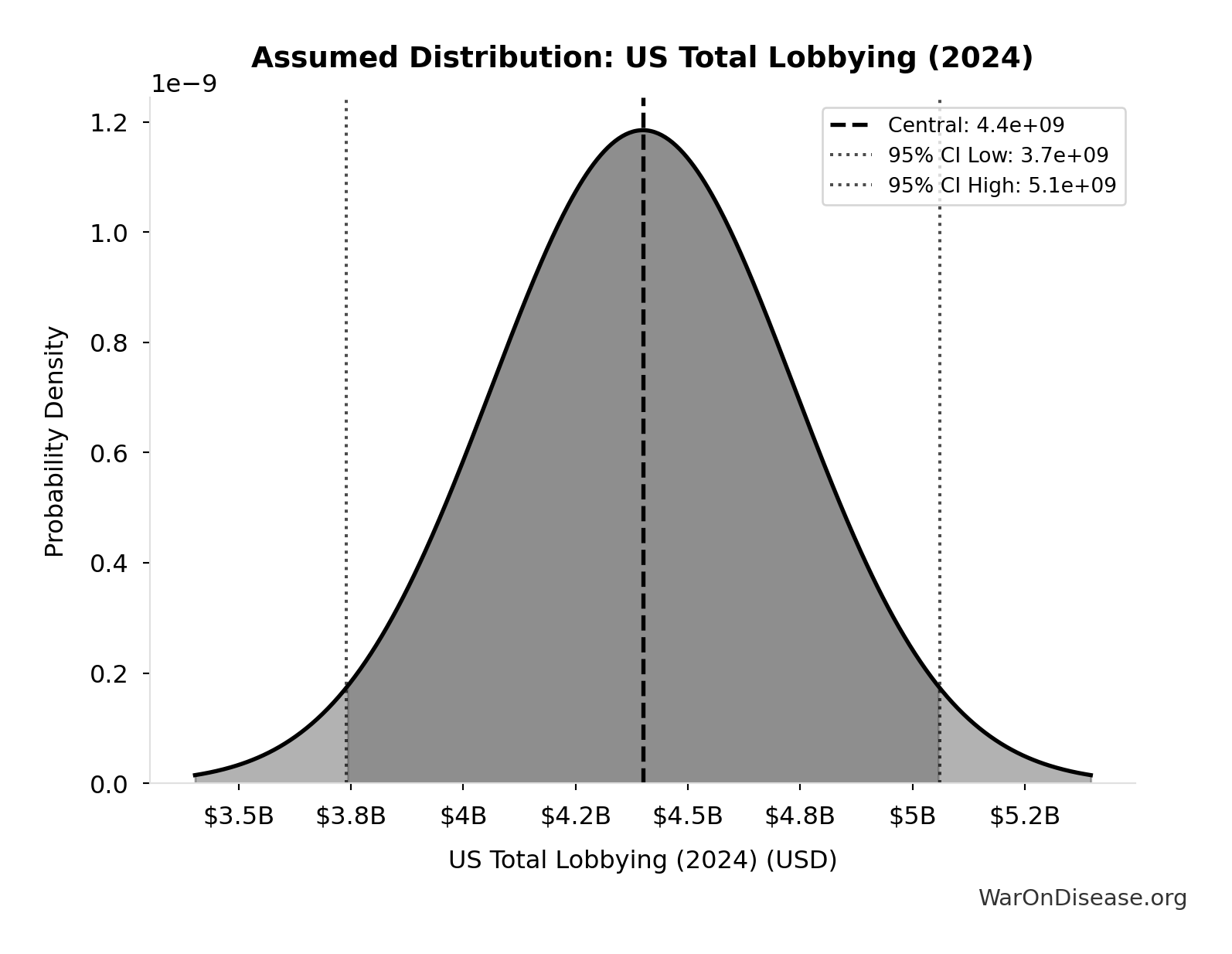
US Total Lobbying (2024): $4.4B
Total US federal lobbying expenditure in 2024 (record year). Source: OpenSecrets.
Source:125
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$3.74B, $5.06B]
What this means: This estimate has moderate uncertainty. The true value likely falls between $3.74B and $5.06B (±15%). This represents a reasonable range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
✓ High confidence
Core Definitions
Fundamental parameters and constants used throughout the analysis.
dFDA Annual Trial Funding: $21.8B
Assumed annual funding for dFDA pragmatic clinical trials (~$21.8B/year). Source-agnostic: could come from military reallocation, philanthropy, or government appropriation.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Fixed
Core definition
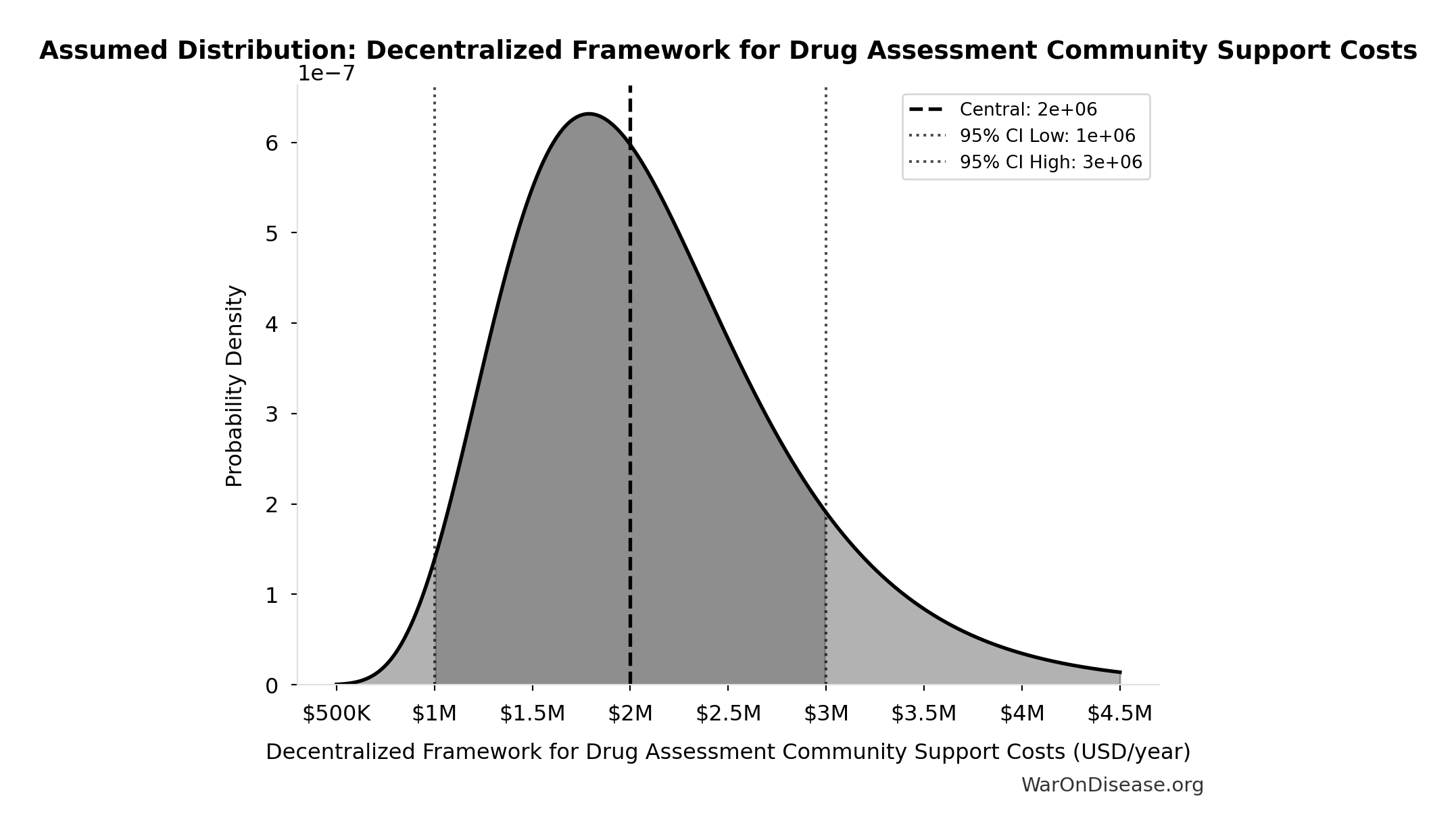
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Community Support Costs: $2M
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment community support costs
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$1M, $3M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between $1M and $3M (±50%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
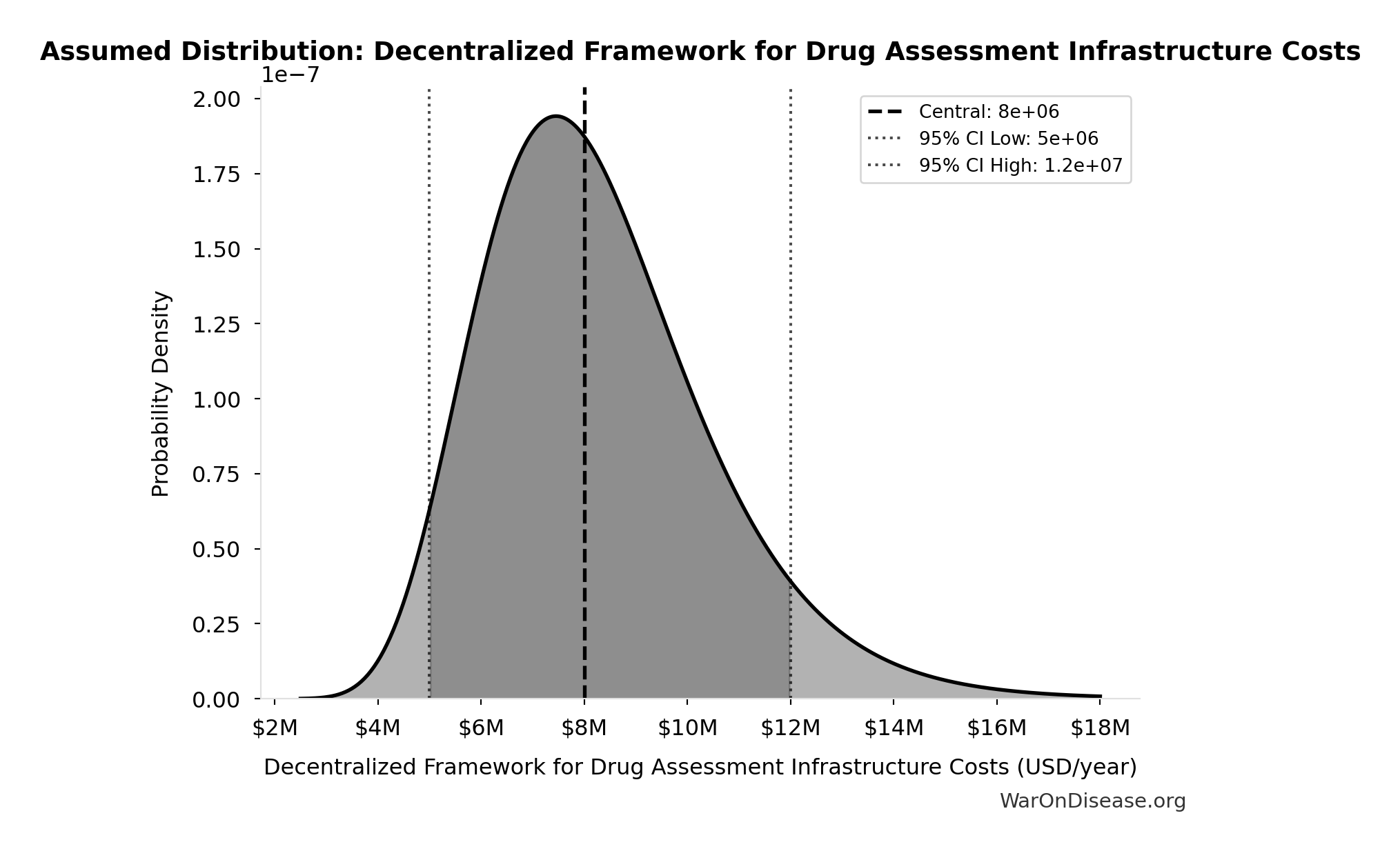
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Infrastructure Costs: $8M
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment infrastructure costs (cloud, security)
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$5M, $12M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between $5M and $12M (±44%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
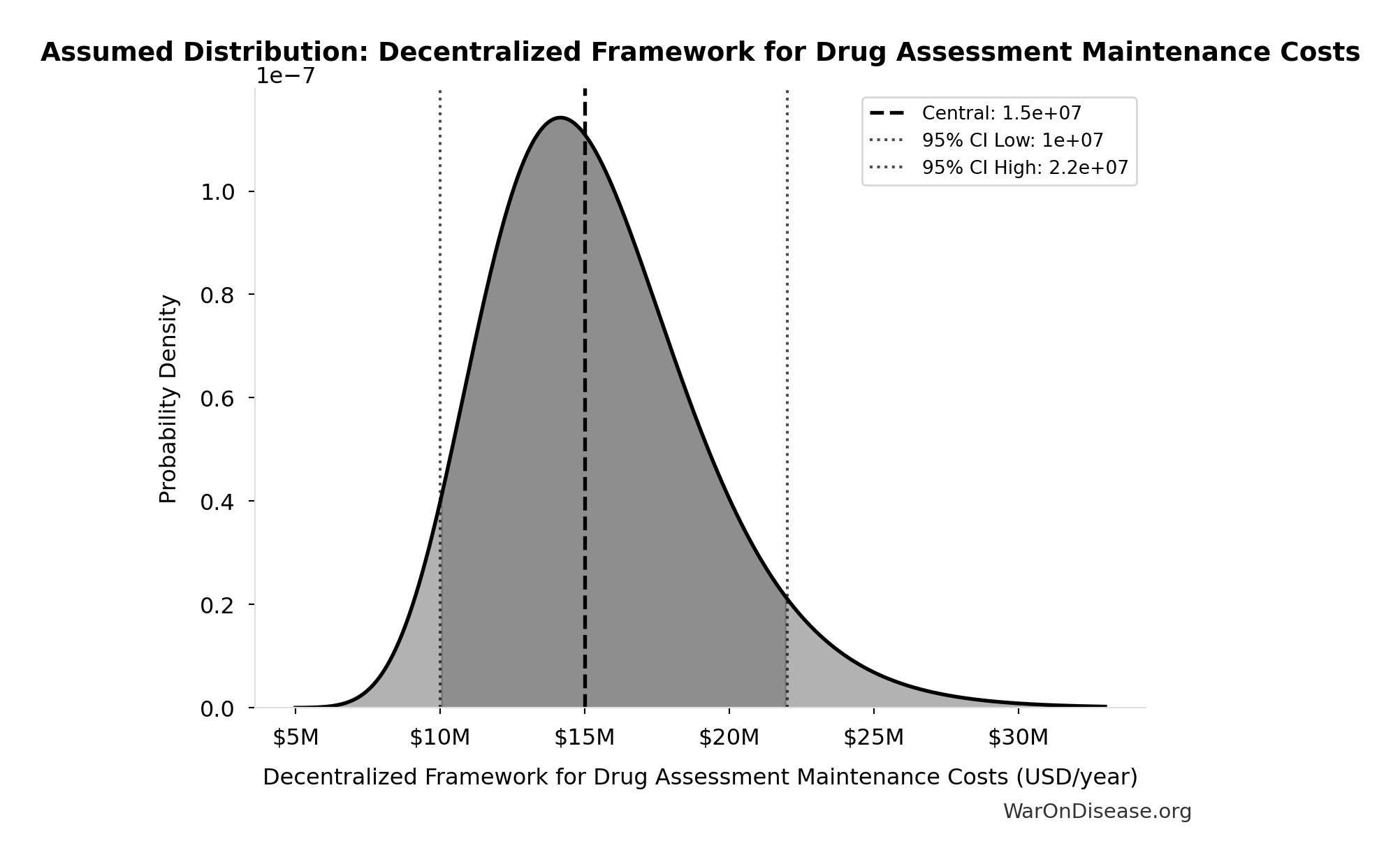
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Maintenance Costs: $15M
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment maintenance costs
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$10M, $22M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between $10M and $22M (±40%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
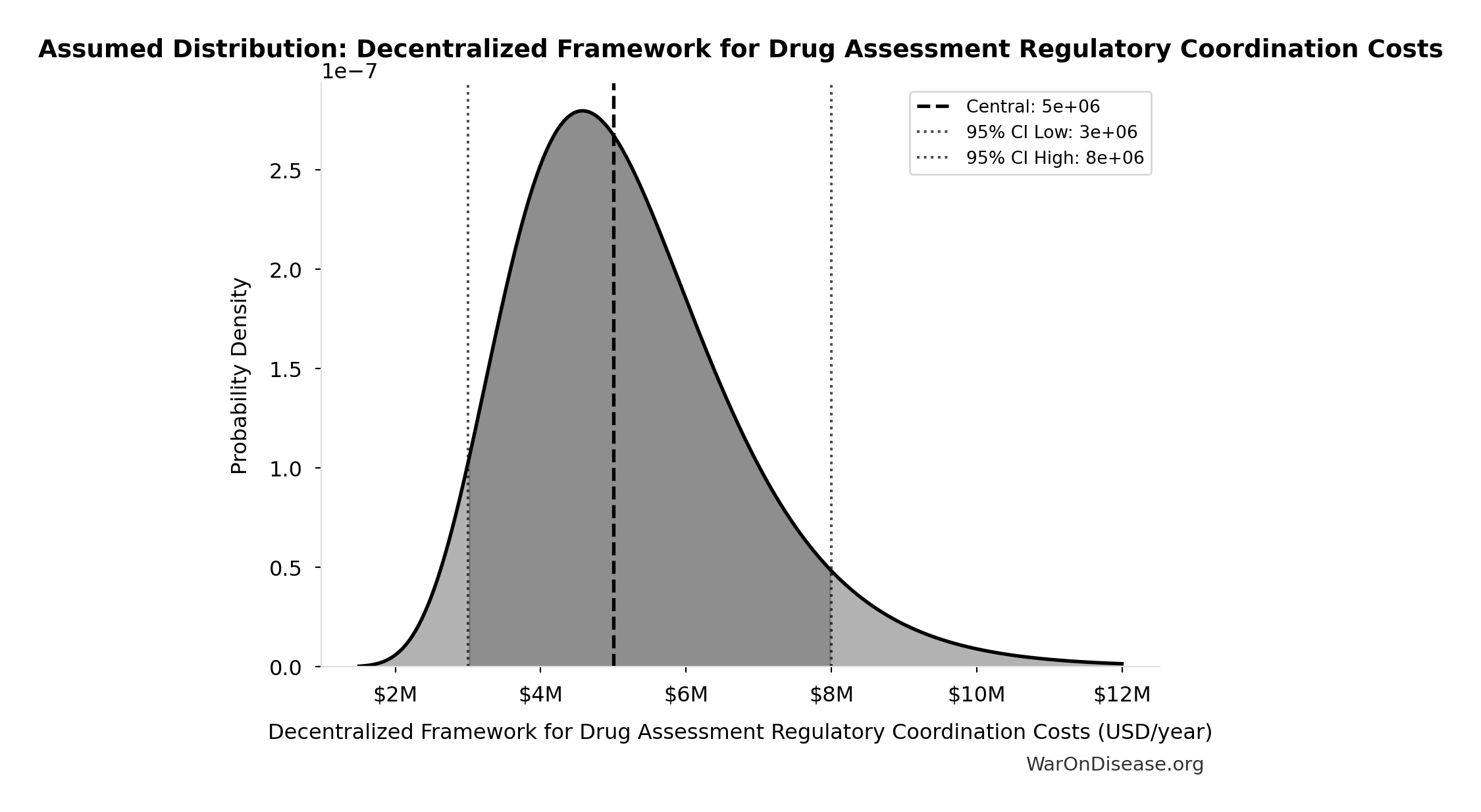
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Regulatory Coordination Costs: $5M
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment regulatory coordination costs
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$3M, $8M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between $3M and $8M (±50%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
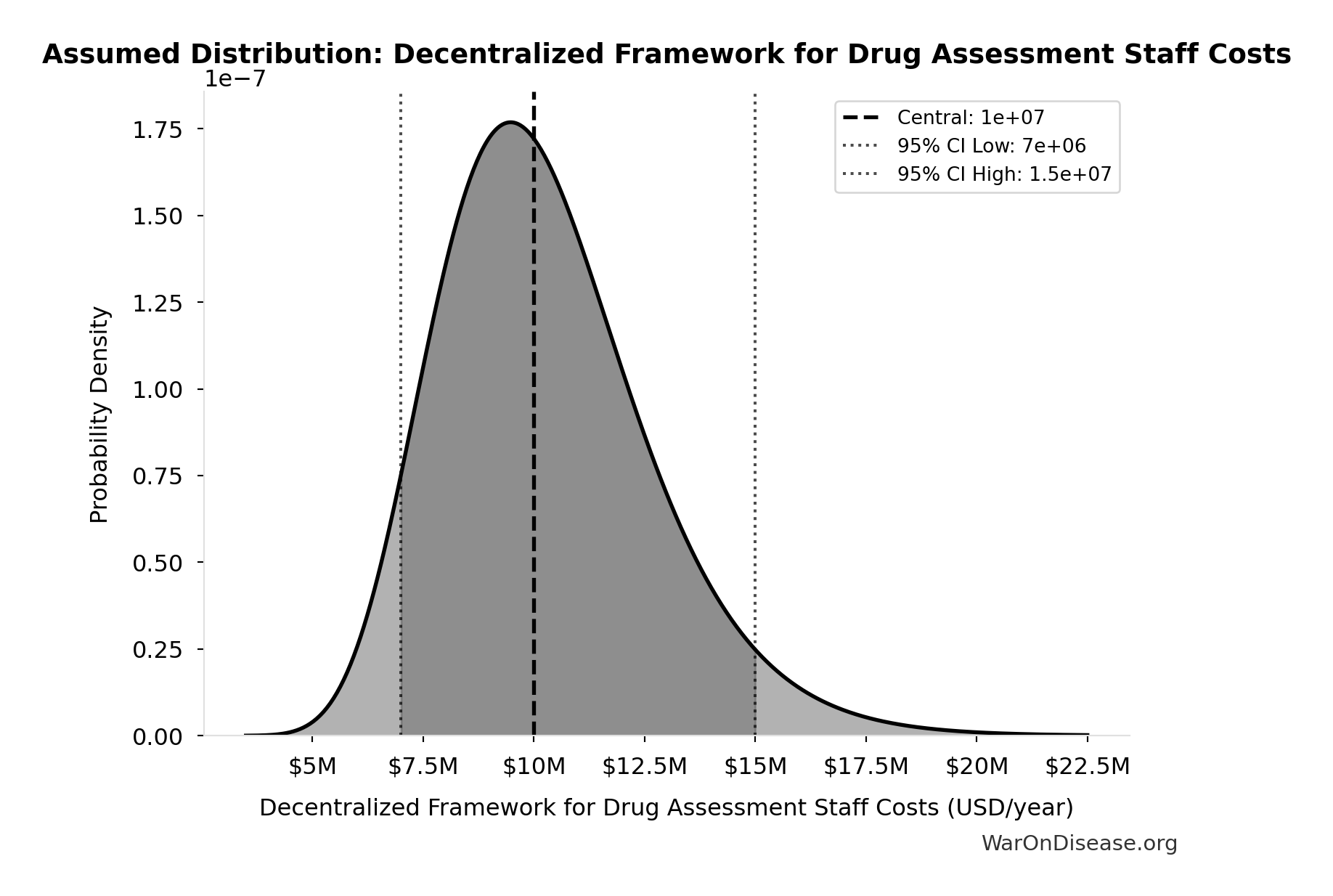
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment Staff Costs: $10M
Decentralized Framework for Drug Assessment staff costs (minimal, AI-assisted)
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$7M, $15M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between $7M and $15M (±40%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
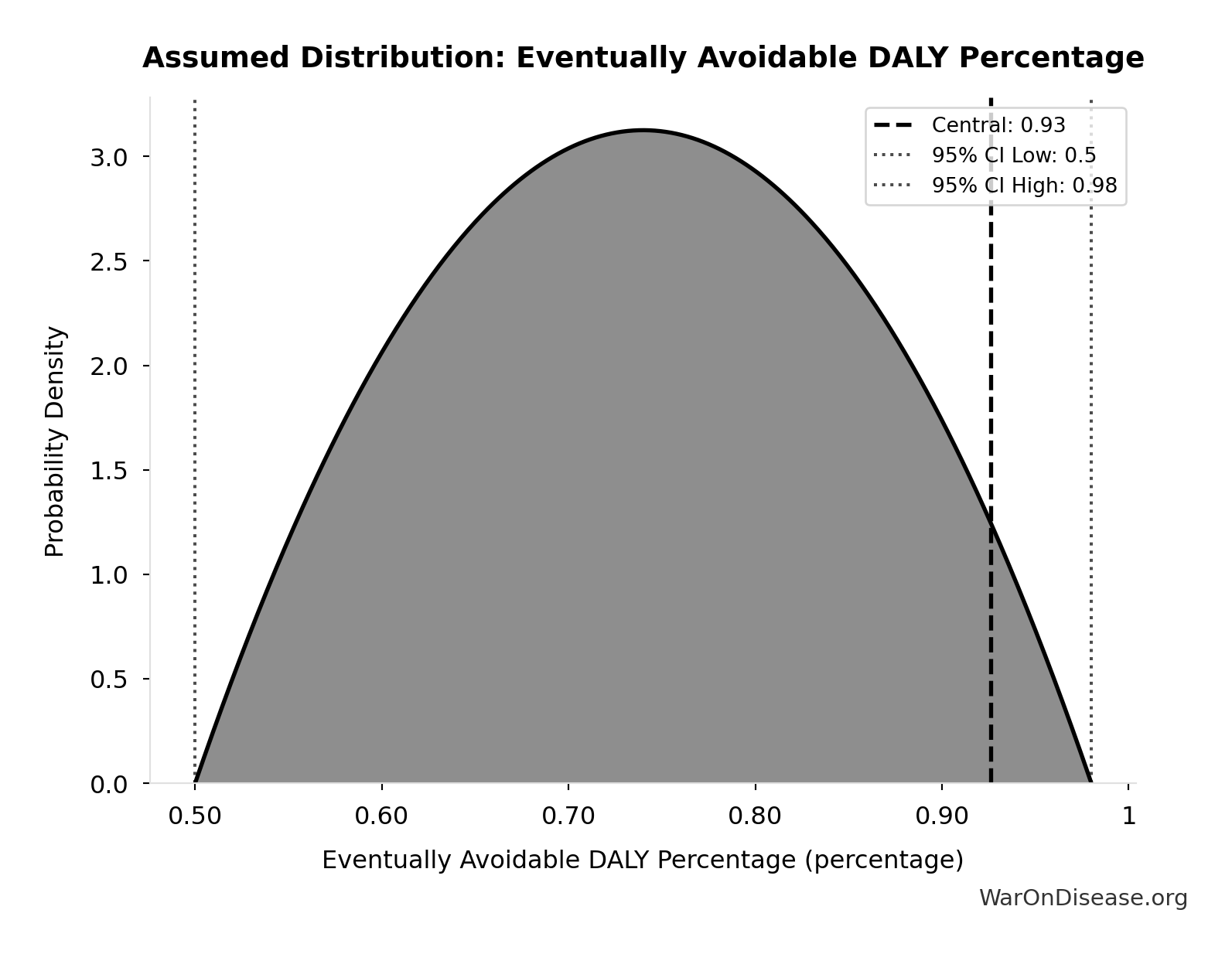
Eventually Avoidable DALY Percentage: 92.6%
Percentage of DALYs that are eventually avoidable with sufficient biomedical research. Uses same methodology as EVENTUALLY_AVOIDABLE_DEATH_PCT. Most non-fatal chronic conditions (arthritis, depression, chronic pain) are also addressable through research, so the percentage is similar to deaths.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [50%, 98%] • Distribution: Beta
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between 50% and 98% (±26%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The beta distribution means values are bounded and can skew toward one end.
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
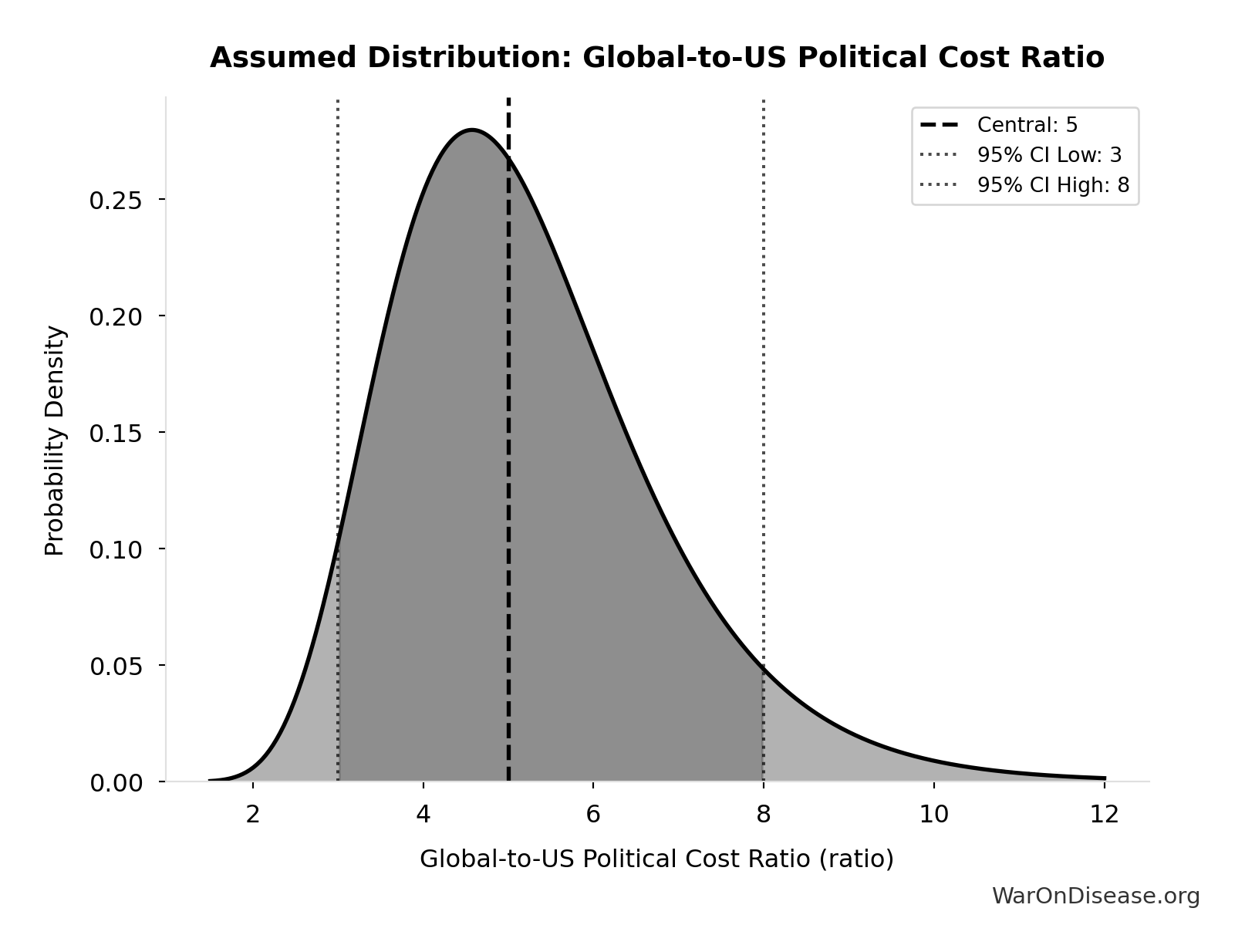
Global-to-US Political Cost Ratio: 5:1
Ratio of global to US political reform costs. Based on discretionary spending ratio (~9x) discounted by ~50% for less transparent/expensive non-US political systems. Range 3-8 reflects uncertainty about non-US political dynamics and hidden influence channels.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [3:1, 8:1] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: There’s significant uncertainty here. The true value likely falls between 3:1 and 8:1 (±50%). This represents a wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
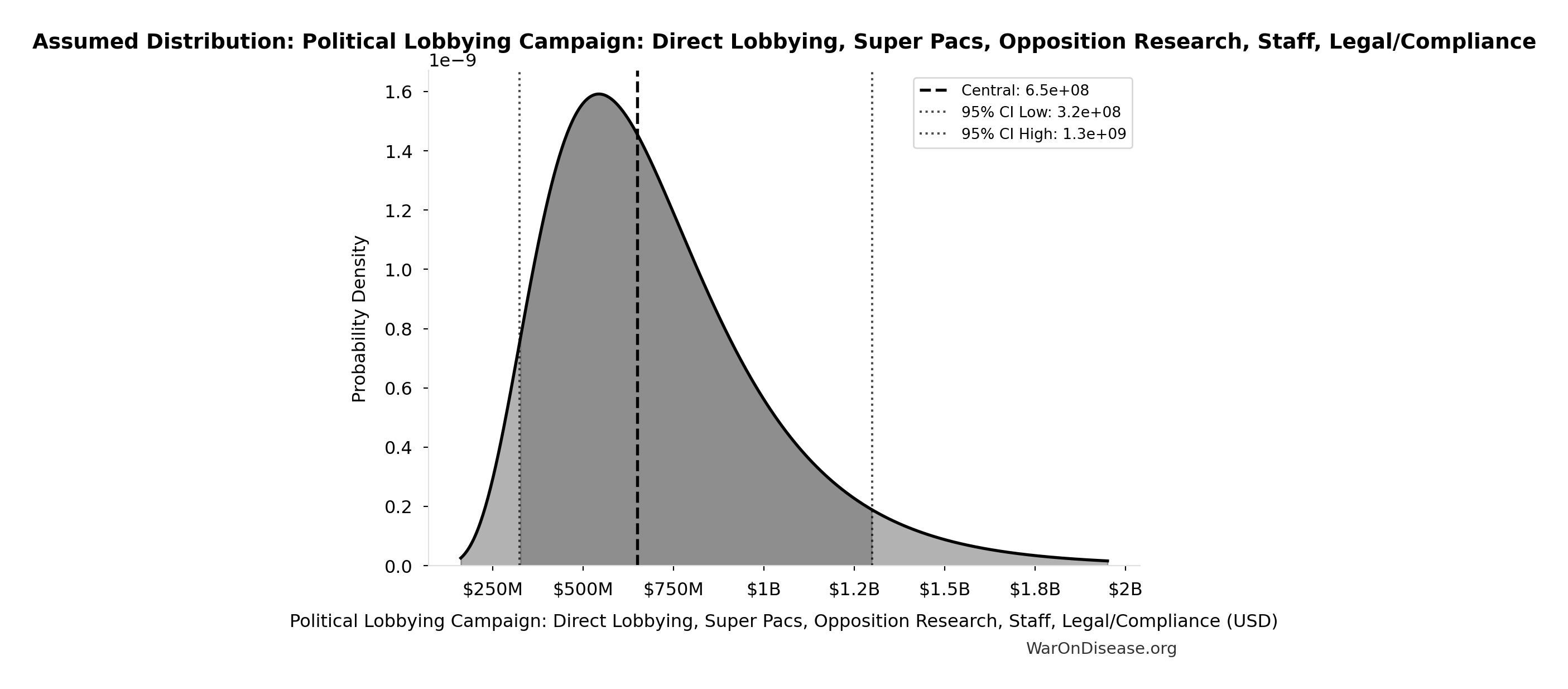
Political Lobbying Campaign: Direct Lobbying, Super Pacs, Opposition Research, Staff, Legal/Compliance: $650M
Political lobbying campaign: direct lobbying (US/EU/G20), Super PACs, opposition research, staff, legal/compliance. Budget exceeds combined pharma ($300M/year) and military-industrial complex ($150M/year) lobbying to ensure competitive positioning. Referendum relies on grassroots mobilization and earned media, while lobbying requires matching or exceeding opposition spending for political viability.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$325M, $1.3B] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between $325M and $1.3B (±75%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
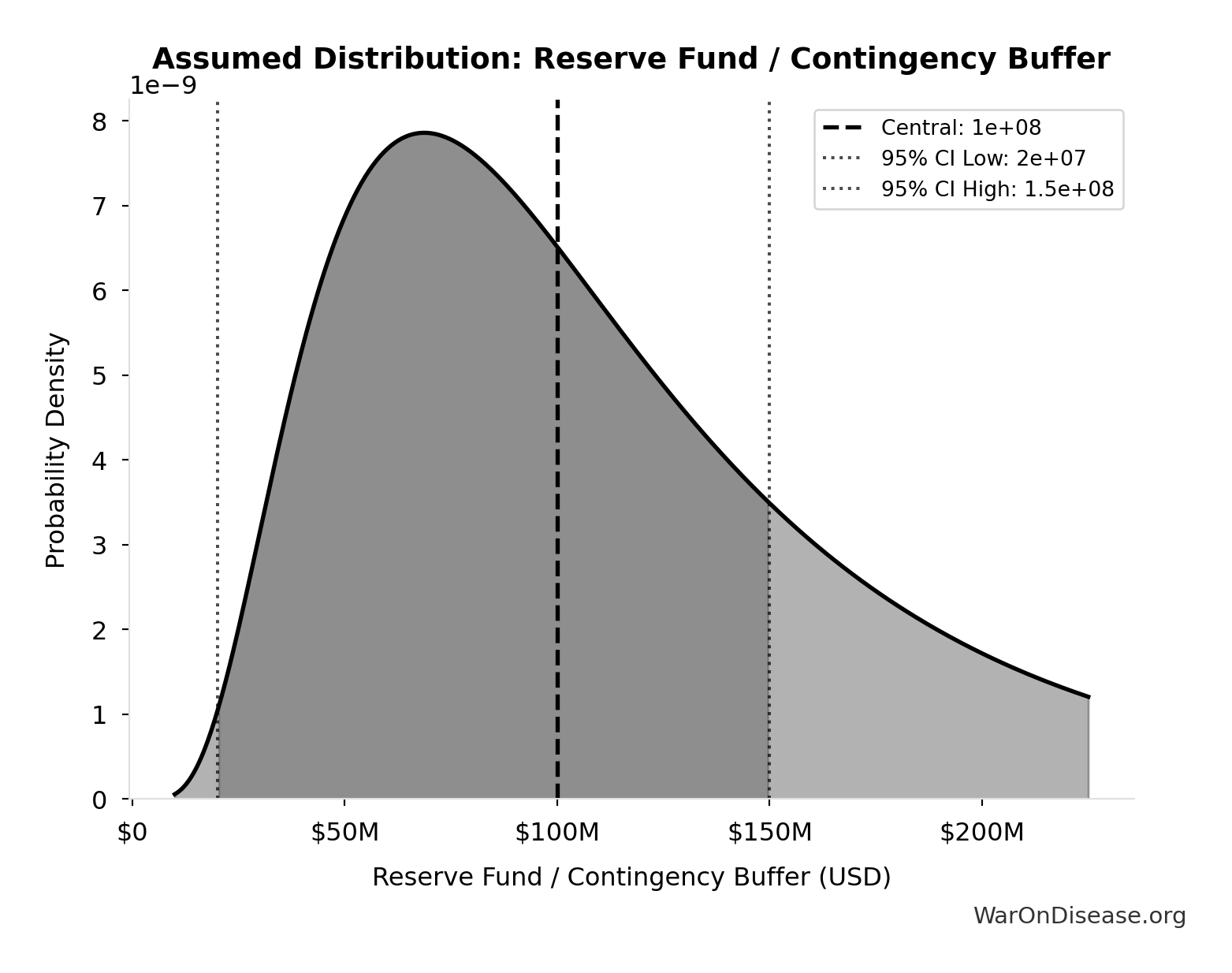
Reserve Fund / Contingency Buffer: $100M
Reserve fund / contingency buffer (10% of total campaign cost). Using industry standard 10% for complex campaigns with potential for unforeseen legal challenges, opposition response, or regulatory delays. Conservative lower bound of $20M (2%) reflects transparent budget allocation and predictable referendum/lobbying costs.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [$20M, $150M] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between $20M and $150M (±65%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition
1% Reduction in Military Spending/War Costs from Treaty: 1%
1% reduction in military spending/war costs from treaty
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Fixed
Core definition
US Congress Members: 535 members
Total members of US Congress (100 senators + 435 representatives)
Uncertainty Range
Technical: Distribution: Fixed
Core definition
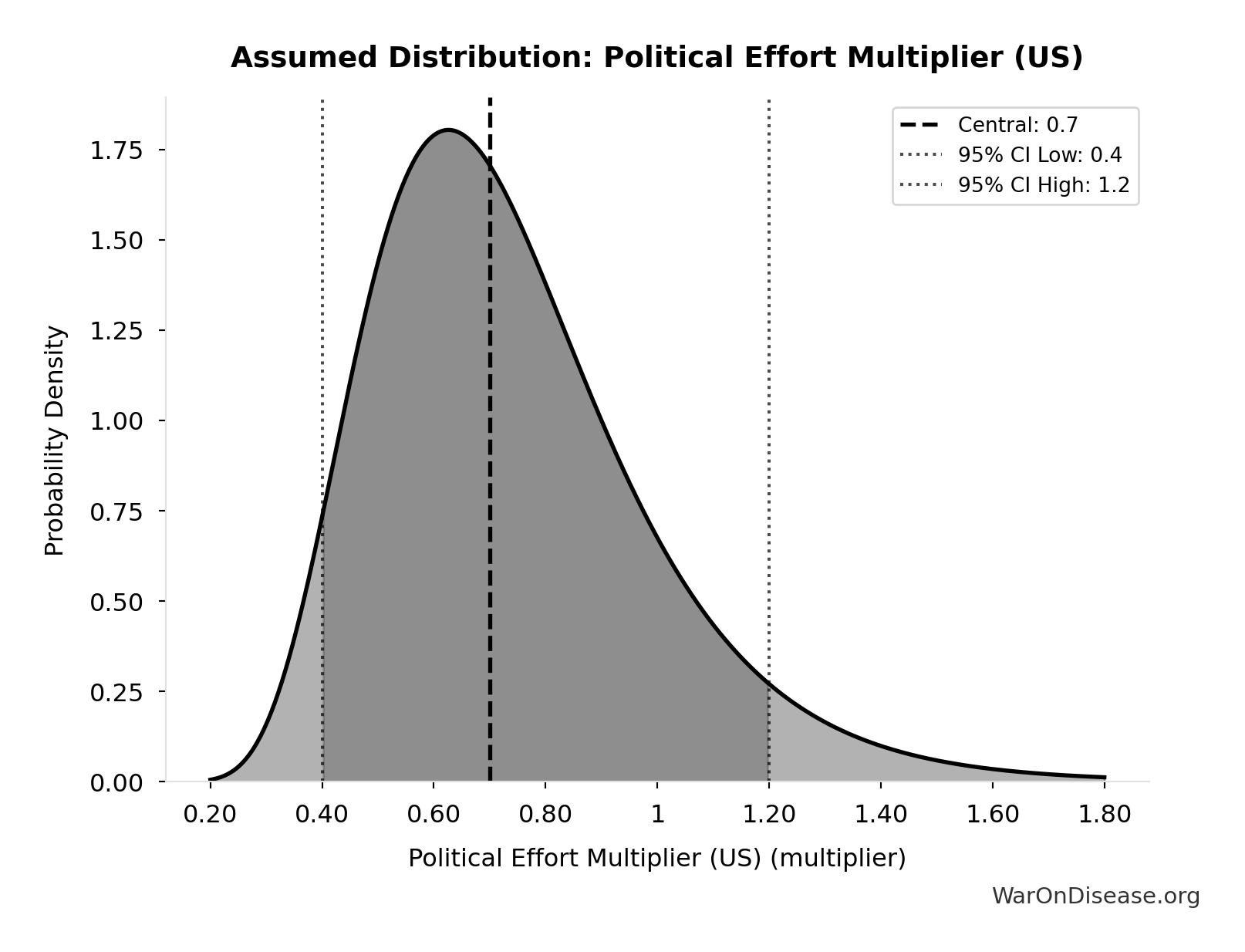
Political Effort Multiplier (US): 0.7x
Fraction of campaign + lobbying spending needed to achieve policy reform. Accounts for efficiency gains from coordination, message clarity, and public interest alignment. Range 0.4-1.2 reflects uncertainty about political dynamics.
Uncertainty Range
Technical: 95% CI: [0.4x, 1.2x] • Distribution: Lognormal
What this means: This estimate is highly uncertain. The true value likely falls between 0.4x and 1.2x (±57%). This represents a very wide range that our Monte Carlo simulations account for when calculating overall uncertainty in the results.
The lognormal distribution means values can’t go negative and have a longer tail toward higher values (common for costs and populations).
Input Distribution
This chart shows the assumed probability distribution for this parameter. The shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval where we expect the true value to fall.
Core definition